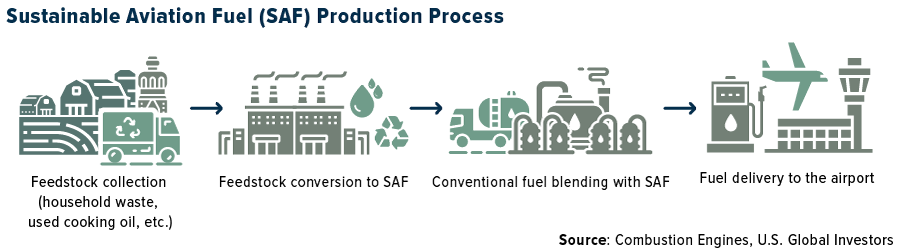
Airport Saf Global Production And Usage 2020-2026

The aviation industry, a significant contributor to global carbon emissions, is under immense pressure to decarbonize. With air travel projected to rebound strongly in the coming years, the urgent need for sustainable alternatives to traditional jet fuel is intensifying. Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) has emerged as a promising solution, but its current production and adoption rates lag far behind what's required to meet ambitious climate targets.
This article examines the global production and usage of SAF from 2020 to 2026, analyzing key trends, challenges, and future prospects. It will delve into factors influencing SAF development, including technological advancements, policy incentives, feedstock availability, and infrastructure limitations. The analysis considers projections from reputable organizations and highlights the gap between current SAF capacity and the projected demand needed to achieve meaningful emission reductions.
SAF Production: A Nascent Industry (2020-2023)
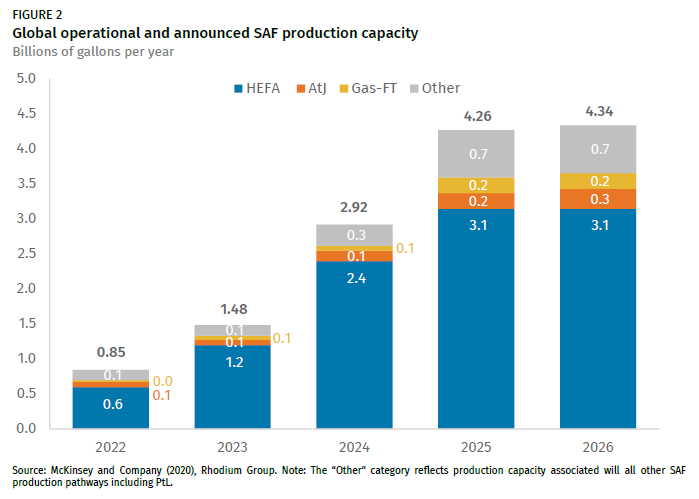
The period between 2020 and 2023 witnessed the very beginnings of a scaled-up SAF industry. Production volumes remained extremely low, accounting for a fraction of the total jet fuel demand globally. The International Air Transport Association (IATA) estimated that SAF accounted for less than 0.1% of total jet fuel consumption during this period.
Several factors contributed to this slow start. High production costs, limited availability of sustainable feedstocks (such as waste oils, algae, and agricultural residues), and a lack of dedicated infrastructure for SAF production and distribution presented significant barriers.
Despite these challenges, there were positive developments. Several airlines began piloting SAF usage on select routes, demonstrating the technical feasibility of using SAF in existing aircraft engines. Governmental bodies, particularly in Europe and North America, started introducing policies to incentivize SAF production and adoption, such as tax credits and mandates.
SAF Usage: Early Adoption and Pilot Programs
SAF usage during this period was largely driven by early adopters and pilot programs. Airlines like KLM, United Airlines, and Lufthansa conducted flights powered by SAF blends to showcase their commitment to sustainability. These initiatives helped raise awareness and build confidence in SAF technology.
However, widespread adoption was hindered by the significant price premium of SAF compared to conventional jet fuel. Airlines were reluctant to absorb these additional costs without clear regulatory frameworks and consumer willingness to pay a premium for greener flights.
Infrastructure constraints also played a role. Many airports lacked the facilities to store, blend, and deliver SAF, limiting the availability of SAF to specific locations.
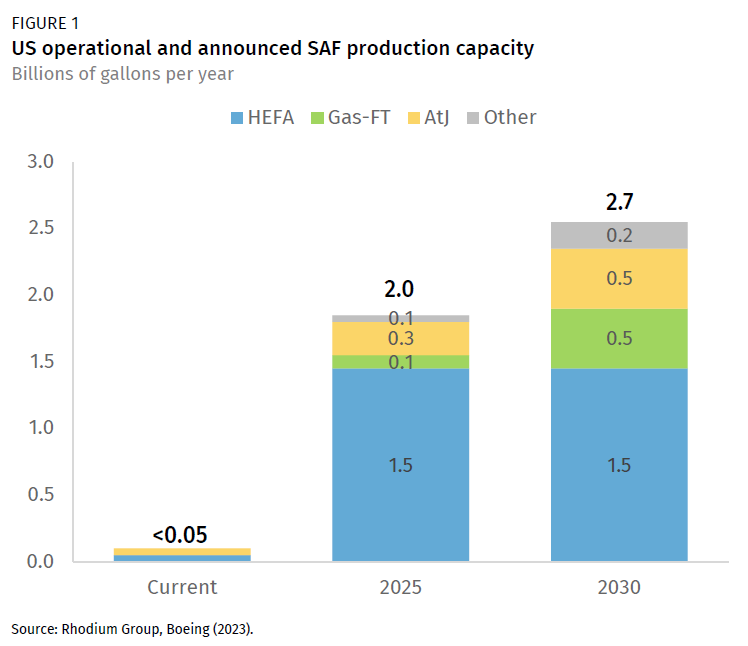
Production Capacity Expansion: 2024-2026 Projections
Looking ahead to 2024-2026, projections indicate a significant increase in SAF production capacity. Investments in new SAF production facilities are expected to come online, boosting overall supply. Organizations such as BloombergNEF and ICAO (International Civil Aviation Organization) anticipate a substantial ramp-up in SAF production during this period.
However, it's important to note that these projections are subject to uncertainty. The actual rate of production growth will depend on factors such as the timely completion of planned facilities, the availability of feedstocks, and the continued support from governments and industry stakeholders.
Even with increased production, the supply of SAF is expected to remain far below the demand required to achieve net-zero emissions targets. The gap between supply and demand presents a major challenge for the aviation industry.
Factors Influencing SAF Production and Usage
Several key factors will influence the future trajectory of SAF production and usage. Technology advancements are crucial. Developing more efficient and cost-effective SAF production processes, utilizing a wider range of feedstocks, and reducing the carbon intensity of SAF production are essential.
Policy incentives play a critical role. Strong regulatory frameworks, including mandates, tax credits, and carbon pricing mechanisms, can incentivize both SAF production and adoption. Collaboration between governments, industry, and research institutions is needed to develop and implement effective policies.
Feedstock availability is another crucial factor. Ensuring a sustainable and reliable supply of feedstocks, such as waste oils, algae, and agricultural residues, is essential for scaling up SAF production. Investing in research and development to explore new and innovative feedstock sources is also important.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the growing interest in SAF, significant challenges remain. The high production cost of SAF compared to conventional jet fuel is a major barrier to widespread adoption. Addressing this cost differential will require technological advancements, economies of scale, and policy support.
Infrastructure limitations also pose a challenge. Airports need to invest in the infrastructure required to store, blend, and deliver SAF. This includes upgrading existing facilities and building new ones.
However, the SAF industry also presents significant opportunities. Scaling up SAF production can create new jobs, stimulate economic growth, and contribute to a more sustainable future for the aviation industry.
Conclusion: The Path Forward for SAF
While SAF production and usage have made significant strides in recent years, substantial acceleration is needed to meet the ambitious decarbonization goals set by the aviation industry. The period from 2020 to 2026 represents a critical phase in the development of the SAF market, with increased production capacity expected but significant challenges remaining.
To realize the full potential of SAF, collaboration between governments, industry, and research institutions is essential. Investing in technology advancements, implementing supportive policies, and ensuring a sustainable feedstock supply are crucial steps towards a cleaner and more sustainable aviation industry.
Ultimately, the future of flight depends on the successful development and deployment of SAF. The next few years will be decisive in determining whether SAF can truly take off and help the aviation industry reach its net-zero emissions targets. Without significant investment and commitment, the promise of SAF risks remaining grounded.


_Market_Analysis.jpg)
_Market_Bar.jpg)







-MARKET-IMAGE-3.webp)
