Which Of The Following Structures Monitors Blood Pressure

Maintaining stable blood pressure is crucial for overall health, impacting everything from kidney function to cardiovascular well-being. But what specific structures within the body are responsible for continuously monitoring this vital sign? The answer lies within a complex interplay of sensors and control centers, primarily involving the baroreceptors, the kidneys, and the brain.
Understanding these structures and their functions is key to comprehending how the body regulates blood pressure and how disruptions can lead to conditions like hypertension.
The Baroreceptors: Immediate Responders
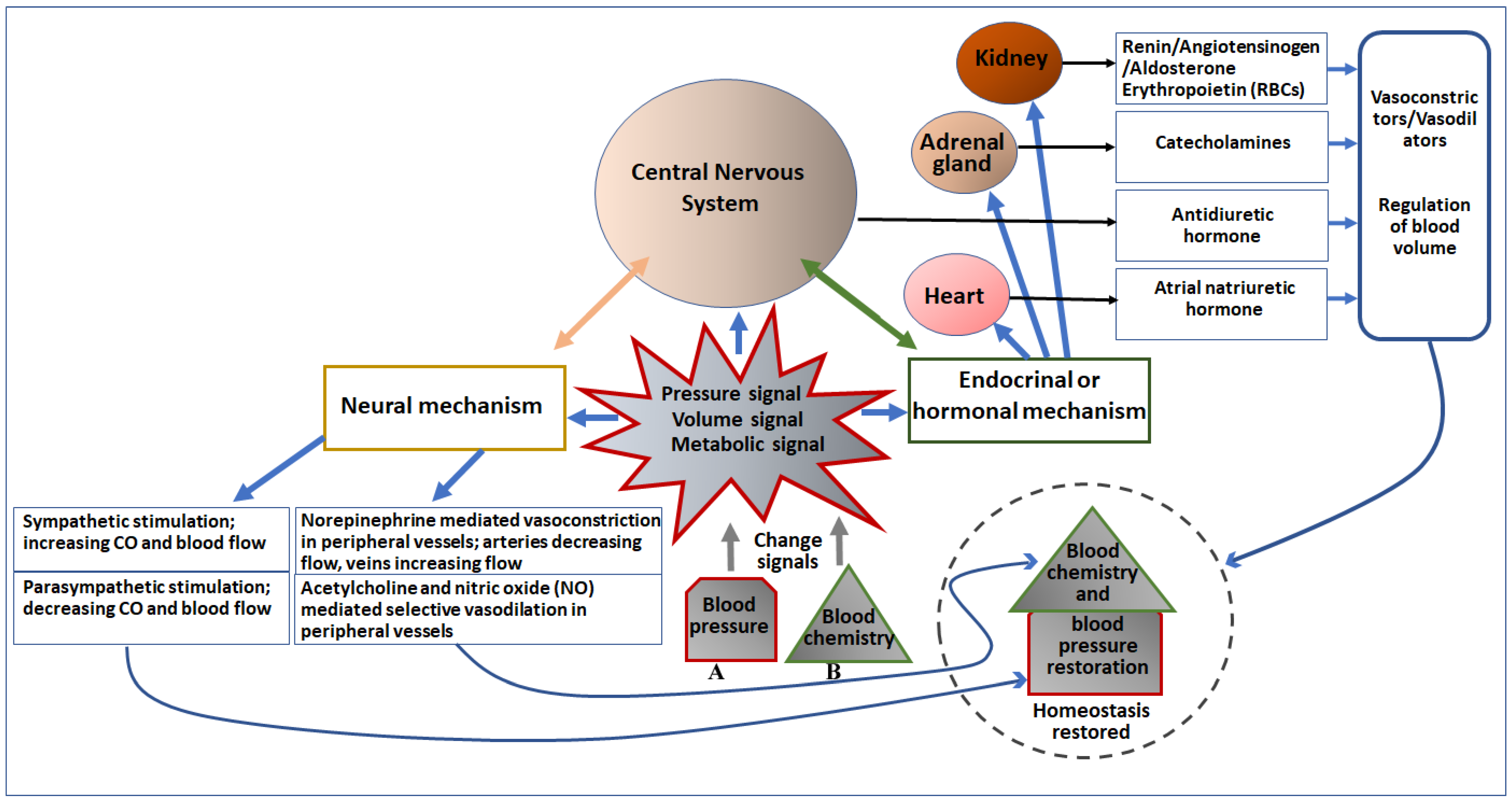
Baroreceptors are specialized nerve endings that act as pressure sensors. They are strategically located in the walls of major blood vessels, particularly the aortic arch and the carotid sinuses, near the heart and neck respectively.
These sensors detect changes in the stretching of the vessel walls, reflecting fluctuations in blood pressure.
When blood pressure rises, the vessel walls stretch more, stimulating the baroreceptors to send signals to the brainstem.
Conversely, when blood pressure drops, the baroreceptors signal a decrease in stretching.
These signals are crucial for initiating rapid adjustments to maintain blood pressure homeostasis.
How Baroreceptors Work
The brainstem receives signals from the baroreceptors and processes this information. This initiates a cascade of responses to either raise or lower blood pressure.
If blood pressure is high, the brainstem can decrease heart rate and dilate blood vessels (vasodilation) to lower the pressure.
If blood pressure is low, the brainstem can increase heart rate and constrict blood vessels (vasoconstriction) to raise the pressure.
This rapid response system is essential for managing short-term blood pressure fluctuations, such as those that occur during exercise or changes in posture.
The Kidneys: Long-Term Regulation
While baroreceptors provide immediate responses, the kidneys play a crucial role in long-term blood pressure regulation. They achieve this primarily by controlling blood volume and electrolyte balance.
The kidneys constantly filter blood and regulate the amount of sodium and water that are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream.
If blood pressure is high, the kidneys excrete more sodium and water, reducing blood volume and lowering blood pressure.
Conversely, if blood pressure is low, the kidneys retain sodium and water, increasing blood volume and raising blood pressure.
The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS)
A key mechanism employed by the kidneys is the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS). This hormonal system plays a critical role in regulating blood pressure and fluid balance.
When blood pressure drops, the kidneys release an enzyme called renin.
Renin initiates a chain reaction that ultimately leads to the production of angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor that also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal glands.
Aldosterone promotes sodium and water retention by the kidneys, further increasing blood volume and raising blood pressure.
The Brain: Central Control
The brain, specifically the brainstem and the hypothalamus, serves as the central command center for blood pressure regulation. It receives input from baroreceptors, chemoreceptors (which detect blood oxygen and carbon dioxide levels), and other sensory receptors throughout the body.
The brain integrates this information and coordinates appropriate responses through the autonomic nervous system, which controls heart rate, blood vessel constriction, and hormone release.
The brainstem's vasomotor center is particularly important in controlling blood vessel tone.
The hypothalamus also plays a role by influencing the release of hormones that affect blood pressure, such as antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which promotes water retention.
The Interplay of Structures
These three structures – baroreceptors, kidneys, and brain – do not operate in isolation. They constantly communicate and coordinate their actions to maintain stable blood pressure.
For example, when blood pressure drops, baroreceptors signal the brainstem, which increases heart rate and constricts blood vessels.
Simultaneously, the kidneys release renin, activating the RAAS to increase blood volume and further raise blood pressure. The brain will also affect the water level in the blood to ensure stability.
This integrated response ensures that blood pressure remains within a narrow, healthy range.
Impact and Significance
Understanding the structures that monitor blood pressure is crucial for diagnosing and treating conditions like hypertension. Many common blood pressure medications target specific components of this system, such as the RAAS.
For example, ACE inhibitors block the production of angiotensin II, while beta-blockers reduce heart rate and contractility.
Furthermore, lifestyle modifications, such as reducing sodium intake and maintaining a healthy weight, can also help to regulate blood pressure by influencing the function of these structures.
Ultimately, a deeper understanding of the body's blood pressure monitoring system empowers individuals to take proactive steps to protect their cardiovascular health.