Accounting Costs And Economic Costs Differ Because

Businesses face a critical financial reality: what you think you're spending isn't the whole story. A significant discrepancy exists between accounting costs, readily visible in financial statements, and economic costs, which paint a more complete, yet often overlooked, picture of resource utilization.
This difference, stemming from the inclusion of opportunity costs in the economic calculation, can dramatically alter decision-making and profitability assessments for any organization, regardless of size or sector.
The Divide: Accounting vs. Economic Costs
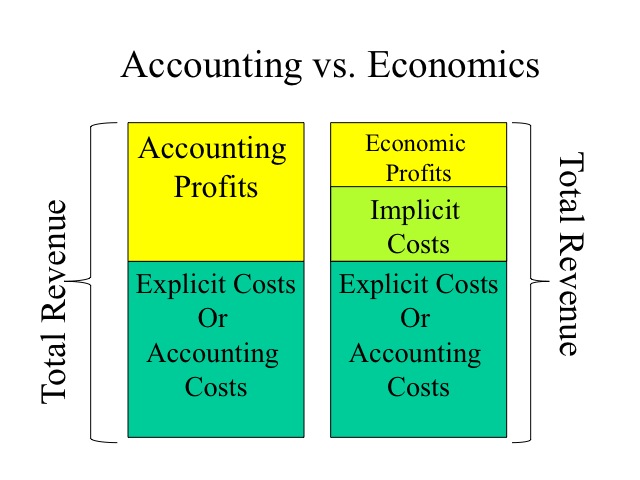
Accounting costs are explicit, representing actual cash outflows for expenses like wages, rent, materials, and utilities. They are documented and form the basis of traditional financial reporting, adhering to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
Economic costs, however, encompass both explicit accounting costs and implicit opportunity costs. Opportunity cost represents the value of the next best alternative foregone when a particular choice is made.
For example, consider a small business owner who uses a building they already own for their operations. Accounting costs would reflect property taxes and maintenance. Economic costs would also include the rent the owner could have earned by leasing the building to someone else.
Opportunity Cost: The Hidden Expense
The inclusion of opportunity cost is where the two accounting methodologies diverge. It's a crucial consideration, especially for businesses making investment decisions or resource allocation choices. Failing to account for opportunity cost can lead to suboptimal decisions.
A farmer choosing to plant wheat instead of corn incurs an opportunity cost equal to the potential profit they could have made from the corn crop. A tech company deciding to develop a new software feature instead of focusing on marketing its existing product incurs the lost revenue from that marketing effort.
Opportunity costs are subjective and often difficult to quantify precisely, requiring careful analysis and judgment. This complexity contributes to why they are typically excluded from standard accounting practices.
Impact on Business Decisions
Ignoring the distinction between accounting costs and economic costs can have significant repercussions. For example, a business might appear profitable based solely on accounting figures. However, when the opportunity cost of resources is factored in, the business could actually be generating negative economic profits.
This misrepresentation can lead to poor investment decisions, inefficient resource allocation, and ultimately, reduced long-term profitability. It's essential to consider opportunity costs when evaluating the true cost of any business venture.
Companies like Google and Apple, known for their rigorous strategic planning, reportedly utilize economic cost analysis to inform their investment decisions, ensuring they are allocating resources to the most profitable opportunities.
Real-World Implications
A study by the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) found that businesses that actively consider opportunity costs in their decision-making processes demonstrate greater long-term financial resilience. The study highlighted the importance of understanding the full cost implications of choices.
Startups, in particular, need to be aware of this discrepancy. Founders often forgo salaries to reinvest in the business. The opportunity cost of that foregone salary needs to be factored into the overall financial assessment.
Furthermore, universities use opportunity cost to evaluate the profitability of their programs and decide on resource allocation. They could offer more specialized services if resources were available.
Navigating the Complexity
Businesses can bridge the gap between accounting costs and economic costs by implementing more comprehensive cost-benefit analyses. This involves identifying and quantifying, as accurately as possible, the opportunity costs associated with various decisions.
Techniques like shadow pricing and sensitivity analysis can be used to estimate the value of foregone alternatives. Engaging with economic consultants may provide expert insights into assessing the true cost of business activities.
Managers should be trained to recognize and incorporate opportunity costs into their decision-making frameworks. A culture of awareness regarding the full cost of resources is critical for making sound economic choices.
Next Steps and Ongoing Developments
The debate regarding the best way to integrate opportunity costs into financial reporting is ongoing. The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) continues to explore potential methods for improving the transparency and completeness of cost information.
In the meantime, businesses should proactively adopt internal practices that address the limitations of traditional accounting and incorporate a broader economic perspective. Ignoring opportunity cost is simply not a viable option in today's competitive environment.
The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) offers resources and training programs designed to help businesses better understand and manage economic costs. Continuous learning and adaptation are essential for navigating the complex financial landscape.