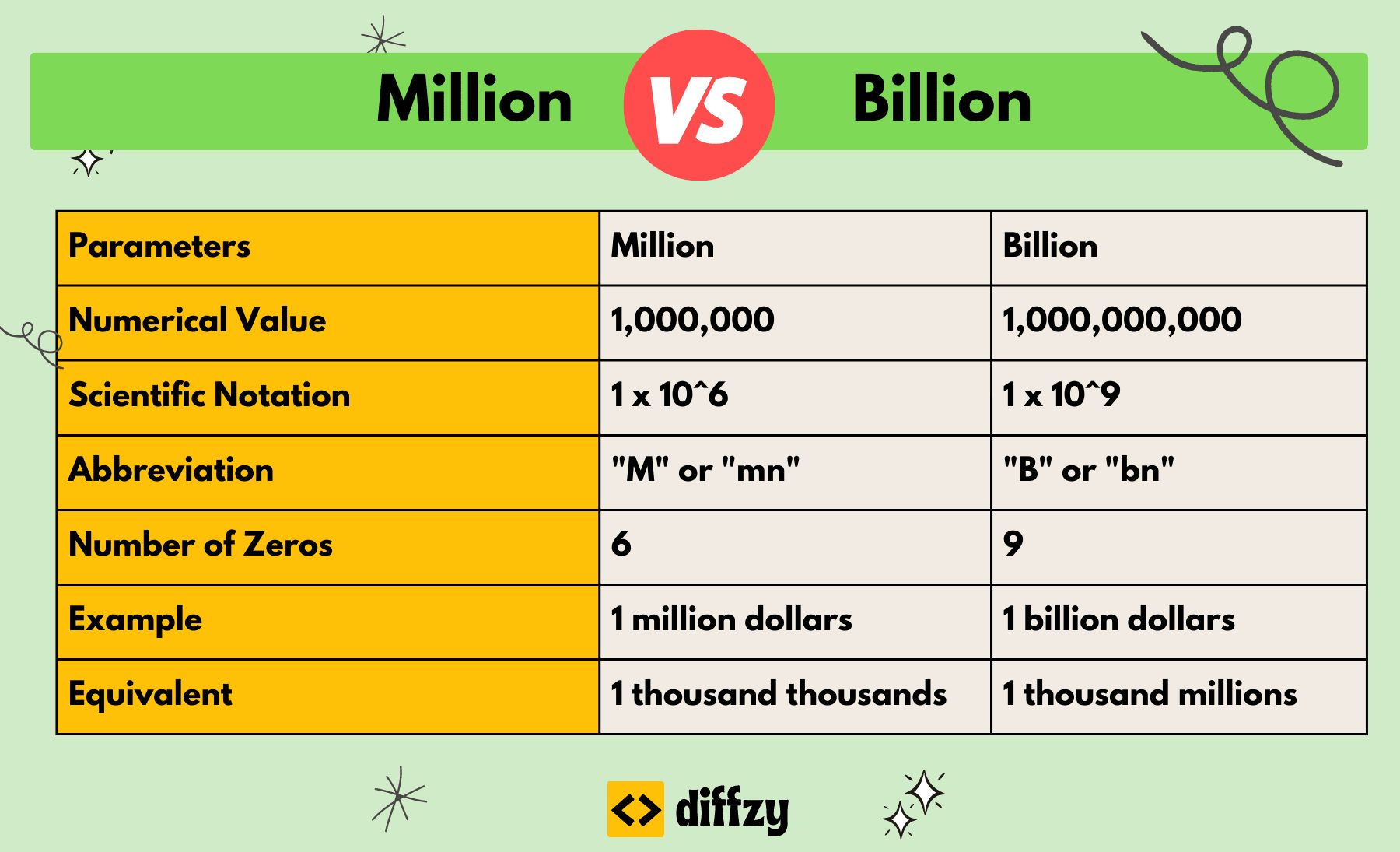
5 Billion Divided By 300 Million

The stark calculation – 5 billion divided by 300 million – echoes through economic discussions, policy debates, and everyday conversations. It represents, in its most basic form, roughly $16,666.67 per person. However, this simple arithmetic masks a complex web of issues surrounding resource allocation, economic disparity, and the enduring quest for a more equitable society.
At its heart, this figure serves as a powerful, albeit simplistic, illustration of potential resource redistribution. This could be in the context of a national budget, a specific economic stimulus package, or even global aid initiatives. The nut graf unpacks the nuances of this seemingly straightforward calculation. It explores its implications for individuals, communities, and the broader economic landscape. It requires a deep dive into the sources of the $5 billion, the criteria for its allocation, and the potential impact on various segments of the population.
Understanding the $5 Billion
The origin of the $5 billion is crucial to understanding its potential impact. Is it a government surplus? A private sector investment? Or an international aid package? Knowing the source provides context for the intended beneficiaries and the potential restrictions on its use.
For example, if the $5 billion stems from a government surplus, its allocation might be subject to political maneuvering and competing priorities. Different political factions could advocate for various uses, such as infrastructure development, tax cuts, or social programs.
Alternatively, if the sum represents a private sector investment, the focus would likely be on maximizing returns and creating economic opportunities. This could translate into job creation, innovation, and increased productivity, but might not directly address existing inequalities.
The 300 Million: A Closer Look
Similarly, understanding the “300 million” is equally important. Does this figure represent the entire population of a country? Or a specific demographic group? The answer shapes the perspective on how the $5 billion should be distributed and what impact it might have.
If the 300 million represents the total population, the $16,666.67 per capita figure provides a broad overview of potential resource availability. However, it doesn't account for existing income disparities or the specific needs of vulnerable populations. Income inequality is a critical factor in determining the true impact of resource allocation.
If the figure pertains to a specific demographic group, such as low-income families or unemployed individuals, the $16,666.67 could represent a significant boost to their financial well-being. This could enable them to access essential services, improve their living standards, and invest in their future.
Distribution Methods and Their Consequences
The method of distributing the $5 billion is critical to ensuring its effectiveness and fairness. A lump-sum payment to each individual would have a different impact than investing in public services or targeted programs. Each option carries its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
A direct cash transfer, while seemingly straightforward, could be subject to misuse or inefficient spending. Some argue that individuals might not have the financial literacy or resources to manage a large sum of money effectively. Others argue that it empowers individuals to make their own choices and address their specific needs.
Investing in public services, such as education, healthcare, or infrastructure, could create long-term benefits for the entire population. This approach could improve access to essential services, create job opportunities, and boost economic growth. Investing in infrastructure is often seen as a catalyst for economic development.
Targeted programs, designed to address specific needs of vulnerable populations, could be the most effective way to reduce inequality and improve social outcomes. These programs could provide job training, affordable housing, or access to healthcare for those who need it most.
The Role of Economic Policy and Social Equity
The allocation of the $5 billion cannot be divorced from broader economic policies and considerations of social equity. The impact of this sum will be significantly influenced by the prevailing economic conditions, existing social safety nets, and the overall political climate. Effective resource allocation requires a holistic approach.
Tax policies, for example, play a crucial role in determining how wealth is distributed and whether the benefits of economic growth are shared equitably. Progressive tax systems, where higher earners pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes, can help fund social programs and reduce income inequality. Progressive taxation is a key tool for wealth redistribution.
Social safety nets, such as unemployment benefits, food stamps, and affordable housing programs, provide a crucial buffer for vulnerable populations during economic downturns. Strengthening these programs can help mitigate the negative consequences of poverty and inequality. Robust social safety nets are essential for mitigating economic hardship.
The political climate also influences resource allocation. Political ideologies, lobbying efforts, and public opinion all play a role in shaping policy decisions and determining how resources are distributed. Understanding the political dynamics is essential for navigating the complex landscape of resource allocation.
Looking Ahead: Towards a More Equitable Future
The calculation of 5 billion divided by 300 million serves as a starting point for a larger conversation about resource allocation, economic disparity, and the pursuit of a more equitable society. While the simple arithmetic provides a basic framework, the true challenge lies in implementing policies and programs that effectively address the root causes of inequality and create opportunities for all.
To achieve a more equitable future, we need to move beyond simplistic calculations and embrace a holistic approach. This requires understanding the complex interplay of economic forces, social factors, and political dynamics that shape our society. Systemic change is necessary to address deeply rooted inequalities.
Ultimately, the allocation of resources should be guided by the principles of fairness, justice, and opportunity. By investing in education, healthcare, and infrastructure, we can create a society where everyone has the chance to thrive. By strengthening social safety nets and addressing systemic inequalities, we can ensure that the benefits of economic growth are shared more equitably. The pursuit of a more just and equitable society is an ongoing endeavor.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/BiggerThanMillion-58b734085f9b5880803990ff.jpg)