Active Artificially Acquired Immunity Is A Result Of

Imagine a world where even the most formidable adversaries—unseen viruses and bacteria—can be met with a shield forged not by chance, but by carefully guided design. Picture tiny soldiers, trained in advance, standing ready to defend your body's fortress. This isn't science fiction; it's the remarkable reality of active artificially acquired immunity, a cornerstone of modern healthcare that protects us from preventable diseases.
At its heart, active artificially acquired immunity is the protection you gain when your body learns to fight off a specific disease after being exposed to a weakened or inactive form of it, usually through vaccination. This process stimulates your immune system to create antibodies and memory cells, offering long-term defense against future infections. Understanding this process unlocks insights into how we can proactively safeguard our health and the health of our communities.
The Immune System: A Natural Defender
To understand artificially acquired immunity, we first need to appreciate the innate power of our immune system. Think of it as a complex, layered defense network constantly working to identify and neutralize threats. From the physical barriers of our skin to the specialized cells patrolling our bloodstream, the immune system is always on guard.
However, our natural defenses aren't always enough. Some pathogens are too aggressive, or our bodies need a head start to mount an effective response. This is where the concept of acquired immunity becomes critical.
Acquired Immunity: Learning from Experience
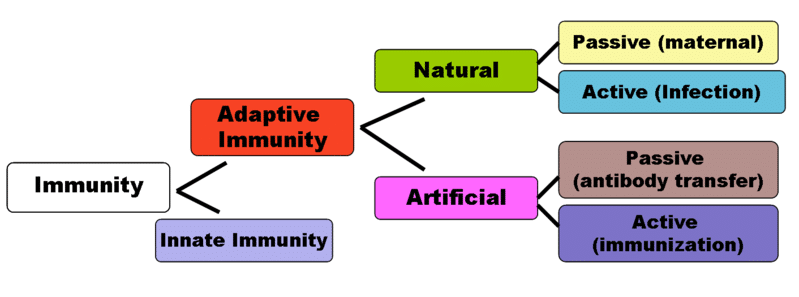
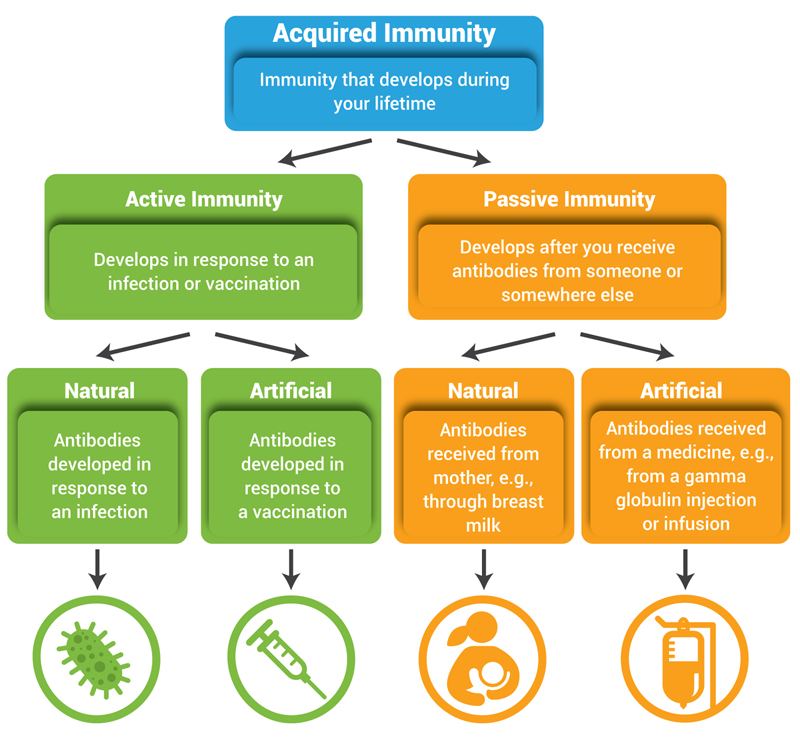
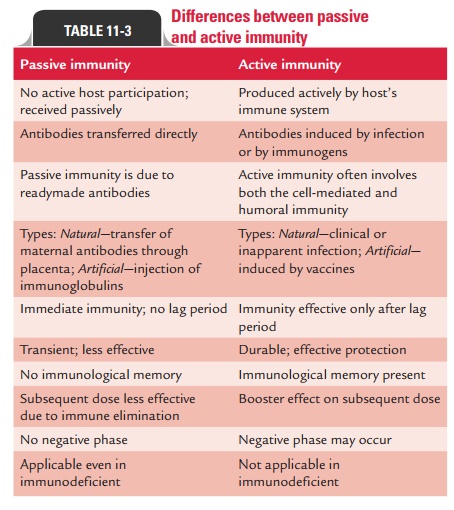
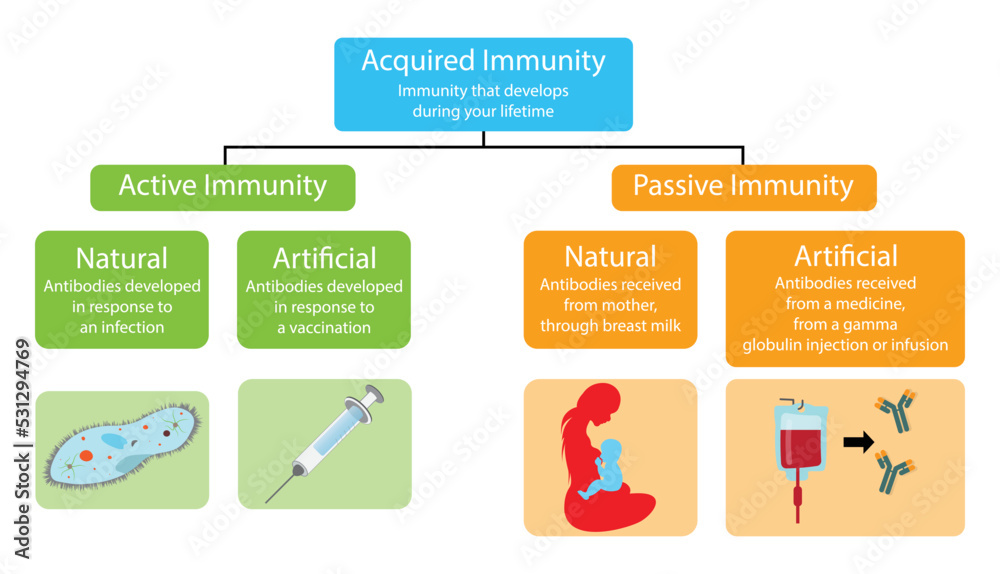
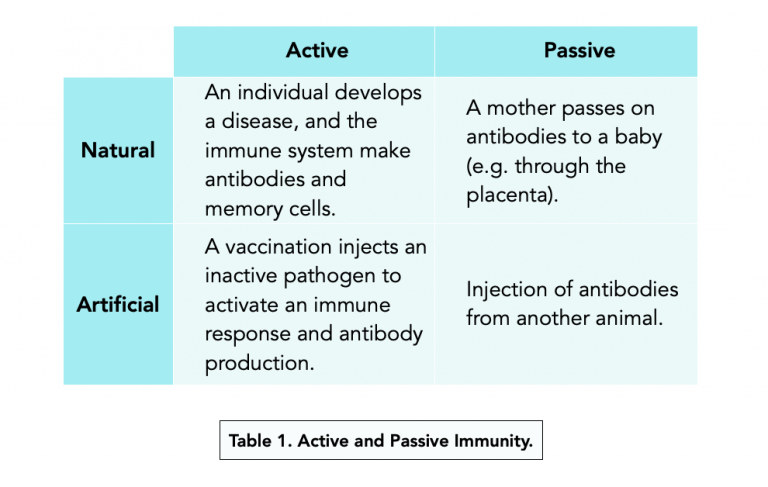
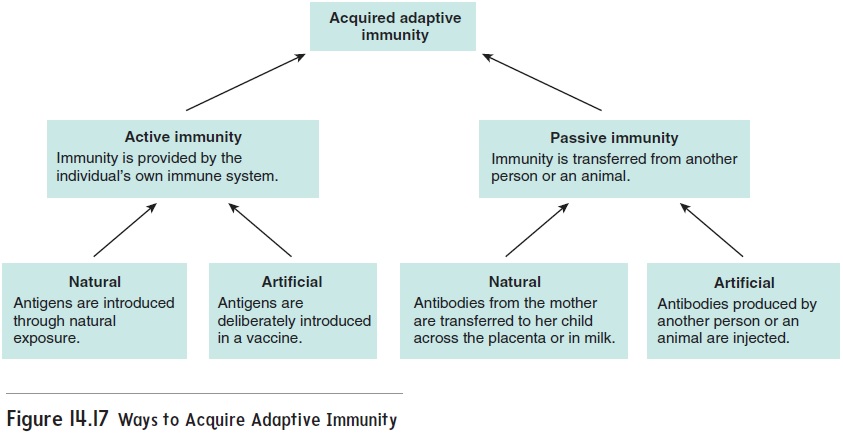
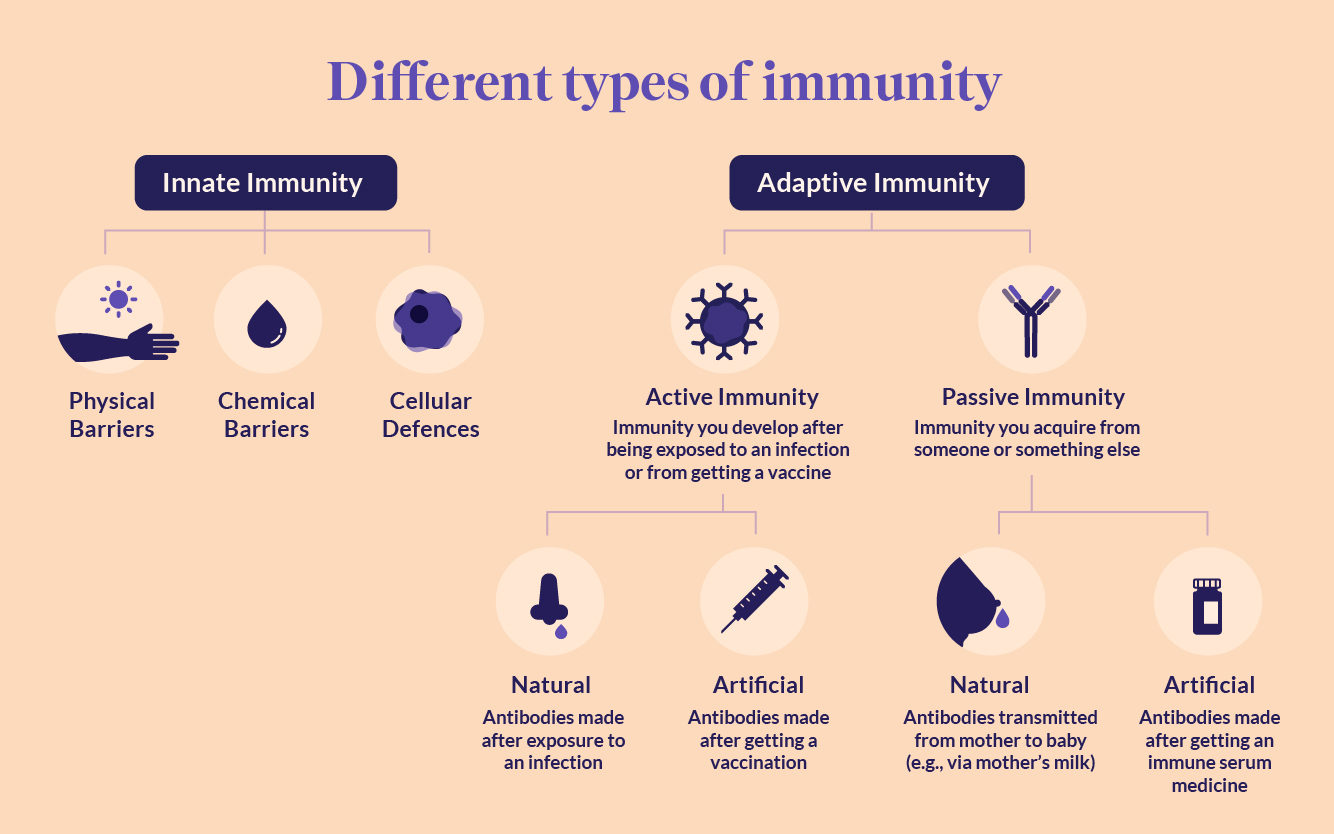
Acquired immunity is built over time, as our bodies encounter different pathogens. There are two main types: passive and active. Passive immunity is temporary, like when a newborn receives antibodies from their mother through the placenta or breast milk.
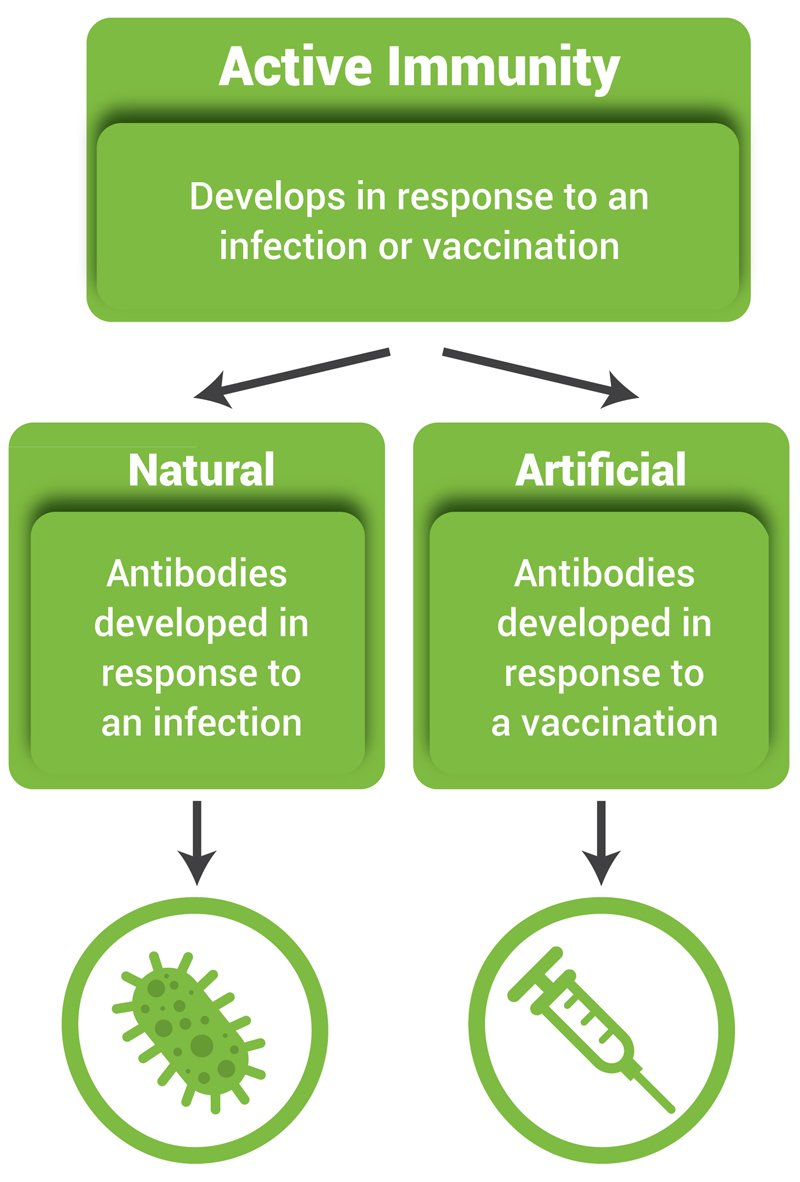
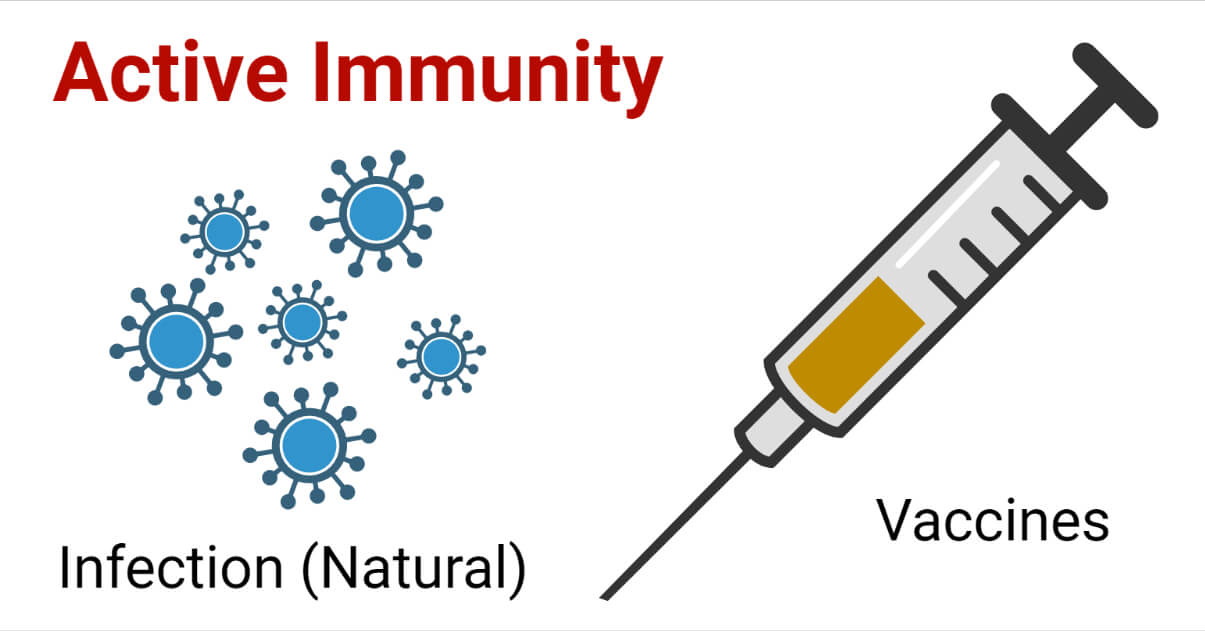
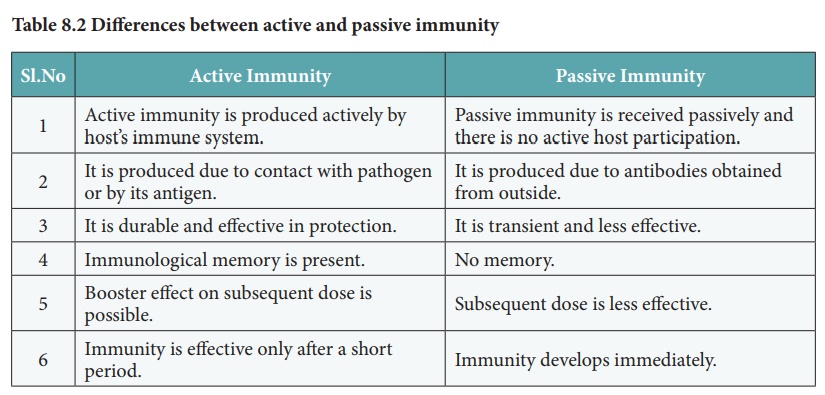
Active immunity, on the other hand, is long-lasting. It develops when our immune system actively produces antibodies in response to an infection or vaccination. Active immunity essentially "trains" the immune system to remember and react quickly to specific threats.
There are two ways of acquiring active immunity: naturally and artificially.
Active Artificially Acquired Immunity: Vaccination as Education
Active artificially acquired immunity is achieved through vaccination. Vaccines introduce a weakened or inactive form of a pathogen (virus or bacteria) into the body. This exposure doesn't cause the disease, but it tricks the immune system into thinking it's under attack.
In response, the immune system produces antibodies specific to that pathogen. More importantly, it creates memory cells. These memory cells "remember" the pathogen and can quickly launch a strong immune response if the real threat ever appears. This process is akin to showing your body a wanted poster of the pathogen, preparing it for future encounters.
Types of Vaccines: Different Approaches to Protection
Over the years, scientists have developed various types of vaccines, each with its own approach to stimulating immunity. Inactivated vaccines use pathogens that have been killed, while live-attenuated vaccines use weakened versions of the pathogen.
Subunit, recombinant, polysaccharide, and conjugate vaccines use specific parts of the pathogen, like proteins or sugars, to trigger an immune response. mRNA vaccines, a relatively new technology, deliver genetic instructions that teach our cells to make a harmless piece of the pathogen, prompting the immune system to react.
Each type of vaccine has its advantages and disadvantages, but they all share the same goal: to safely stimulate active immunity without causing disease.
The Significance of Active Artificially Acquired Immunity
The impact of active artificially acquired immunity on global health has been immense. Vaccination programs have eradicated diseases like smallpox and have dramatically reduced the incidence of others, such as polio and measles.
These successes have not only saved countless lives but have also improved the quality of life for millions more. By preventing disease, vaccines reduce the burden on healthcare systems and allow individuals to live healthier, more productive lives.
The World Health Organization (WHO) considers vaccination one of the most successful and cost-effective health interventions available.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the overwhelming evidence supporting the safety and effectiveness of vaccines, challenges remain. Vaccine hesitancy, driven by misinformation and mistrust, can undermine vaccination efforts.
It's crucial to rely on credible sources of information, such as healthcare professionals and reputable scientific organizations. Like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), when making decisions about vaccination.
Furthermore, ongoing research is essential to develop new and improved vaccines for emerging and existing diseases. The development of COVID-19 vaccines in record time demonstrates the power of scientific innovation in addressing global health threats.
The Future of Immunity
Active artificially acquired immunity is a remarkable achievement of modern science, a testament to our ability to understand and harness the power of the immune system. As we continue to learn more about immunology, we can expect even more sophisticated and effective vaccines to emerge.
From personalized vaccines tailored to individual needs to new strategies for combating chronic diseases, the future of immunity holds immense promise. By embracing scientific advancements and promoting vaccine confidence, we can create a healthier and more resilient world for all.
Active artificially acquired immunity isn’t just a scientific concept; it’s a story of human ingenuity, a beacon of hope in the fight against disease, and a reminder of our collective responsibility to protect ourselves and each other.