Which Processes Increase A Population's Size

Across the globe, populations are in constant flux. Some regions grapple with aging populations and declining birth rates, while others face rapid growth and its associated challenges. Understanding the dynamics that drive population size is crucial for policymakers, researchers, and anyone concerned with the future of our planet.
This article delves into the key processes that contribute to population growth. It will explore the interplay of birth rates, death rates, migration, and various socioeconomic factors that shape the size of a population. By examining these elements, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of what drives population increase and its implications for the future.
The Core Components of Population Growth
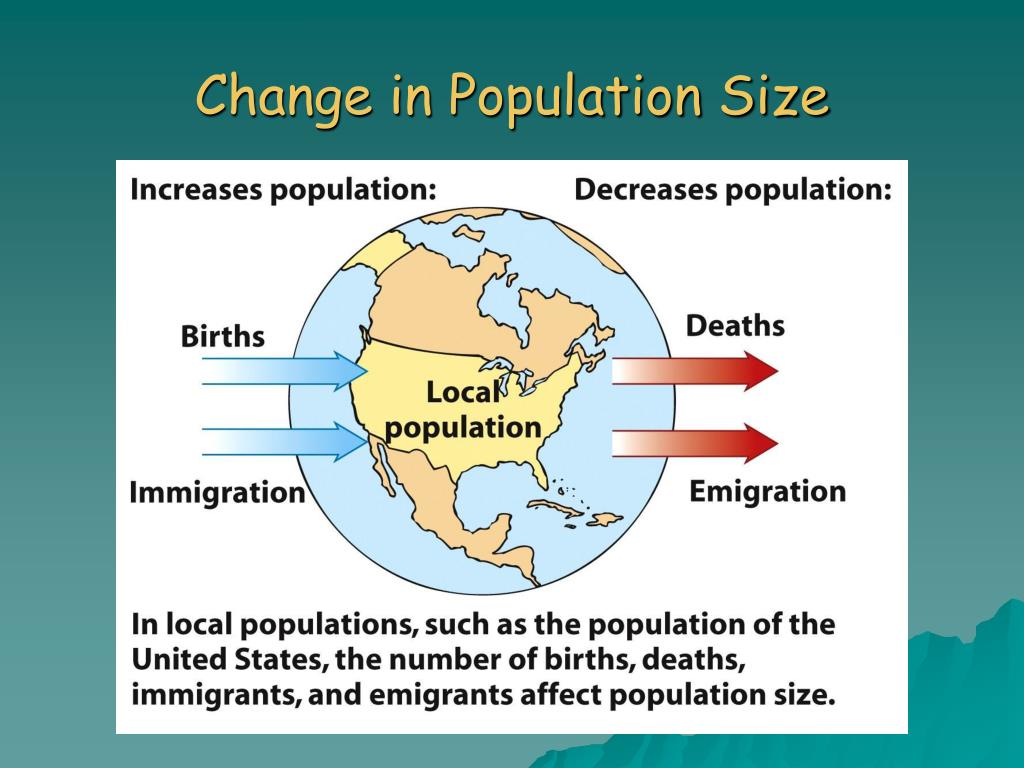
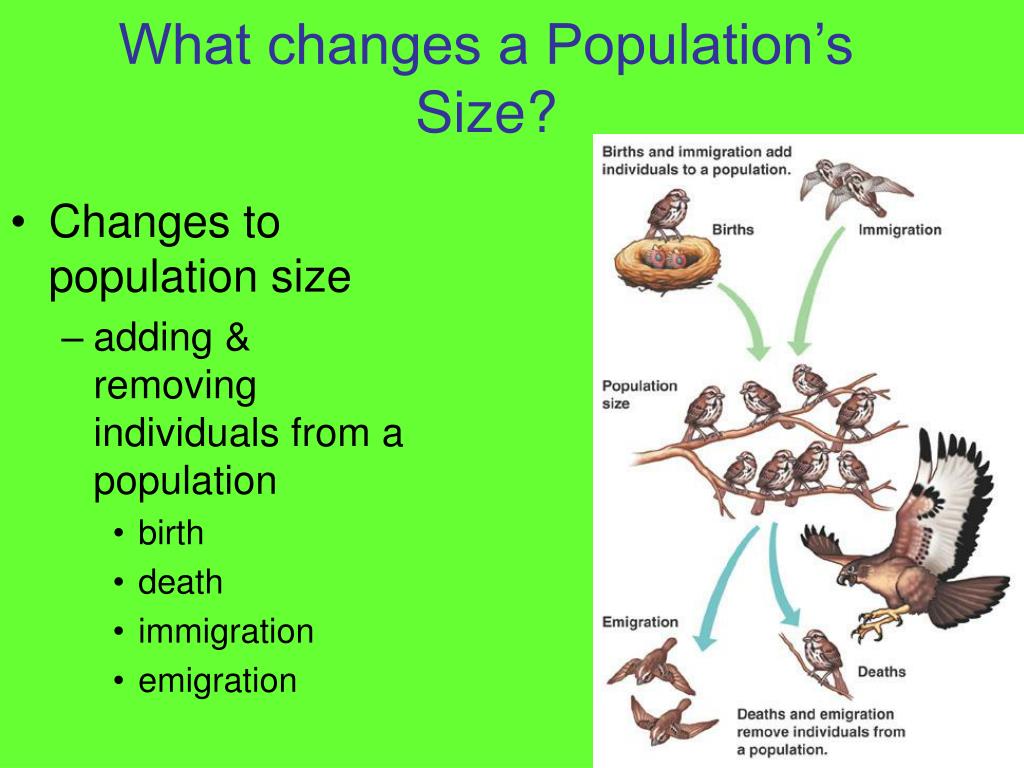
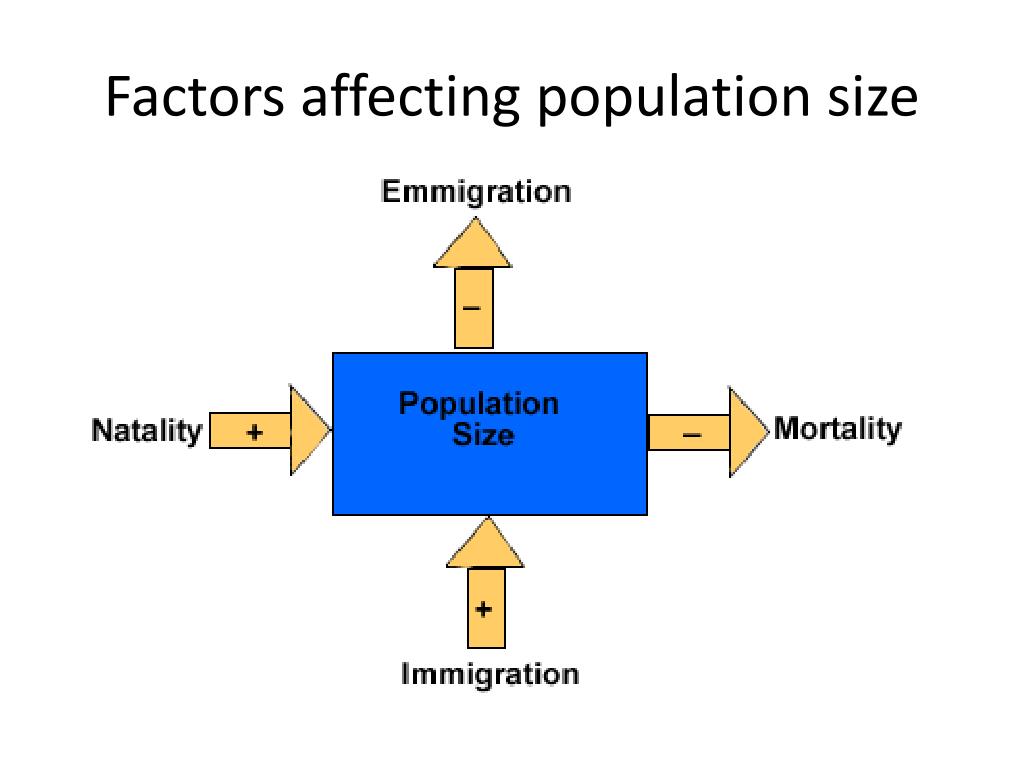
The most fundamental equation for understanding population change is relatively simple: Population Growth = (Births + Immigration) - (Deaths + Emigration). This equation highlights the four main processes at play.
Birth Rate: The Engine of Growth
The birth rate, often expressed as the number of live births per 1,000 people per year, is a primary driver of population increase. Higher birth rates directly translate to a larger population, all other factors being equal.
Several factors influence birth rates. These include access to family planning resources, cultural norms, levels of education (especially for women), economic conditions, and government policies.
For example, countries with limited access to contraception often experience higher birth rates than those with widespread availability.
Mortality Rate: Counteracting Growth
The mortality rate, or death rate, is the number of deaths per 1,000 people per year. It acts as a counterbalance to birth rates, slowing down population growth or even causing it to decline.
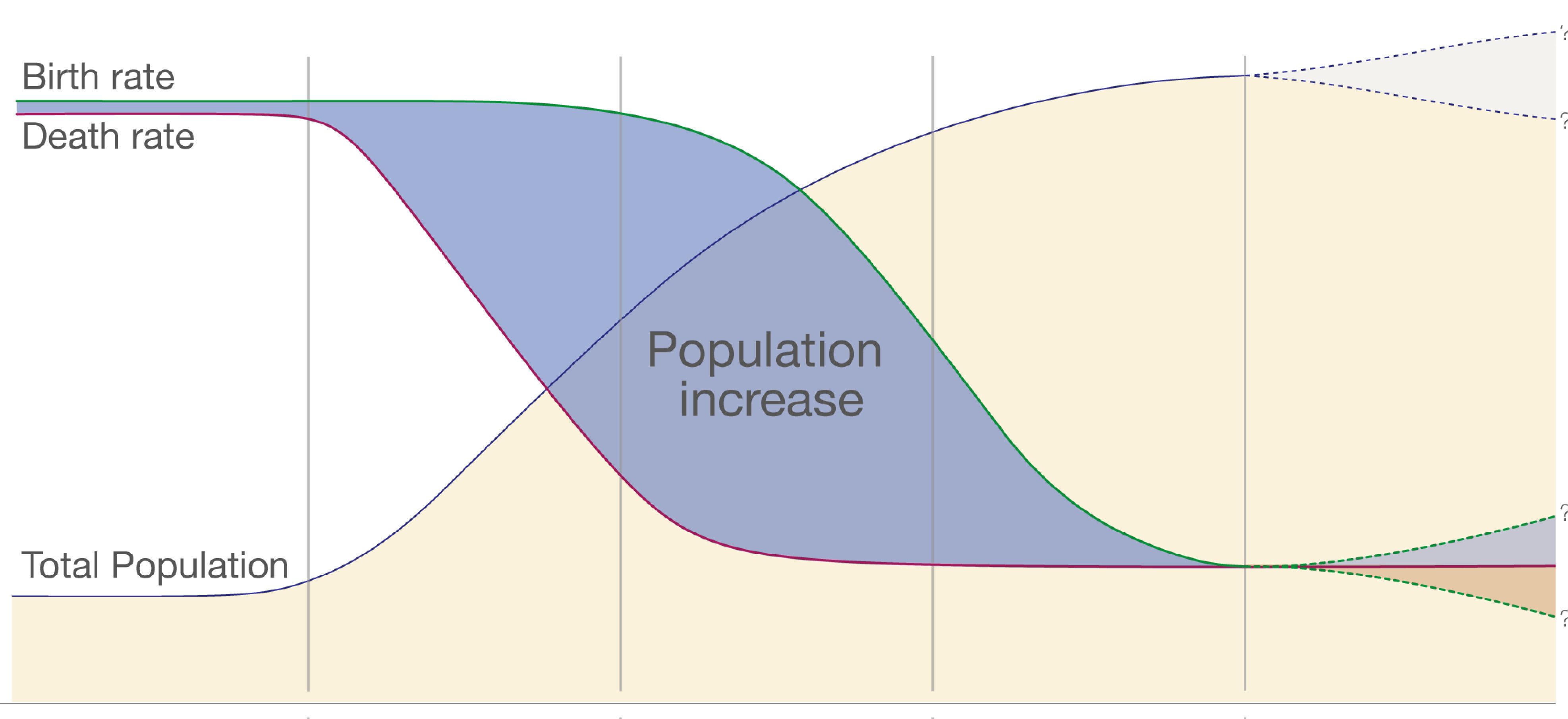
Significant improvements in healthcare, sanitation, and nutrition have led to dramatic declines in mortality rates worldwide over the past century. These advancements mean people are living longer and fewer infants are dying, contributing to population growth.
However, factors like disease outbreaks, conflicts, and natural disasters can significantly increase mortality rates, temporarily slowing or reversing population growth trends.
Migration: Reshaping Populations
Migration, the movement of people from one place to another, plays a crucial role in shaping population size at both the regional and national levels. Immigration (people entering a region) adds to the population, while emigration (people leaving a region) subtracts from it.
Migration patterns are influenced by a complex interplay of economic, social, and political factors. These include the availability of jobs, political stability, and the presence of established immigrant communities.
Regions with strong economies and stable political environments often attract immigrants, leading to population growth. Conversely, regions experiencing conflict or economic hardship may see an outflow of people, resulting in population decline.
Factors Influencing the Core Components
The core components of population growth are not isolated variables. They are deeply intertwined with a range of social, economic, and environmental factors.
Socioeconomic Development
Economic development often leads to lower birth rates. As countries become wealthier, access to education and healthcare improves, and women have more opportunities outside of the home.
These factors often lead to families choosing to have fewer children. However, economic development also typically leads to increased life expectancy, further complicating population growth dynamics.
According to the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), investing in women's education and reproductive health is crucial for achieving sustainable population growth.
Healthcare and Public Health
Improvements in healthcare have dramatically reduced mortality rates, especially among infants and children. Vaccination programs, access to clean water, and advancements in medical treatments have all contributed to increased life expectancy.
Public health initiatives play a critical role in controlling the spread of infectious diseases, further reducing mortality. However, new challenges such as antibiotic resistance and emerging diseases continue to pose threats to global health.
The World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes the importance of strengthening healthcare systems to ensure equitable access to quality care and improve overall population health.
Government Policies
Government policies can significantly influence population growth rates. These policies range from those promoting family planning to those providing incentives for having children.
For instance, some countries offer financial incentives to families with multiple children in an effort to boost birth rates. Other governments invest heavily in family planning services to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their reproductive health.
Policies related to immigration also have a direct impact on population size. Immigration laws determine who can enter a country and how long they can stay, influencing the rate of population growth.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Population Growth
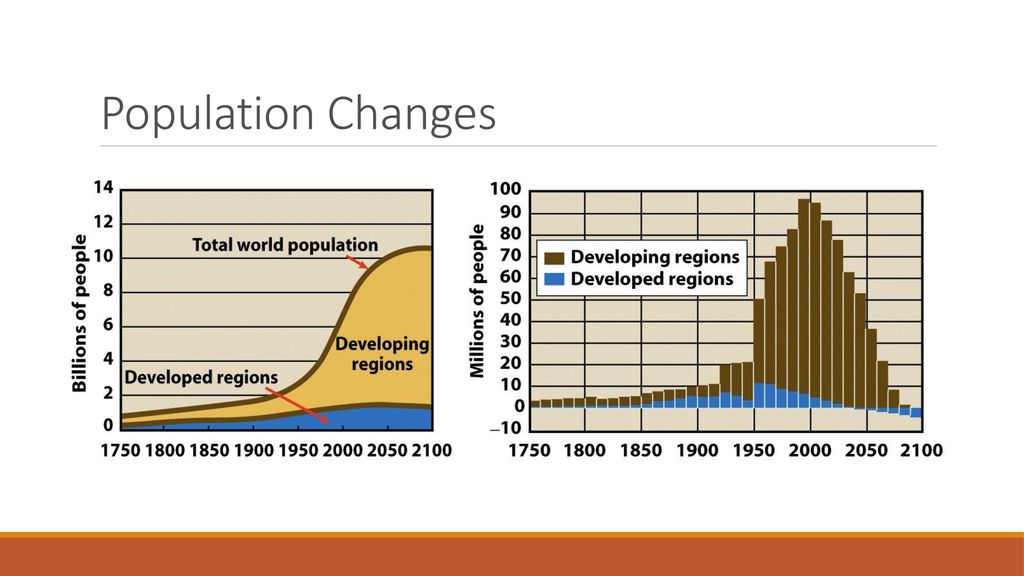
The global population is projected to continue growing for several decades, although the rate of growth is slowing. According to the United Nations, the world population is expected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050.
This growth will be unevenly distributed, with the majority of the increase occurring in developing countries. This will lead to significant challenges related to resource management, infrastructure development, and environmental sustainability.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, including investments in education, healthcare, and sustainable development. By understanding the processes that drive population growth, we can better prepare for the future and work towards a more sustainable and equitable world.