A Change In Stockholders' Equity Is Caused By:
The financial health of a company is often gauged by its stockholders' equity, a critical metric reflecting the owners' stake in the business. Changes to this figure are not arbitrary; they are the result of specific activities that can provide significant insights into a company's performance and future trajectory. Understanding the drivers behind these fluctuations is crucial for investors, analysts, and anyone seeking to understand the true value of a business.
This article delves into the core causes of changes in stockholders' equity, examining the key transactions and events that directly influence this vital component of a company's balance sheet. We'll explore how these changes reflect a company's operational success, strategic decisions, and overall financial stability.
What Drives Stockholders' Equity?
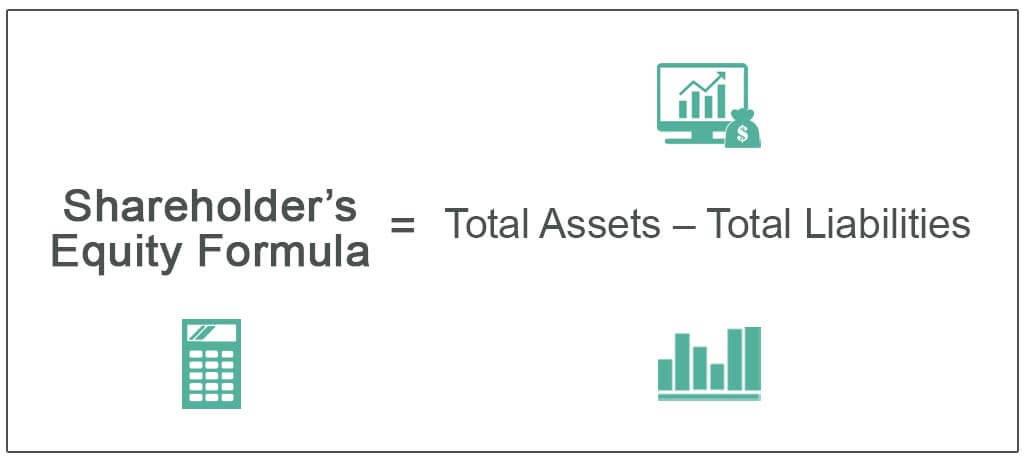
Stockholders' equity, also known as owners' equity or net worth, represents the residual interest in the assets of an entity after deducting its liabilities. It is essentially what would be left for the shareholders if all the company's assets were sold and all its debts were paid off. Changes in this value are directly linked to the company's profitability and its decisions regarding capital distribution and reinvestment.
Net Income or Net Loss: The Primary Driver
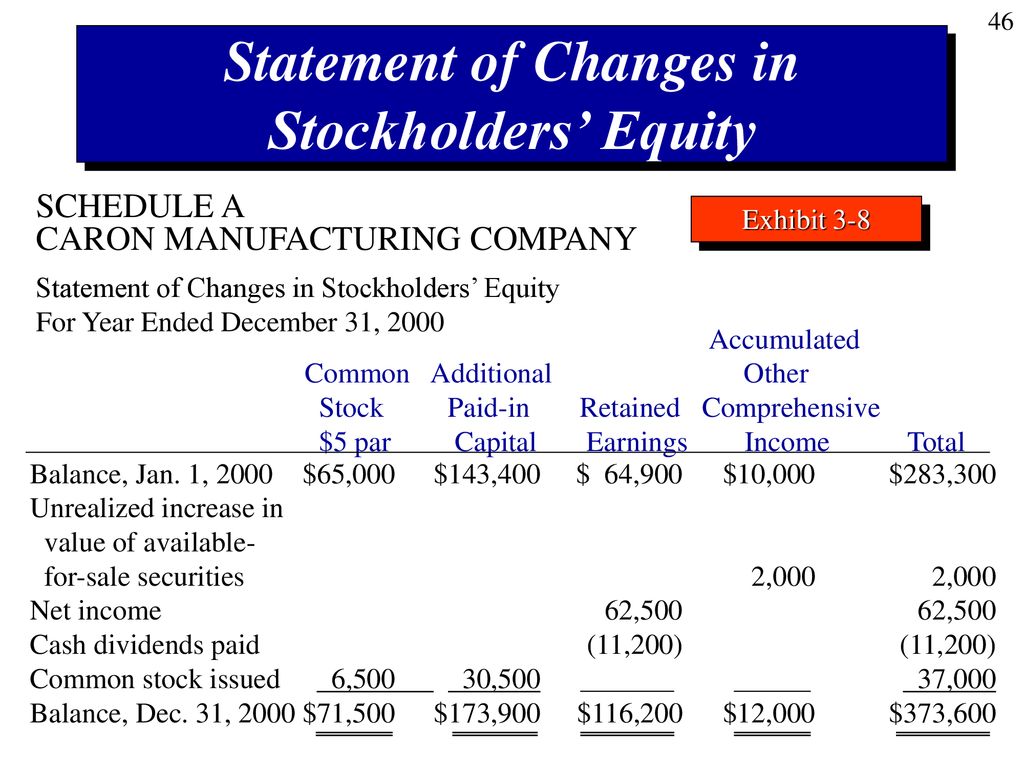
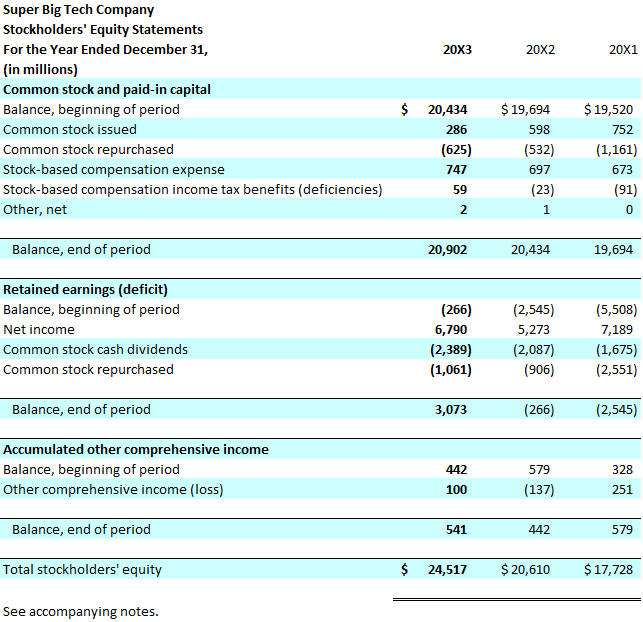
The most significant driver of change in stockholders' equity is net income. A company's profitability directly increases its retained earnings, which is a component of stockholders' equity. Conversely, a net loss decreases retained earnings, negatively impacting the overall equity position.
For instance, if Company X reports a net income of $1 million, this amount is added to the retained earnings, boosting stockholders' equity. If, however, Company X experiences a net loss of $500,000, this loss is deducted from retained earnings, diminishing the equity value.
Dividends: Distributing Profits to Shareholders
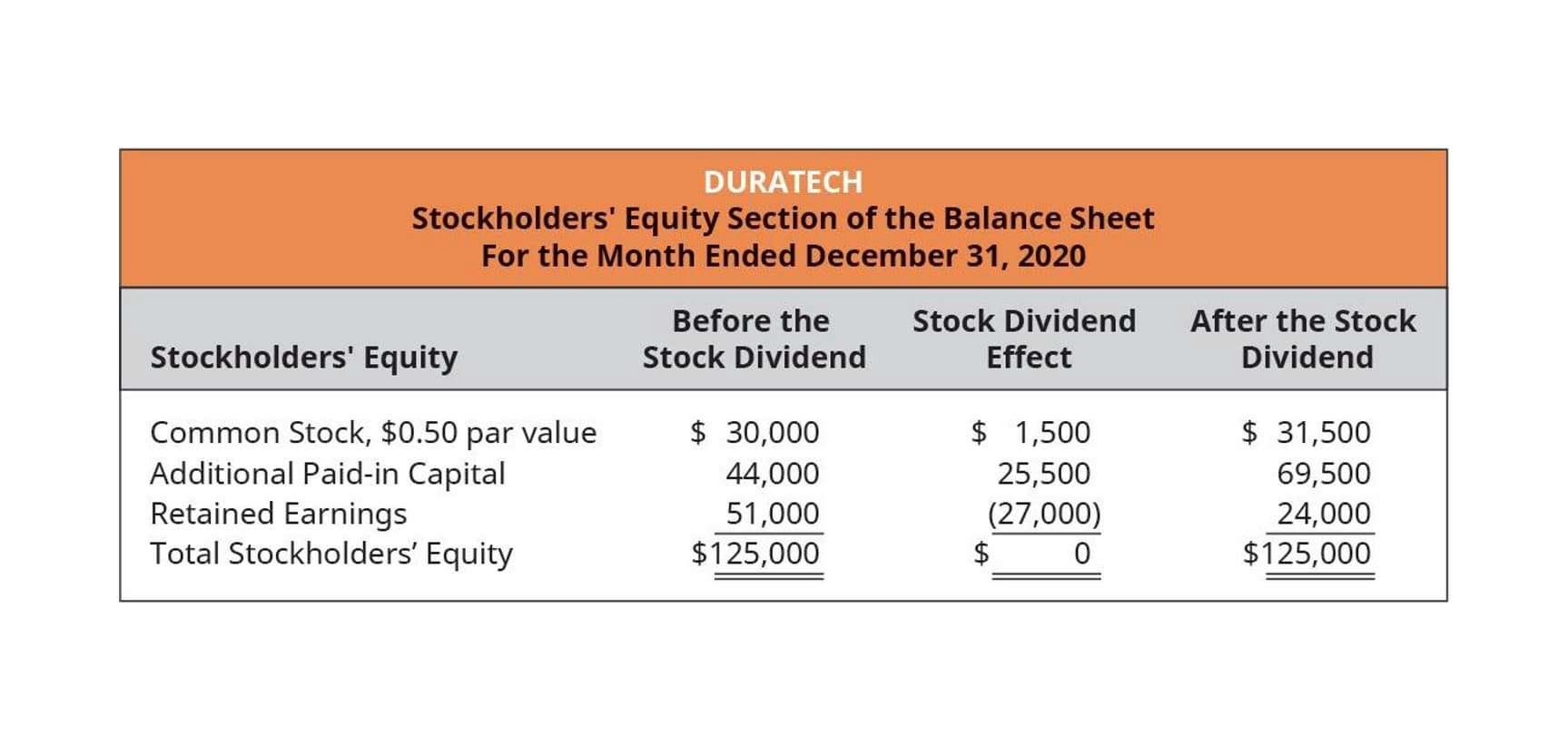
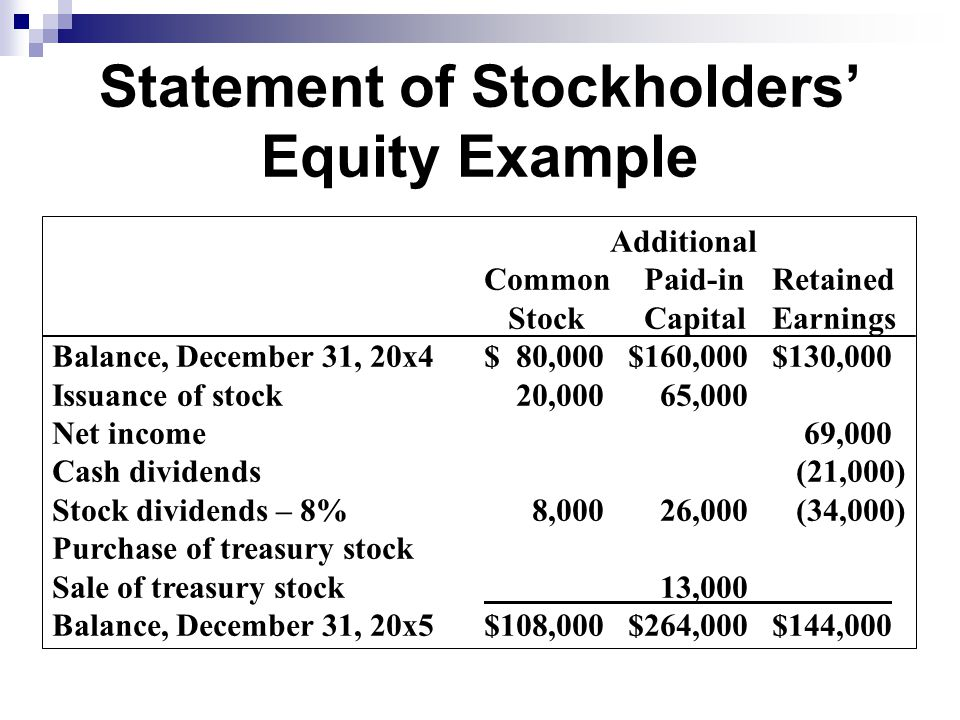
While net income increases equity, the payment of dividends reduces it. Dividends represent a distribution of a portion of the company's profits to its shareholders. This reduces the amount of retained earnings available within the company, thus decreasing stockholders' equity.
When Company Y declares and pays $200,000 in dividends, this amount is deducted from the retained earnings, directly reducing the stockholders' equity. Companies often balance the need to reward shareholders with dividends against the desire to reinvest profits for future growth.
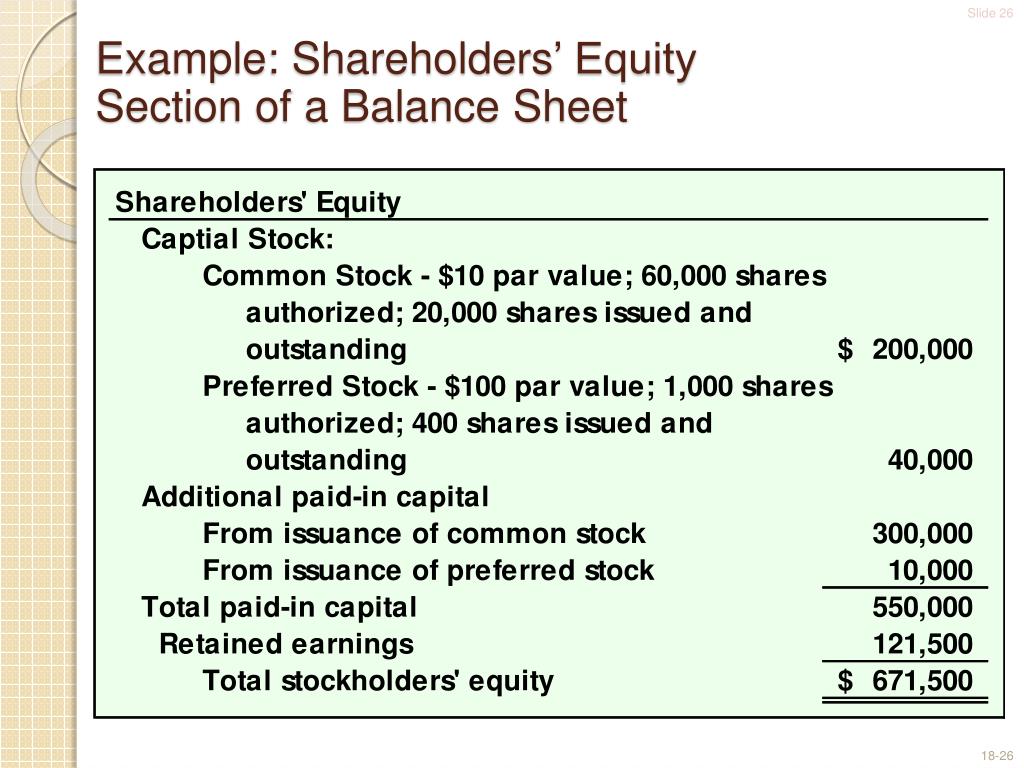
Issuance of Stock: Raising Capital from Investors
Another way to increase stockholders' equity is through the issuance of new stock. When a company sells shares of its stock to investors, it receives cash or other assets in exchange. This increases both the assets and the stockholders' equity of the company.
If Company Z issues 10,000 shares of common stock at $10 per share, it receives $100,000 in cash, which increases both its assets and its stockholders' equity. This is a common method for companies to raise capital for expansion, acquisitions, or debt reduction.
Repurchase of Stock: Reducing Outstanding Shares
Conversely, when a company repurchases its own stock (treasury stock), it decreases stockholders' equity. The cash used to buy back the stock reduces the company's assets, and the treasury stock is recorded as a reduction in stockholders' equity.
If Company A repurchases 5,000 shares of its own stock at $15 per share, it spends $75,000 in cash, reducing its assets. This $75,000 is also reflected as a decrease in stockholders' equity, specifically in the treasury stock account.
Other Comprehensive Income (OCI): Beyond Net Income
Other Comprehensive Income (OCI) includes items that are not recognized in net income but still affect stockholders' equity. These items can include unrealized gains or losses on certain investments, foreign currency translation adjustments, and changes in pension liabilities.
For example, if a company has investments in securities that have increased in value but have not been sold, the unrealized gain is reported in OCI, increasing stockholders' equity. OCI provides a more complete picture of a company's financial performance than net income alone.
Accounting Changes and Prior Period Adjustments
Occasionally, a company may need to make adjustments to its financial statements due to changes in accounting principles or errors in prior periods. These adjustments can directly impact retained earnings and, therefore, stockholders' equity. Correcting an error from a previous year that overstated expenses would lead to an increase in retained earnings and a corresponding increase in stockholders' equity.
"Understanding the intricacies of stockholders' equity is paramount for investors aiming to make informed decisions," states Dr. Emily Carter, a finance professor at the University of California, Berkeley. "It's not just about the bottom line; it's about understanding the story behind the numbers."
Significance and Impact
Changes in stockholders' equity offer crucial insights into a company's financial health and management decisions. A consistent increase in equity, driven by strong net income and prudent capital allocation, typically signals a healthy and well-managed company. Conversely, a declining equity position, particularly due to consistent losses or excessive dividend payouts, may raise concerns about the company's long-term viability.
Investors carefully monitor these changes to assess the value of their investments and make informed decisions about buying, selling, or holding shares. Analysts use changes in stockholders' equity to evaluate a company's performance and make recommendations to clients. Furthermore, regulators and creditors rely on this information to assess a company's solvency and creditworthiness.
Ultimately, the fluctuations in stockholders' equity are a reflection of a company's operational performance, strategic choices, and overall financial soundness. By understanding the underlying drivers of these changes, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the company's true value and future prospects.









.jpg)