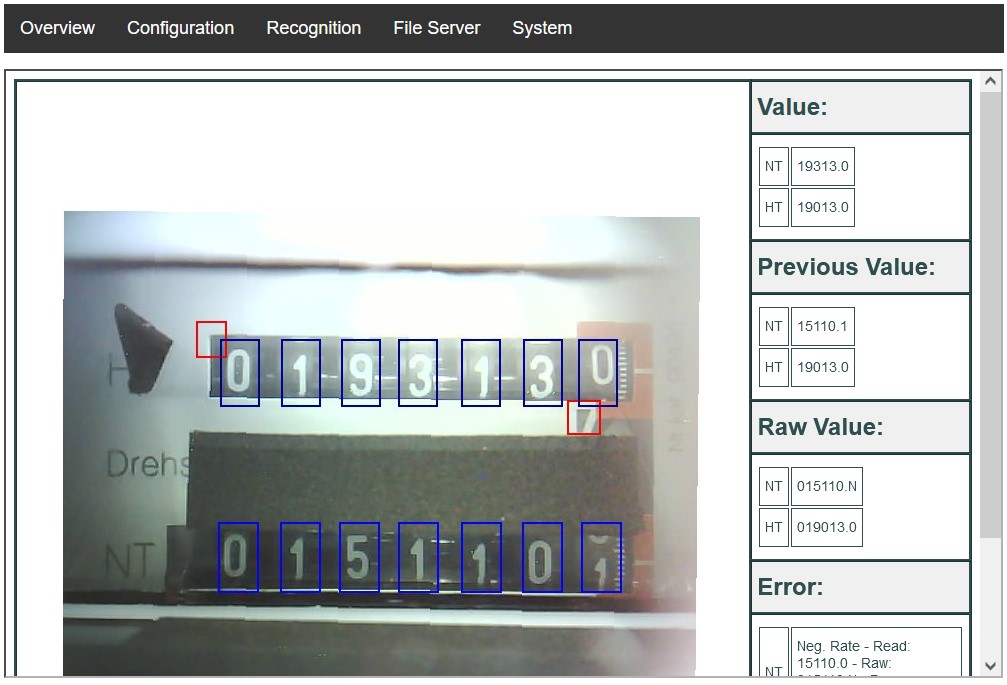
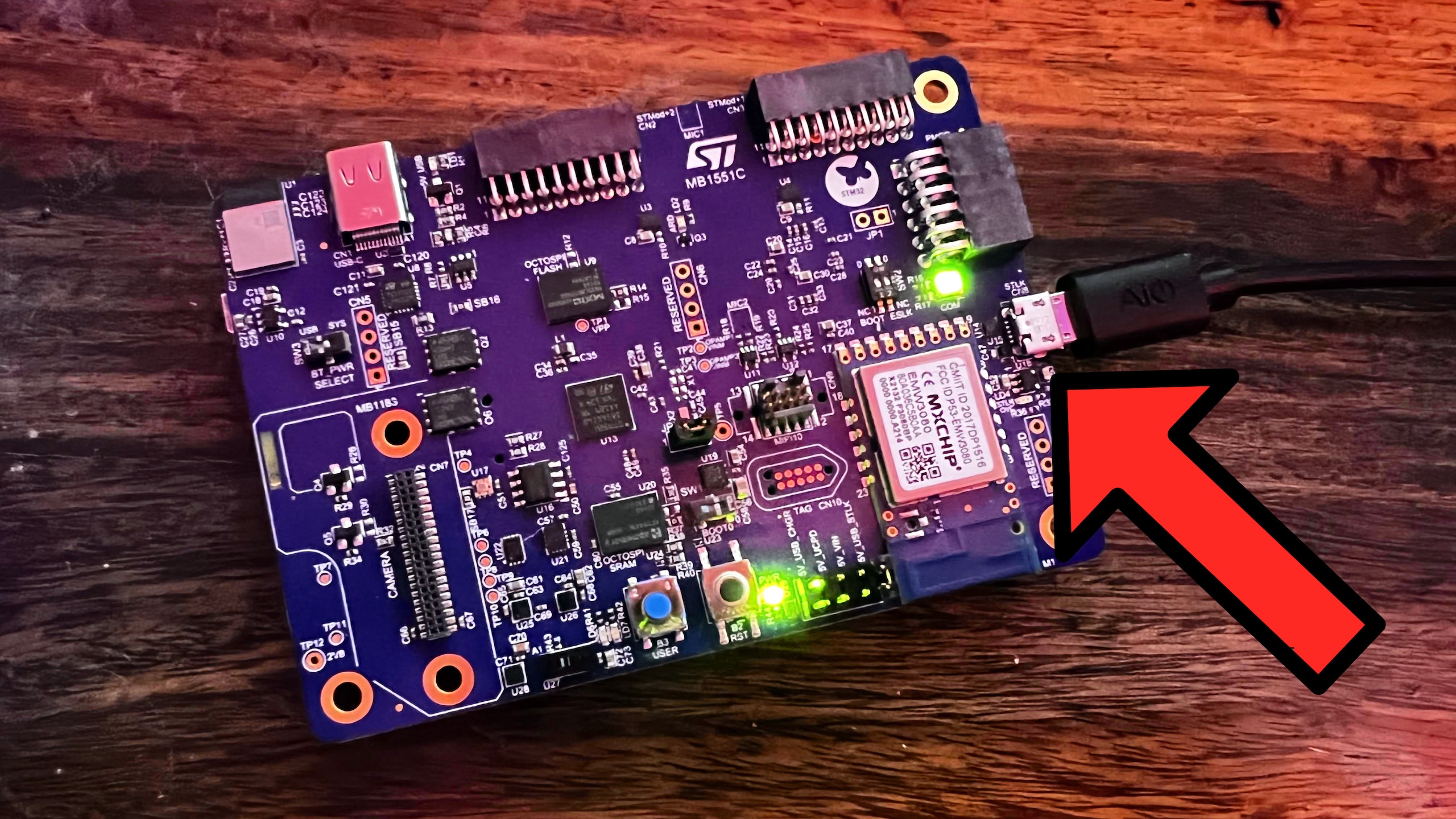
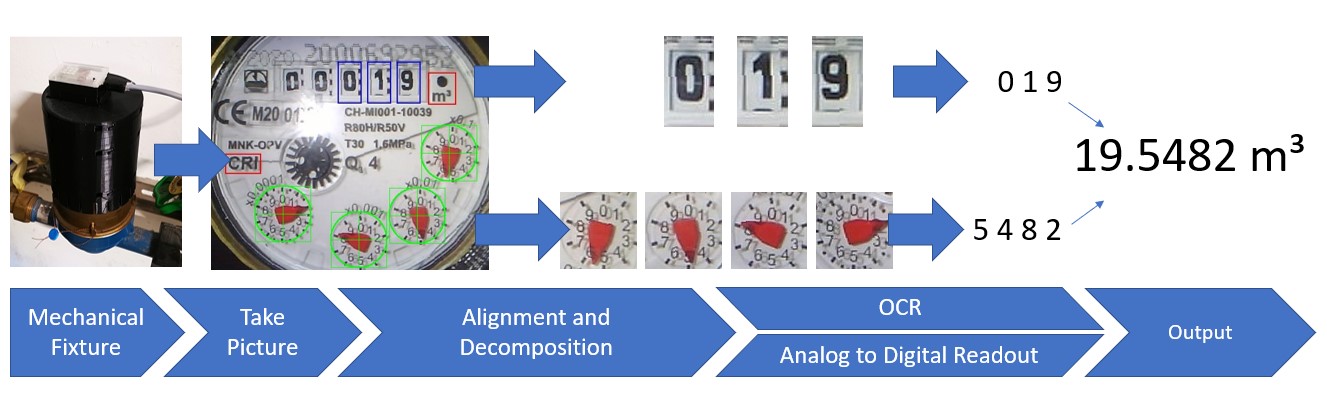
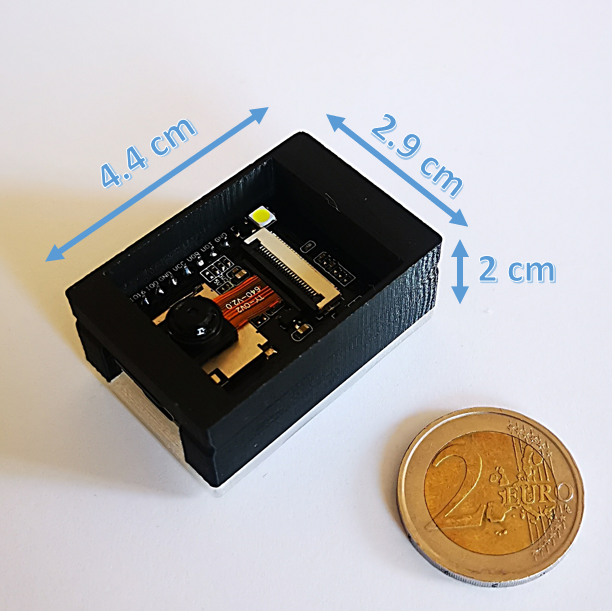
Ai On The Edge External Led
Edge computing, the deployment of processing power closer to the data source, is undergoing a transformation fueled by artificial intelligence (AI). One increasingly visible manifestation of this trend is the adoption of AI-enhanced edge devices, often signaled by external LEDs indicating processing status and AI activity. This convergence promises faster response times, enhanced security, and improved efficiency across various industries, but also raises questions about data privacy and algorithmic transparency.
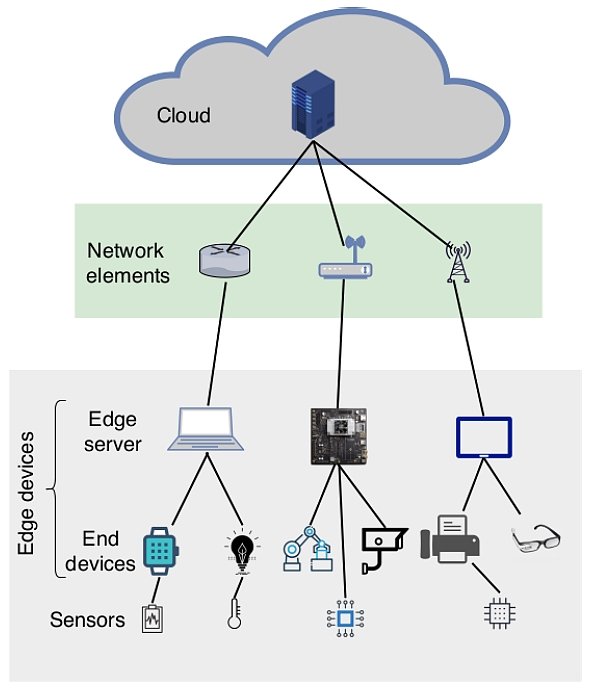
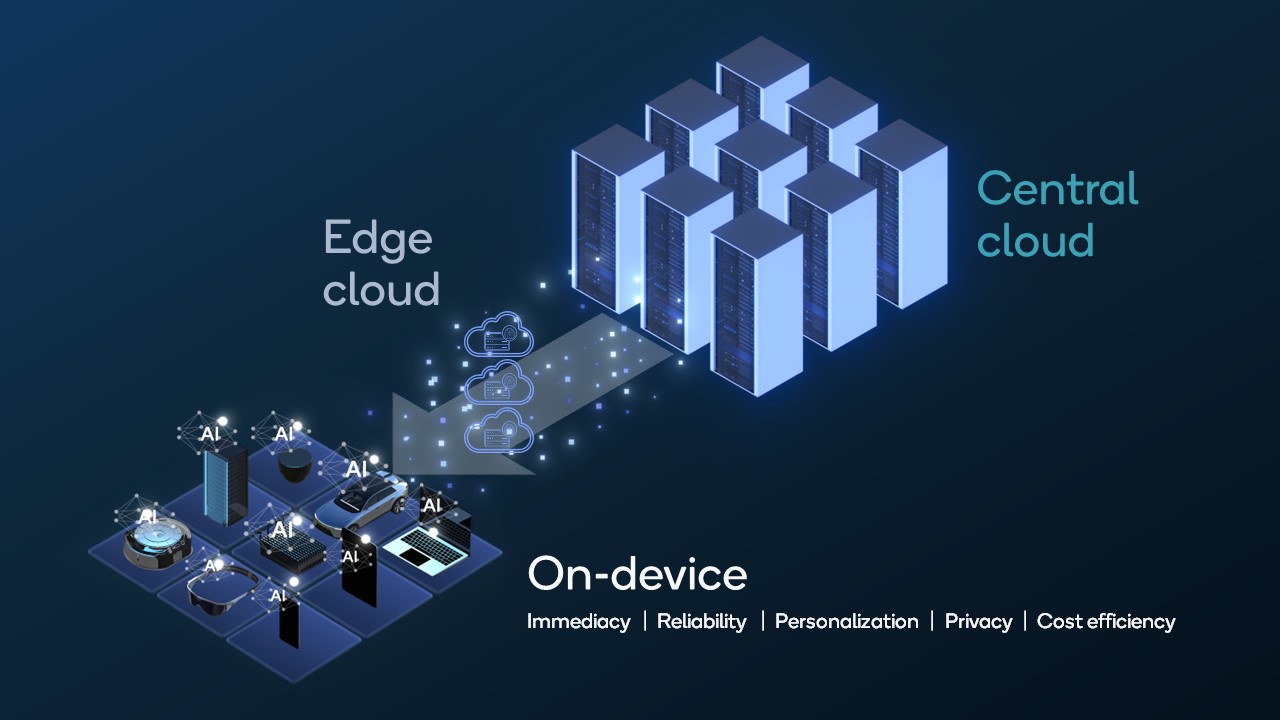
The integration of AI on the edge, visibly marked by external LEDs, represents a significant shift in how we approach data processing. It moves computation away from centralized cloud servers to devices located closer to where data is generated, offering numerous advantages. These advantages include reduced latency, improved bandwidth utilization, and enhanced privacy for sensitive data.
The Rise of AI-Enabled Edge Devices
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has generated an enormous amount of data. Transmitting all of this data to the cloud for processing becomes costly and inefficient. Edge computing addresses this challenge by performing data analysis and decision-making on the device itself or on a nearby server.
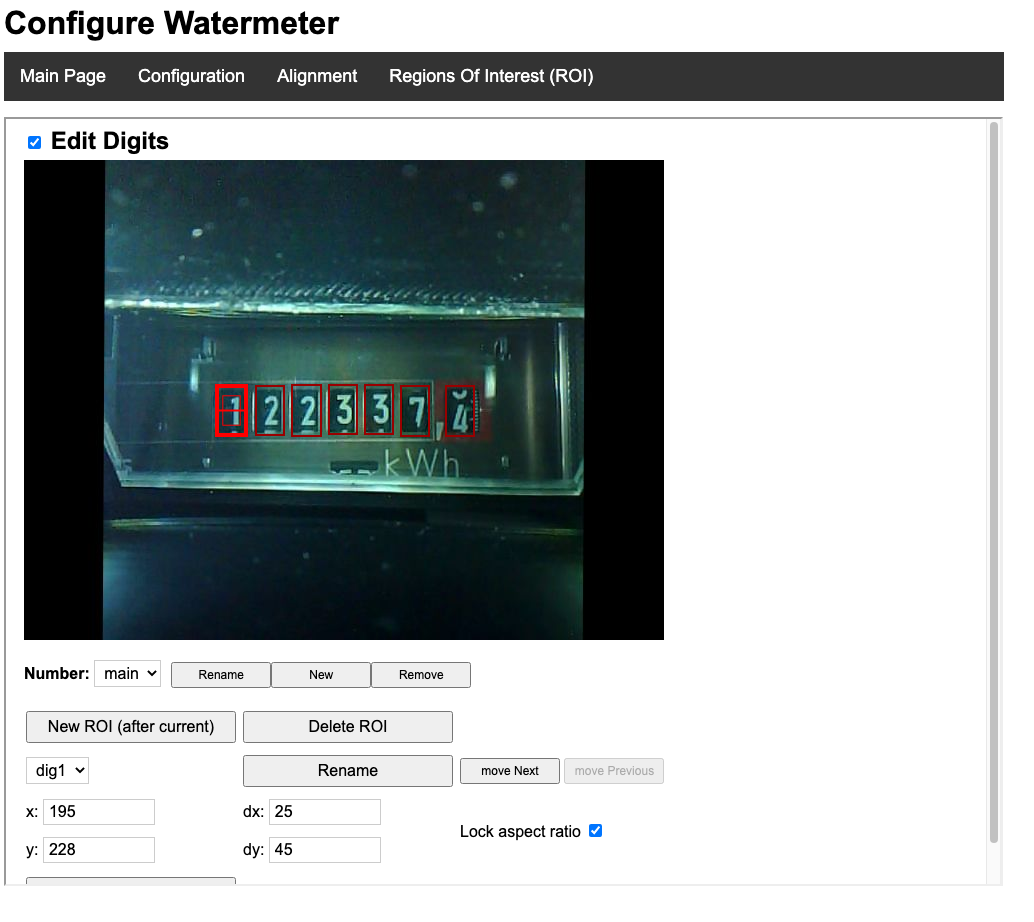
Adding AI to the edge further enhances these capabilities. By embedding AI models directly into edge devices, manufacturers can enable real-time analysis, predictive maintenance, and autonomous operation. The presence of external LEDs often serves as a visual indicator of this AI activity, providing a simple way to monitor device status and performance.
Who is driving this trend?
Major players in the technology sector, including NVIDIA, Intel, and ARM, are actively developing AI-optimized chips and software platforms for edge devices. These companies are collaborating with various industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation, to develop customized AI-powered edge solutions. Startups are also playing a crucial role, innovating in areas like computer vision, sensor fusion, and AI model compression.
What are the key applications?
The applications of AI on the edge are diverse and rapidly expanding. In manufacturing, AI-powered edge devices can monitor equipment performance, detect anomalies, and predict potential failures. This enables proactive maintenance, reduces downtime, and improves overall efficiency.
In healthcare, edge devices can analyze patient data in real-time, providing clinicians with timely insights for diagnosis and treatment. Wearable devices equipped with AI can monitor vital signs, detect falls, and provide personalized health recommendations. Furthermore, smart cameras use AI to detect anomalies, such as a patient that needs assistance.
Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on AI-powered edge computing to process sensor data, navigate roads, and make real-time decisions. Edge devices also play a critical role in smart cities, enabling applications like traffic management, public safety, and energy optimization.
The Significance of External LEDs
While seemingly a minor detail, external LEDs on AI-enabled edge devices serve several important functions. First, they provide a visual indication that the device is operational and actively processing data. Second, they can be programmed to display different colors or patterns to indicate the status of the AI model, such as whether it is running inference, training, or experiencing an error.
Third, LEDs contribute to transparency and trust. By visually signaling AI activity, they can help users understand how the device is functioning and what data is being processed. This is particularly important in applications where AI is used to make decisions that affect individuals or communities.
Potential Impact and Challenges
The rise of AI on the edge holds immense potential to transform various industries and improve our lives. However, it also presents several challenges that need to be addressed. One key challenge is ensuring data privacy and security. As data is processed on the edge, it is crucial to protect it from unauthorized access and misuse.
Another challenge is algorithmic bias. AI models trained on biased data can perpetuate and amplify existing inequalities. It is essential to develop methods for detecting and mitigating bias in AI models used on edge devices.
Furthermore, the increasing reliance on AI raises concerns about job displacement. As AI-powered edge devices automate tasks previously performed by humans, it is important to invest in education and training programs to help workers adapt to the changing job market. Companies such as Google and Microsoft are focusing on education and re-skilling the workforce.
The Future of AI on the Edge
The trend of integrating AI on the edge is expected to continue to accelerate in the coming years. As AI models become more efficient and hardware becomes more powerful, we will see more and more devices equipped with AI capabilities. The ubiquity of these devices, signaled by their blinking LEDs, promises a more intelligent and responsive world.
As edge computing and AI become more intertwined, it is crucial to address the ethical and societal implications of this technology. By focusing on data privacy, algorithmic transparency, and workforce development, we can harness the full potential of AI on the edge while mitigating its risks. The visual cue of an external LED might just be the starting point for a larger conversation about responsible AI deployment in the real world.