Within The Relevant Range Of Activity Blank______.
Imagine a small bakery, the aroma of freshly baked bread swirling through the air. Flour dusts the counters, and the rhythmic churn of the mixer fills the room. But what happens when that bakery, comfortable in its routine, suddenly faces a surge in orders, or conversely, a dramatic drop in demand?
Understanding the concept of the relevant range of activity is crucial for businesses of all sizes, from that small bakery to multinational corporations. It's the sweet spot where a company's cost behavior is predictable and its financial plans hold true. Staying within this range ensures accuracy in budgeting, decision-making, and overall financial health. This article delves into this vital concept, exploring its implications, benefits, and the challenges companies face when venturing outside its boundaries.
The Foundation: Understanding Cost Behavior
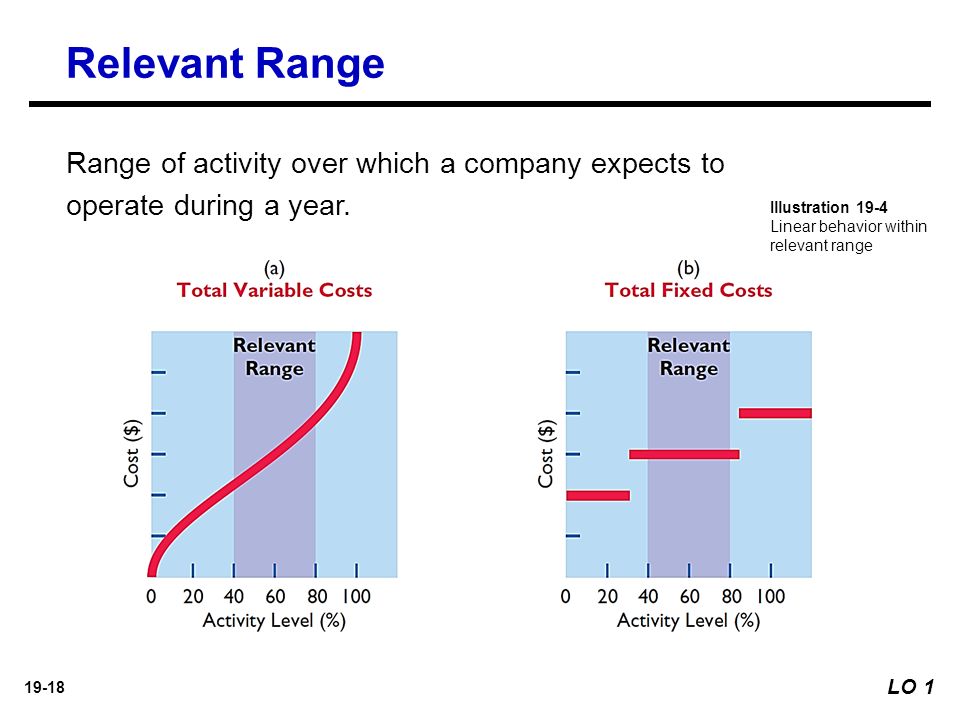
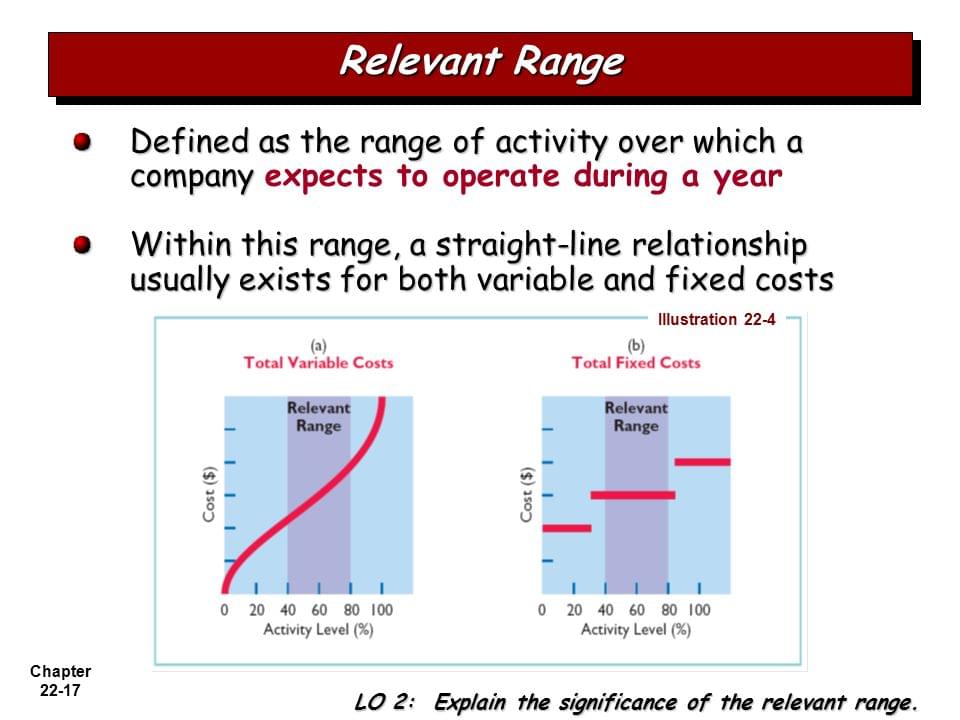
The relevant range is inextricably linked to the way costs behave. Generally, costs are classified as either fixed or variable. Fixed costs, such as rent or insurance, remain constant regardless of the production level, within certain limits.
Variable costs, on the other hand, fluctuate directly with the level of activity. Think of the flour in our bakery; the more bread they bake, the more flour they need. It's a direct relationship.
The Magic Number: Defining the Relevant Range
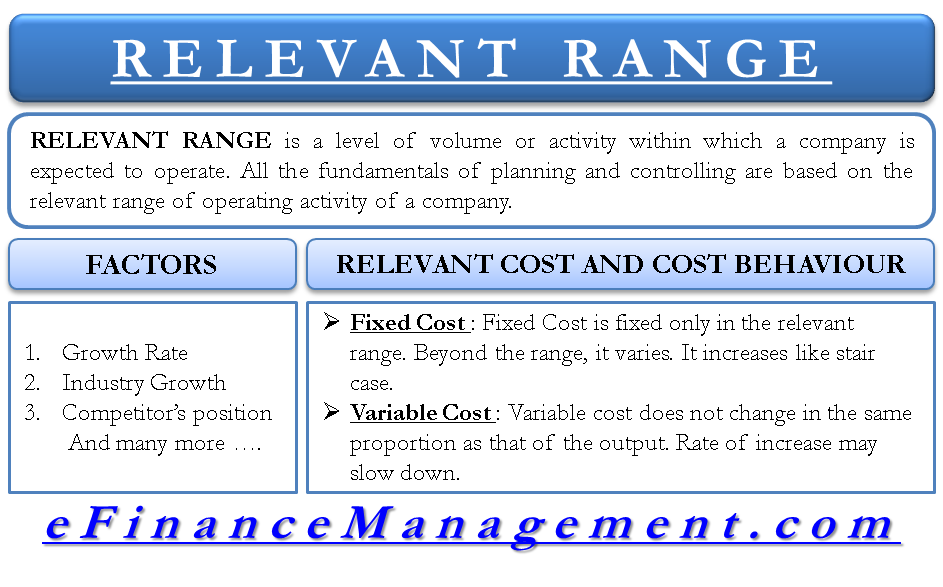
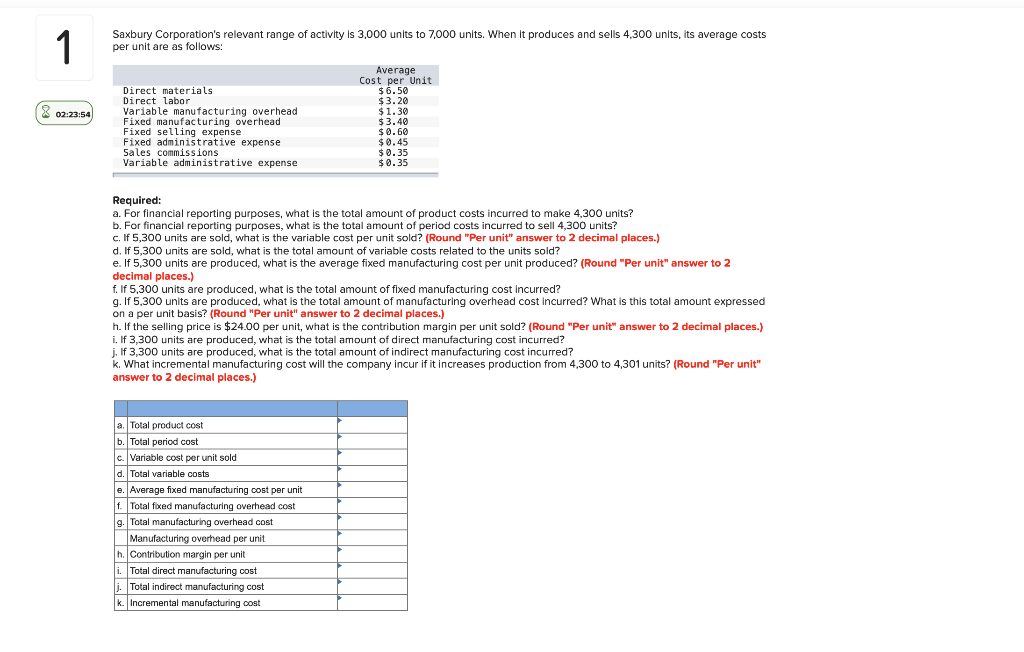
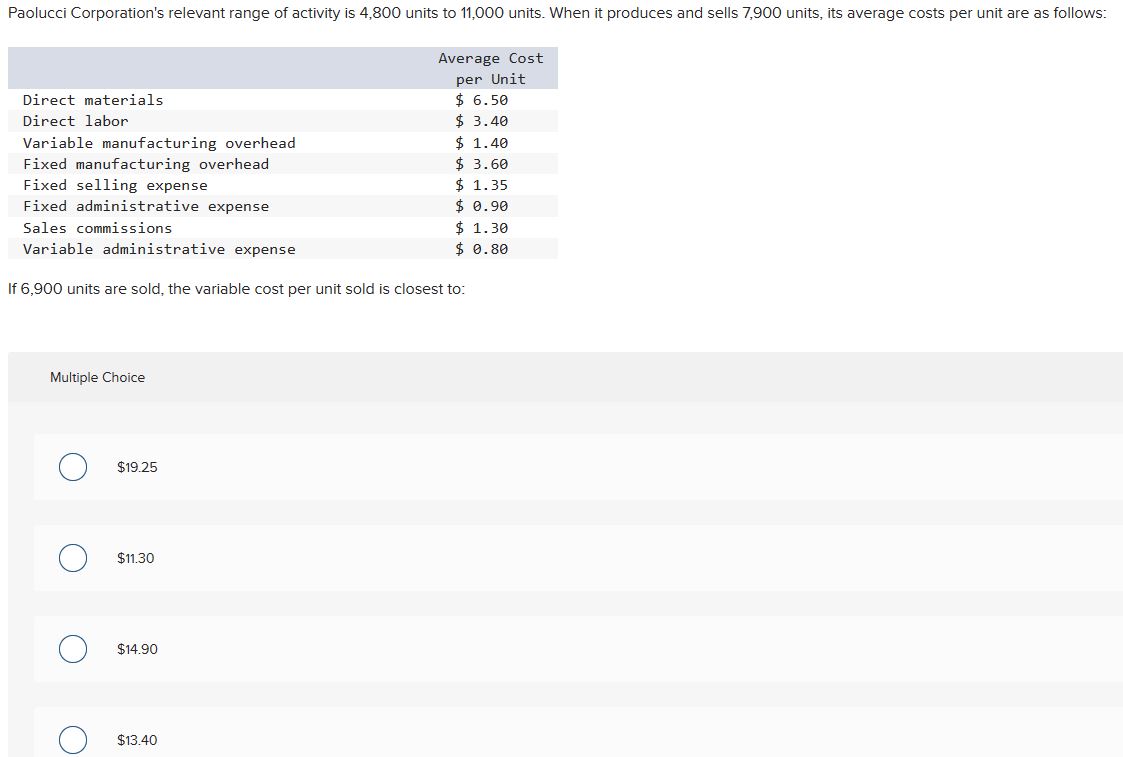
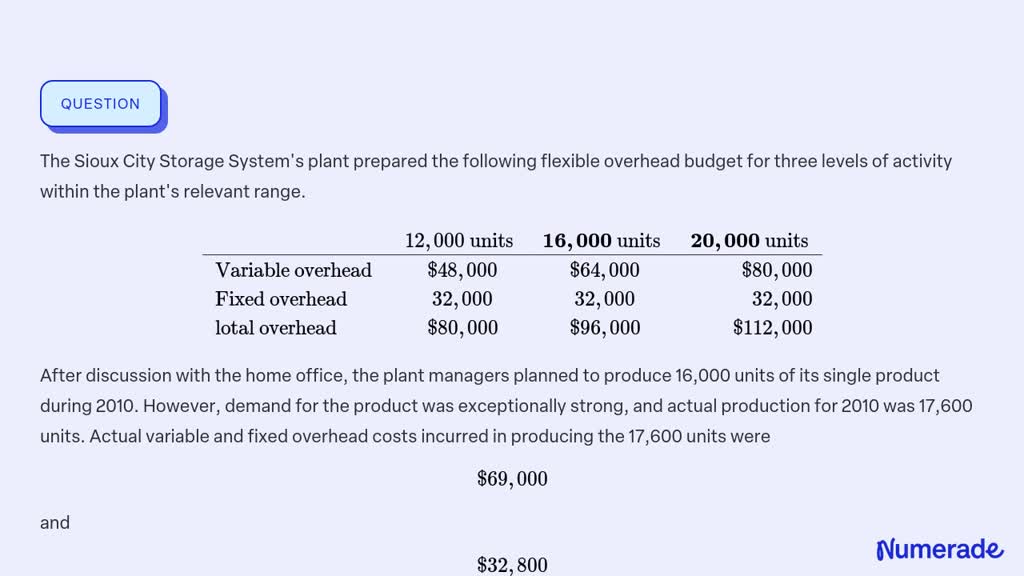
The relevant range of activity is the specific level of activity within which a business expects to operate. It’s the bandwidth where assumptions about fixed and variable costs are reliably accurate. Outside this range, those assumptions begin to break down.
For instance, the bakery’s current oven might be capable of producing between 100 and 500 loaves of bread per day. This could be considered their initial relevant range. Their fixed costs, like rent and the baker's salary, remain constant within this range.
Why is it Important?
Understanding the relevant range offers several significant advantages. It is foundational to budgeting accuracy. It allows for more effective decision-making based on reliable cost estimates.
And it supports the accurate performance evaluation, as expectations are based on realistic assumptions. Think about it, if the bakery manager is judged against a budget that assumed sales of 300 loaves a day, but demand surged to 600, the evaluation would be meaningless.
Beyond the Bakery: Real-World Examples
The concept extends far beyond our bakery example. Consider a manufacturing company. Their relevant range might be defined by the capacity of their existing machinery.
If they need to significantly increase production, they might need to invest in new equipment, thereby increasing their fixed costs and potentially shifting the relevant range. A software company's relevant range might be based on the capacity of their servers.
The Downside: Stepping Outside the Lines
Venturing outside the relevant range can have serious consequences. Cost predictions become unreliable. Decisions based on those inaccurate predictions can lead to inefficiencies or even losses.
Performance evaluations become skewed and demotivating. Imagine the bakery trying to fulfill 1000 loaves a day using only their existing oven. They might need to outsource some of the baking, leading to higher, unanticipated costs.
Fixed Costs Aren't Always Fixed
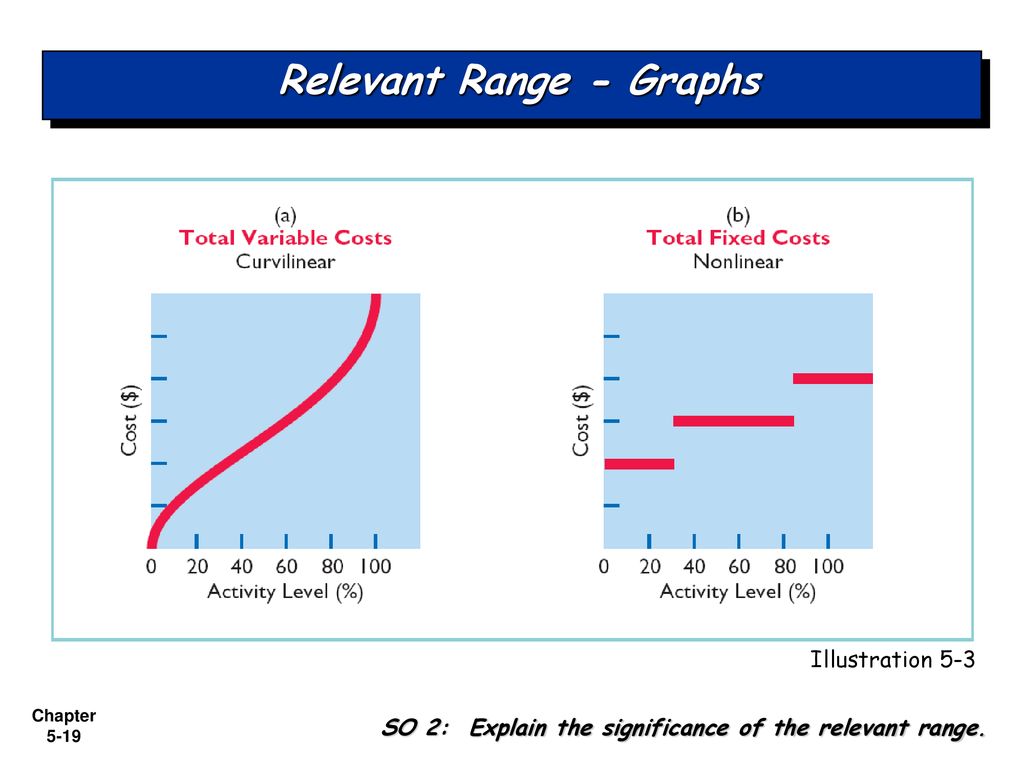
One of the key assumptions within the relevant range is that fixed costs remain constant. But this holds true only within a certain activity level. Beyond that level, fixed costs might jump in steps.
For example, if the bakery expands and needs to rent another space, their fixed rent expense will increase. This introduces a new relevant range with a higher fixed cost structure.
Navigating the Landscape: Practical Considerations
So, how can companies effectively manage the relevant range? The first step is to identify and define the current range based on existing resources and capacity. Regularly review and update the range as the business evolves and grows.
Conduct thorough cost analysis to understand the behavior of both fixed and variable costs. Implement flexible budgeting, which allows for adjustments based on actual activity levels.
The Role of Technology
Modern technology plays a significant role in managing the relevant range. Sophisticated accounting software can track costs in real-time and generate reports that highlight deviations from the expected range. Data analytics tools can help businesses forecast future activity levels and adjust their plans accordingly.
By leveraging technology, businesses can gain a better understanding of their cost structure and make more informed decisions. This creates greater agility to respond to market changes.
Challenges and Considerations
Determining the relevant range isn't always a straightforward process. It requires careful analysis, judgment, and a deep understanding of the business. External factors, such as economic conditions or changes in regulations, can also impact the relevant range.
A sudden surge in demand due to a viral social media post could push the bakery beyond its initial capacity, requiring quick adjustments to their production process and cost structure.
The Human Element
While data and technology are important, don't underestimate the human element. Engaging employees from different departments in the process can provide valuable insights. The baker knows the oven's capabilities intimately; the sales team understands customer demand patterns.
Collaboration ensures that the relevant range is based on a holistic understanding of the business. This promotes ownership and accountability throughout the organization.
Looking Ahead: Embracing Adaptability
In today's dynamic business environment, adaptability is key. Companies need to be prepared to adjust their strategies and operations as circumstances change. Understanding and managing the relevant range is a critical part of that process. By proactively monitoring costs, forecasting activity levels, and embracing flexibility, businesses can navigate the challenges of a constantly evolving market.
The bakery, armed with a clear understanding of its relevant range, can confidently expand its operations, knowing that its financial plans are grounded in reality. And so can any business, no matter how big or small.