A Double-blind Study Of A Vaccine Is One In Which

Imagine a bustling research lab, filled with scientists meticulously labeling vials, their faces illuminated by the soft glow of monitors displaying complex data. The air hums with the quiet energy of discovery, each researcher aware that they are participating in something potentially life-changing. At the heart of it all is a carefully designed study, a double-blind study, a crucial shield against bias in the quest for effective and safe vaccines.
The purpose of this article is to explore the double-blind study. Double-blind studies are a critical tool in scientific research, particularly in the development and evaluation of vaccines. We will delve into what makes them so vital, why they are considered the gold standard, and how they help to ensure that the vaccines we receive are both effective and safe.
Unveiling the Double-Blind Study: A Definition
A double-blind study is a type of clinical trial where neither the participants nor the researchers know who is receiving the actual treatment (e.g., the vaccine) and who is receiving a placebo. This "blinding" is a crucial component of the study's design. It minimizes the risk of bias influencing the results.
In a typical vaccine trial, participants are randomly assigned to either the treatment group or the control group. The treatment group receives the vaccine being tested, while the control group receives a placebo, which is an inactive substance that looks identical to the vaccine.
The blinding process is designed to eliminate any conscious or subconscious influence from either the participants or the researchers. This is because expectations, beliefs, or attitudes can unintentionally skew the results of a study.
Why Double-Blind Studies are Essential
The primary reason for using a double-blind study is to minimize bias. Bias can creep into research in many ways, potentially distorting the true effects of a treatment.
Participant bias, for instance, occurs when a participant's expectations about the treatment influence their reported outcomes. If a participant knows they are receiving the vaccine, they might unconsciously report feeling better, even if the vaccine isn't actually effective.
Similarly, researcher bias can occur when researchers' expectations about the treatment influence how they observe, interpret, or report the data. A researcher who believes strongly in the vaccine's effectiveness might unintentionally look for positive signs in the treatment group, while overlooking or downplaying similar signs in the control group.
By blinding both participants and researchers, double-blind studies help to level the playing field. It ensure that the results are based on the actual effects of the vaccine, rather than influenced by subjective perceptions.
The Historical Context and Evolution
The concept of blinding in clinical trials dates back centuries, but the modern double-blind study design gained prominence in the mid-20th century. Prior to that, many medical treatments were evaluated without rigorous controls, leading to potentially flawed conclusions.
One landmark example that highlighted the need for rigorous study design was the evaluation of the Salk polio vaccine in the 1950s. This massive trial, involving millions of children, used a placebo-controlled design to accurately assess the vaccine's effectiveness.
The success of the Salk polio vaccine trial helped solidify the importance of controlled clinical trials and paved the way for the widespread adoption of the double-blind study methodology. Since then, double-blind studies have become the standard for evaluating new vaccines and other medical treatments.
The Process: From Design to Analysis
Designing a double-blind study requires careful planning and attention to detail. First, a protocol is established, outlining the study's objectives, participant selection criteria, treatment regimen, and data collection methods.
Participants are then randomly assigned to either the treatment group or the control group. This randomization helps to ensure that the two groups are as similar as possible at the outset, minimizing the risk of confounding variables influencing the results.
The vaccine and placebo are prepared in identical-looking containers and labeled with codes to maintain blinding. Researchers and participants are kept unaware of which treatment each participant is receiving throughout the study.
During the study, participants are monitored for any adverse events or signs of illness. Data is collected using standardized methods and recorded in a secure database.
Once the study is complete, the data is analyzed to compare the outcomes in the treatment and control groups. The codes are then unblinded, revealing which participants received the vaccine and which received the placebo.
Statistical analyses are performed to determine whether the vaccine is effective in preventing the targeted disease and whether it is safe for use. If the results are positive, the vaccine can then be submitted to regulatory agencies for approval.
Challenges and Limitations
While double-blind studies are considered the gold standard, they are not without their challenges. Maintaining blinding can be difficult, especially if the vaccine has noticeable side effects. If participants in the treatment group experience side effects that are not present in the control group, it may become apparent which treatment they are receiving.
Ethical considerations can also arise, particularly when studying vaccines for serious or life-threatening diseases. In such cases, it may be considered unethical to withhold the vaccine from a control group, especially if an effective vaccine is already available.
Cost and complexity are also factors to consider. Double-blind studies can be expensive and time-consuming to conduct, requiring significant resources and expertise.
The Future of Vaccine Research
Despite these challenges, double-blind studies will likely remain a cornerstone of vaccine research in the future. However, researchers are also exploring innovative approaches to complement and enhance traditional double-blind study designs.
For example, real-world evidence studies are increasingly being used to assess vaccine effectiveness in broader populations and under real-world conditions. These studies can provide valuable insights that complement the findings of controlled clinical trials.
Additionally, advances in data analytics and artificial intelligence are enabling researchers to analyze complex datasets and identify potential safety signals more quickly and efficiently. These tools can help to improve the safety and effectiveness of vaccines.
Furthermore, adaptive clinical trial designs are gaining popularity. These designs allow researchers to modify the study protocol based on interim data, potentially accelerating the development process while maintaining scientific rigor.
Conclusion: Trusting the Process
Double-blind studies are a fundamental component of ensuring that vaccines are both effective and safe. While not without their challenges, the rigorous design of these studies provides a crucial shield against bias, building public trust in the vaccines that protect us and our communities.
The meticulous work of researchers, guided by the principles of scientific rigor, ultimately leads to the development of life-saving interventions. Understanding the importance of double-blind studies is crucial for fostering informed decision-making and promoting public health.
So, the next time you receive a vaccine, remember the double-blind studies that have helped to ensure its safety and effectiveness. It's a testament to the power of science and the dedication of researchers committed to improving human health.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-a-double-blind-study-2795103_color1-5bf4763f4cedfd002629e836.png)
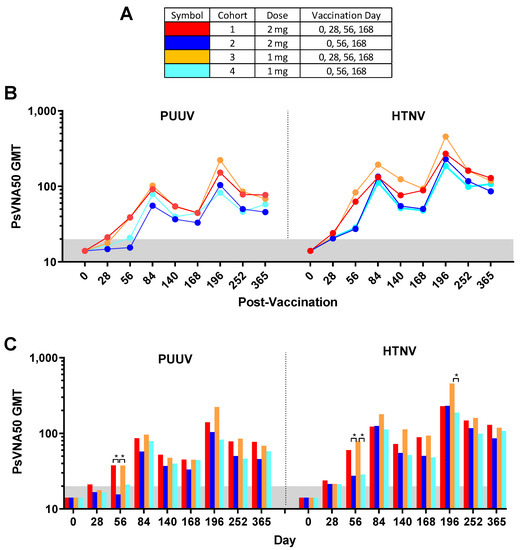
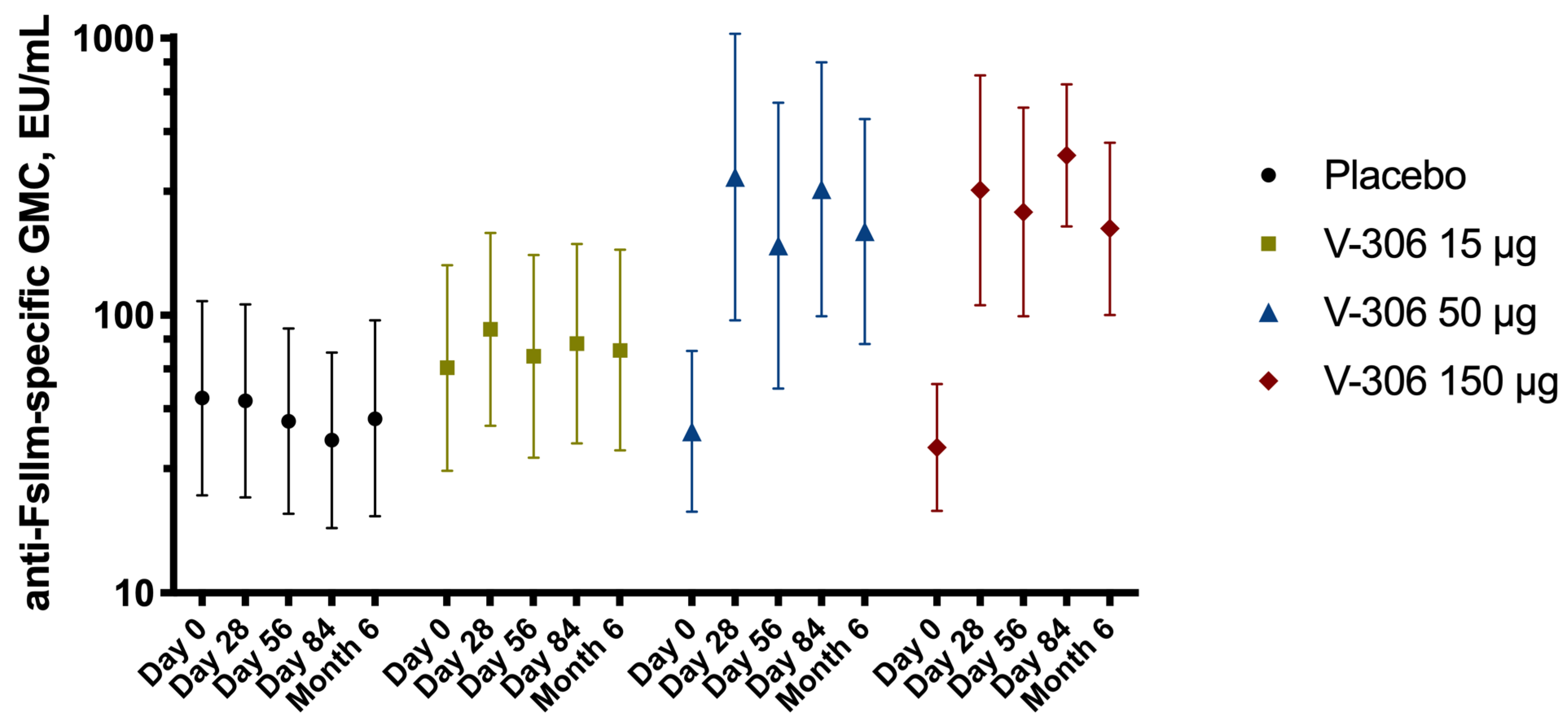
02234-1/asset/9ea6eaf7-c764-480a-8df4-7fe7d09a8d9b/main.assets/gr1_lrg.jpg)