Which Statement Is True Regarding Antipsychotic Medications

Confusion often surrounds the use of antipsychotic medications, particularly regarding their effectiveness, side effects, and appropriate usage. Misinformation can lead to fear and reluctance to seek necessary treatment. This article clarifies common misconceptions and presents a balanced view of these powerful drugs.
At the heart of the discussion is the following question: Which statement is true regarding antipsychotic medications? The answer is complex, as the truth lies in understanding the nuances of these drugs, their varied applications, and the individual patient's response to treatment.
Understanding Antipsychotic Medications
Antipsychotic medications, also known as neuroleptics, are a class of drugs primarily used to manage psychosis. Psychosis is a mental state characterized by a disconnection from reality, often involving hallucinations and delusions.
These medications work by affecting the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, particularly dopamine and serotonin. By modulating these neurotransmitters, antipsychotics can help to alleviate psychotic symptoms and improve cognitive function.
Types of Antipsychotics
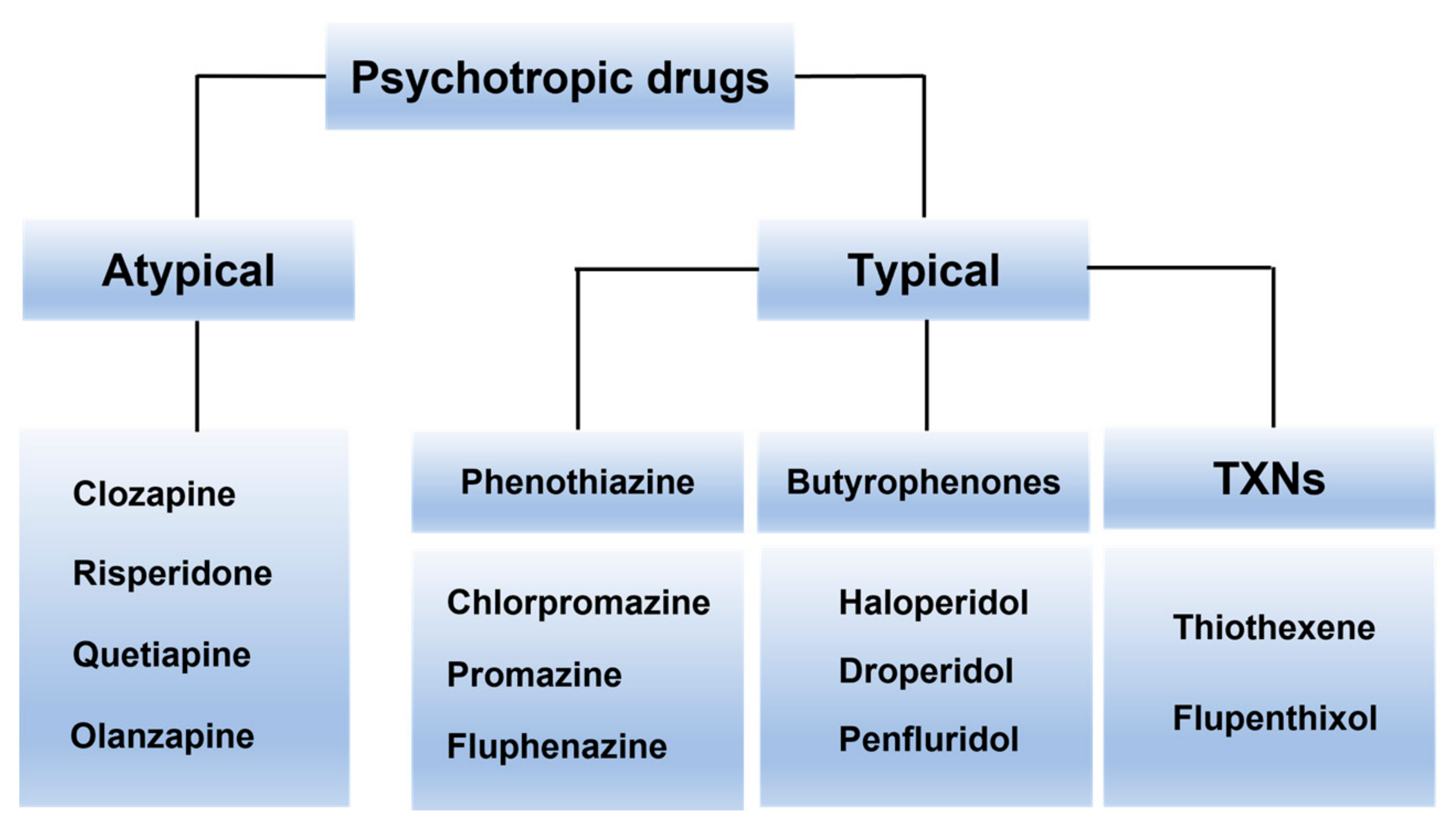
Antipsychotics are broadly categorized into first-generation (typical) and second-generation (atypical) medications. First-generation antipsychotics, such as haloperidol and chlorpromazine, primarily target dopamine receptors.
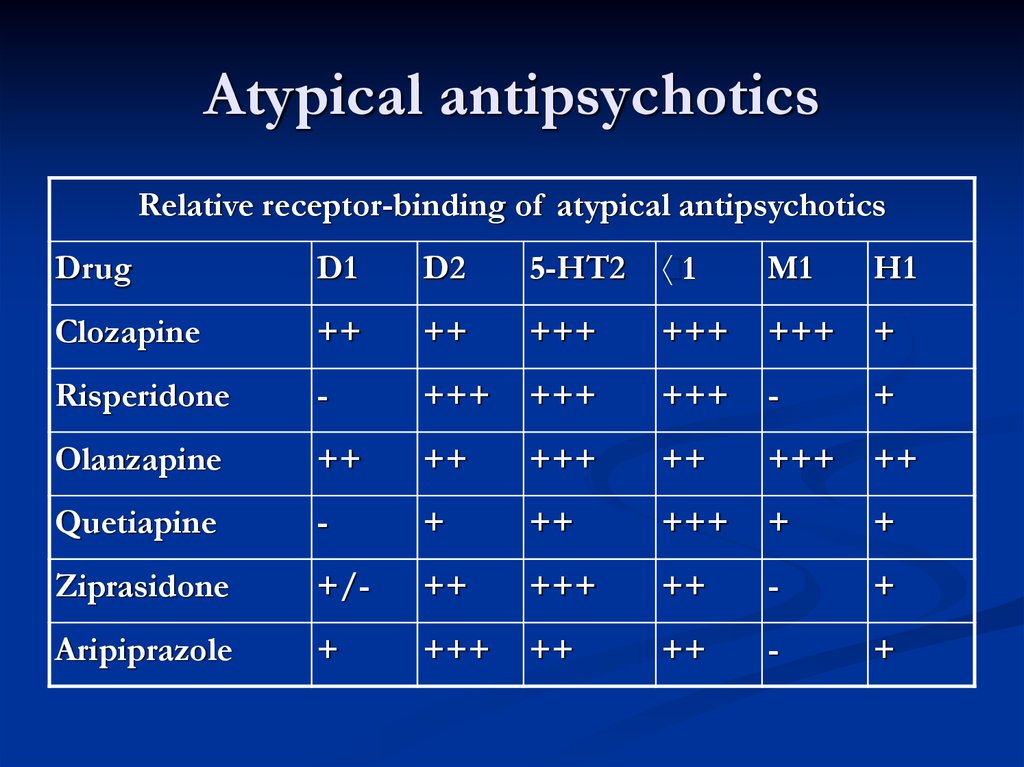
Second-generation antipsychotics, including risperidone, olanzapine, and quetiapine, affect both dopamine and serotonin receptors. This difference in mechanism is believed to contribute to a lower risk of certain side effects, particularly extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), compared to first-generation drugs.
Common Misconceptions and Facts
Misconception: Antipsychotics are only for schizophrenia. Fact: While schizophrenia is a primary indication, these medications are also used to treat bipolar disorder, severe depression with psychotic features, and other mental health conditions.
Misconception: Antipsychotics are a "cure" for mental illness. Fact: Antipsychotics manage symptoms but do not cure underlying conditions. They are often part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes therapy and lifestyle changes.
Misconception: All antipsychotics have the same side effects. Fact: Side effects vary significantly among different antipsychotics. Some common side effects include weight gain, sedation, and metabolic changes, but the likelihood and severity differ depending on the specific medication and individual factors.
The Importance of Individualized Treatment
The effectiveness and tolerability of antipsychotic medications can vary greatly from person to person. What works well for one individual may not be suitable for another.
Therefore, treatment decisions should be made on an individual basis, taking into account the patient's specific diagnosis, symptoms, medical history, and preferences. Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional is crucial to assess the medication's effectiveness and manage any potential side effects.
Dr. Emily Carter, a psychiatrist at the National Institute of Mental Health, emphasizes the importance of open communication between patients and their doctors. "Patients should feel comfortable discussing their concerns and experiences with their medication," she states.
"Finding the right antipsychotic and dosage often requires a trial-and-error approach. Patience and collaboration are essential for achieving optimal outcomes," says Dr. Carter.
Potential Impact and Conclusion
Understanding the truth about antipsychotic medications is vital for reducing stigma and promoting informed decision-making. When used appropriately and under the guidance of a healthcare professional, these medications can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals struggling with psychosis and other mental health conditions.
Education and accurate information are critical for empowering patients and their families to make informed choices about their treatment. By dispelling misconceptions and fostering a more nuanced understanding of these medications, we can help ensure that individuals receive the care they need to lead fulfilling lives.
Ultimately, the true statement regarding antipsychotic medications is that they are powerful tools that can be effective when used appropriately, but they are not without risks. Individualized treatment, open communication, and ongoing monitoring are essential for maximizing benefits and minimizing potential harm.




+Which+of+the+following+statements+regarding+medications+is+FALSE.jpg)



.jpg)



(2)+Unnecessary+Medications.jpg)


