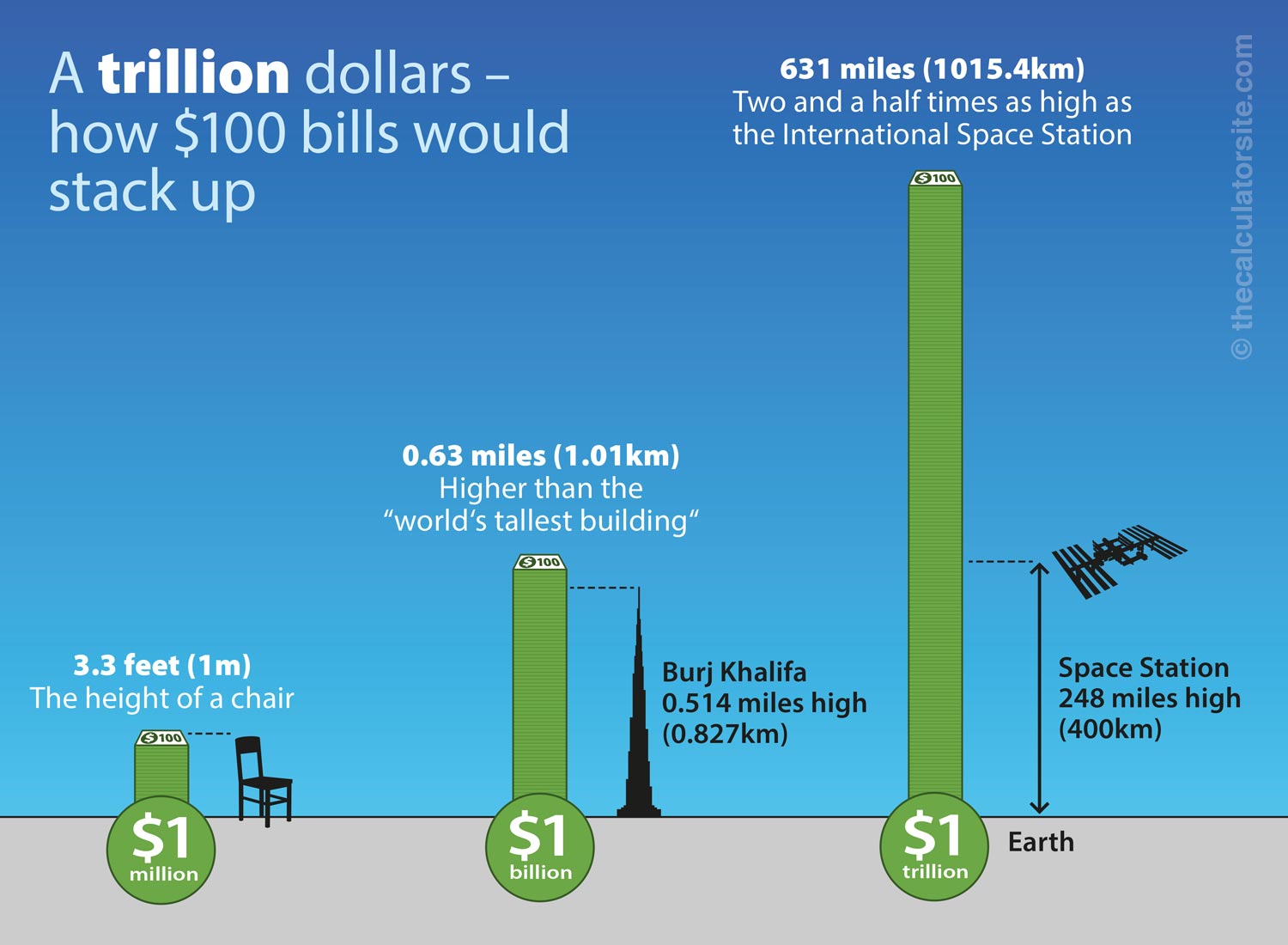
3 Billion Divided By 1 Million

The number 3,000,000,000 divided by 1,000,000 might seem like a simple arithmetic problem. But the implications of this calculation, equaling 3,000, resonate far beyond basic mathematics. They touch upon crucial aspects of global resource allocation, economic disparities, and the effectiveness of aid programs.
This seemingly straightforward division exposes a critical question: what is the tangible impact when vast sums of money are distributed across large populations or numerous initiatives? The answer demands a nuanced examination of how resources are managed, how effectively they reach their intended beneficiaries, and what systemic challenges hinder progress.
The Nut Graf: Deconstructing the Division
At its core, 3 billion divided by 1 million yields 3,000. While the math is irrefutable, the significance depends entirely on the context. Is it $3 billion in aid distributed amongst one million people? Is it $3 billion in investment across one million small businesses? The interpretation drastically shifts depending on the variables involved.
This article unpacks the complexities of this division by exploring several key areas. These are the allocation of international aid, distribution of resources in large-scale projects, and the stark realities of wealth disparity. By analyzing these scenarios, we can gain a deeper understanding of the practical implications of dividing large sums by large populations.
International Aid: A Global Perspective
International aid, often measured in billions of dollars, aims to alleviate poverty and foster development in low-income countries. When $3 billion in aid is theoretically divided among one million individuals, it suggests each person would receive $3,000. However, the reality is far more complex.
According to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), aid disbursement is rarely direct and evenly distributed. Funds are often channeled through governments, NGOs, and international organizations, each taking a percentage for administrative costs and project implementation.
Furthermore, corruption and mismanagement can significantly reduce the amount of aid that actually reaches the intended beneficiaries. The World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) have implemented safeguards to prevent misuse of funds. However, these efforts are not always successful.
A 2023 report by Transparency International revealed that in some countries, up to 30% of aid money is lost due to corruption. This drastically reduces the impact of aid, leaving many vulnerable populations still struggling.
Large-Scale Projects: Infrastructure and Development
Large-scale infrastructure projects, such as building roads, dams, or schools, often involve budgets in the billions. If a $3 billion project is designed to benefit one million people, the per capita investment is again $3,000. However, the impact isn’t always directly proportional.
These projects can generate significant economic benefits. This comes from improved transportation, increased access to education, and enhanced agricultural productivity. These benefits are, however, often unevenly distributed, favoring those with better access to resources or political connections.
Environmental impact assessments are crucial. They minimize potential negative consequences on local communities and ecosystems. But these assessments can add to project costs and sometimes face resistance from stakeholders prioritizing short-term economic gains.
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) emphasizes sustainable development. It highlights that projects should be environmentally sound, socially inclusive, and economically viable. However, achieving this balance remains a significant challenge.
Wealth Disparity: A Stark Reality
The concept of dividing $3 billion by one million can also illuminate the stark reality of wealth disparity. The world's richest individuals and corporations often control vast amounts of wealth. This dwarfs the resources available to the majority of the population.
According to Oxfam, the gap between the rich and poor continues to widen. The wealthiest 1% own more than half of the world’s wealth. This concentration of resources leaves a significant portion of the global population struggling to meet basic needs.
Tax policies and regulations play a crucial role in addressing wealth disparity. Progressive taxation and policies aimed at curbing tax evasion can help redistribute wealth more equitably.
However, these measures often face political opposition from powerful interest groups. They argue that high taxes stifle economic growth and discourage investment.
Challenges and Opportunities
Several challenges hinder the effective allocation of resources. Corruption, mismanagement, lack of transparency, and political instability all contribute to inefficiencies.
Technological advancements offer opportunities to improve resource management and transparency. Blockchain technology, for example, can be used to track aid money and ensure it reaches its intended destination.
Greater involvement of local communities in decision-making processes is crucial. This ensures that projects are aligned with their needs and priorities. It also empowers communities to hold implementers accountable.
Looking Ahead: A Path Forward
The simple calculation of 3 billion divided by 1 million serves as a powerful reminder of the complexities of resource allocation. It highlights the need for more effective strategies to address poverty, promote development, and reduce wealth disparity.
By focusing on transparency, accountability, and community engagement, we can strive to ensure that resources are used more effectively. This will maximizing their impact on the lives of those who need them most.
Ultimately, achieving a more equitable and sustainable world requires a collective effort. It demands collaboration between governments, international organizations, civil society, and the private sector to address the systemic challenges that perpetuate inequality. Only then can the potential of $3,000 per person, when scaled to millions, translate into tangible and lasting improvements in the lives of people across the globe.
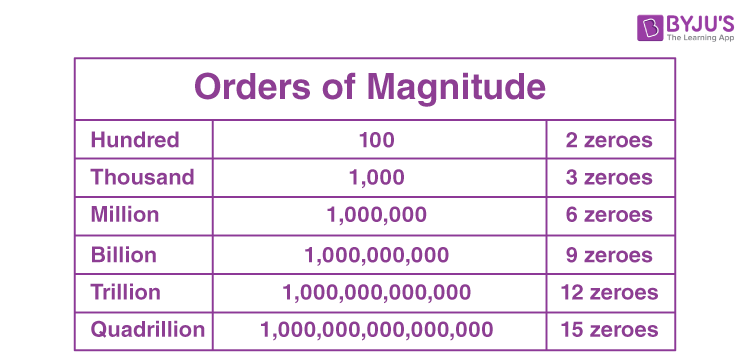







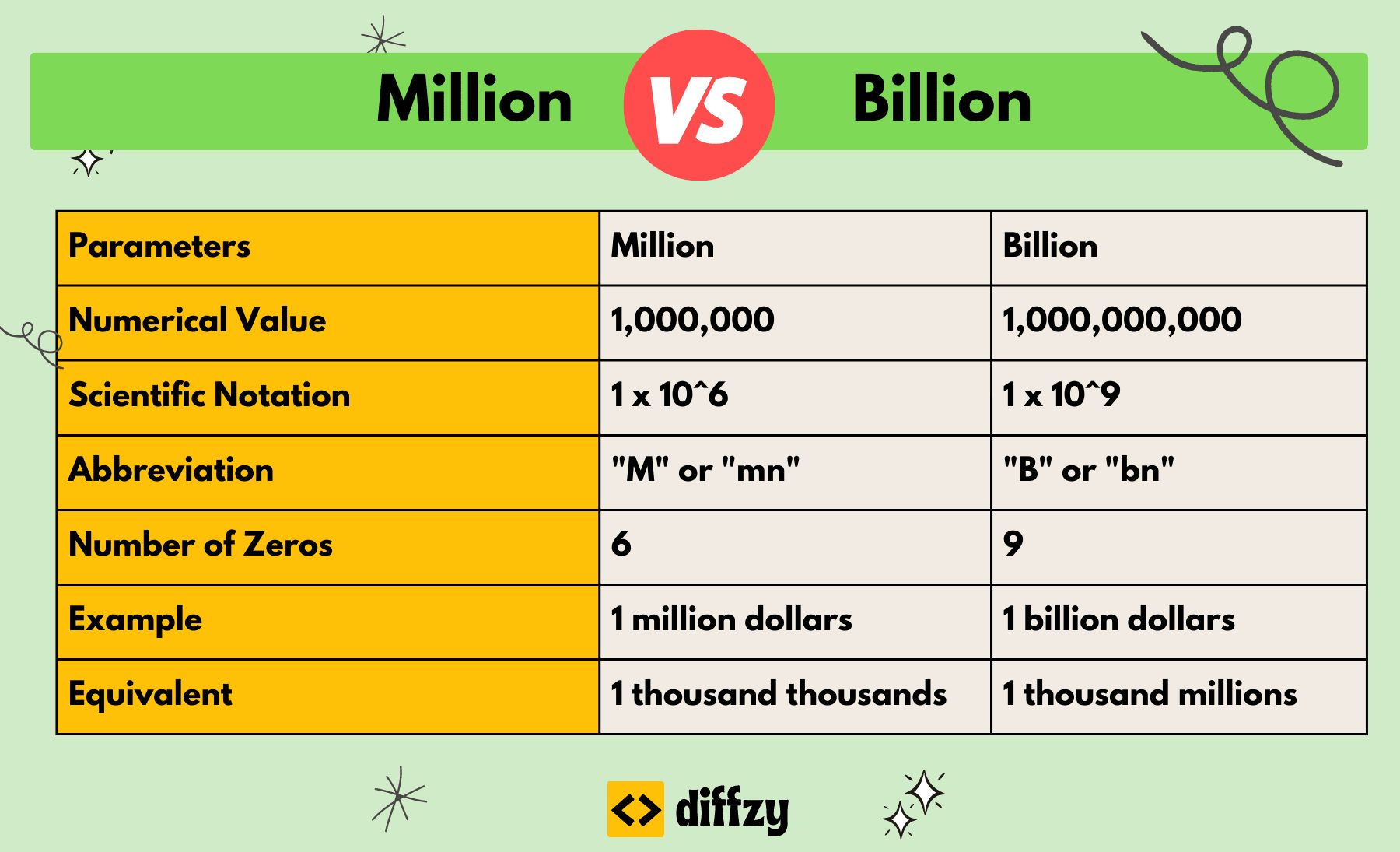
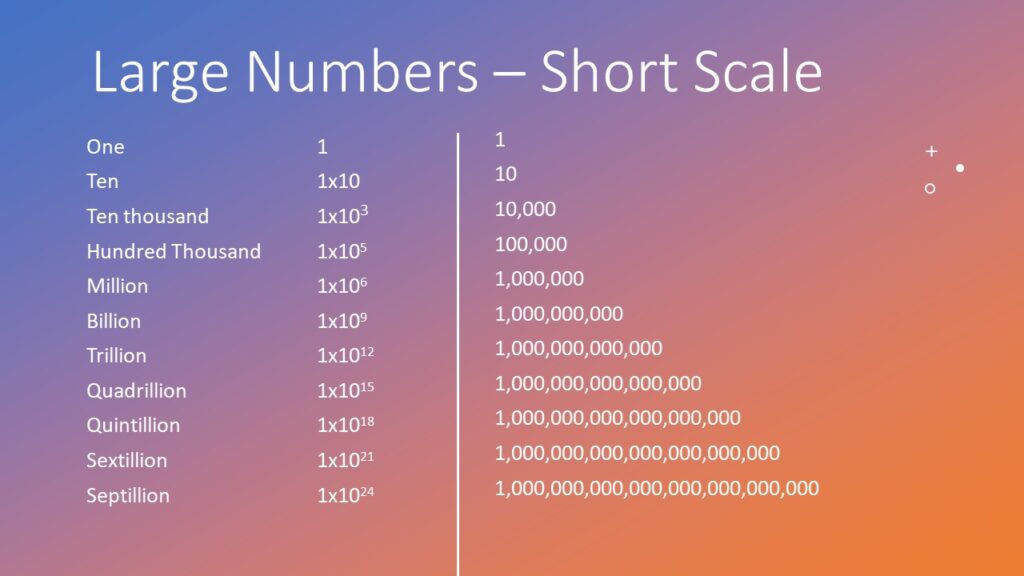


/BiggerThanMillion-58b734085f9b5880803990ff.jpg)