All Of The Following Are Symptoms Of Schizophrenia Except
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/prodromal-schizophrenia-5194244-FINAL-f4e0bb2142a94d73a96f2976c722c4cd.jpg)
The complexities of schizophrenia, a chronic brain disorder affecting millions worldwide, often lead to misconceptions about its symptoms. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing the condition and improving the quality of life for those affected.
Understanding the nuances of schizophrenia, particularly distinguishing actual symptoms from common mischaracterizations, is vital for both the public and healthcare professionals. Misinformation can delay effective intervention and perpetuate stigma.
Deciphering Schizophrenia: Beyond the Stereotypes
This article aims to clarify the core symptoms of schizophrenia, highlighting what it truly entails and dispelling frequently held, inaccurate beliefs. We will explore the established diagnostic criteria and emphasize a symptom that, while often associated with mental illness in general, is *not* a defining characteristic of schizophrenia itself.
The Core Symptoms: A Detailed Look
Schizophrenia is characterized by a cluster of symptoms that fall into distinct categories: positive, negative, and cognitive. The presence and severity of these symptoms vary significantly from person to person.
Positive symptoms refer to experiences that are *added* to a person's reality, such as hallucinations and delusions. Hallucinations involve perceiving things that aren't real, most commonly auditory hallucinations like hearing voices.
Delusions are fixed, false beliefs that are not based in reality and are firmly held despite evidence to the contrary. These can range from paranoid delusions of persecution to grandiose delusions of having special powers or importance.
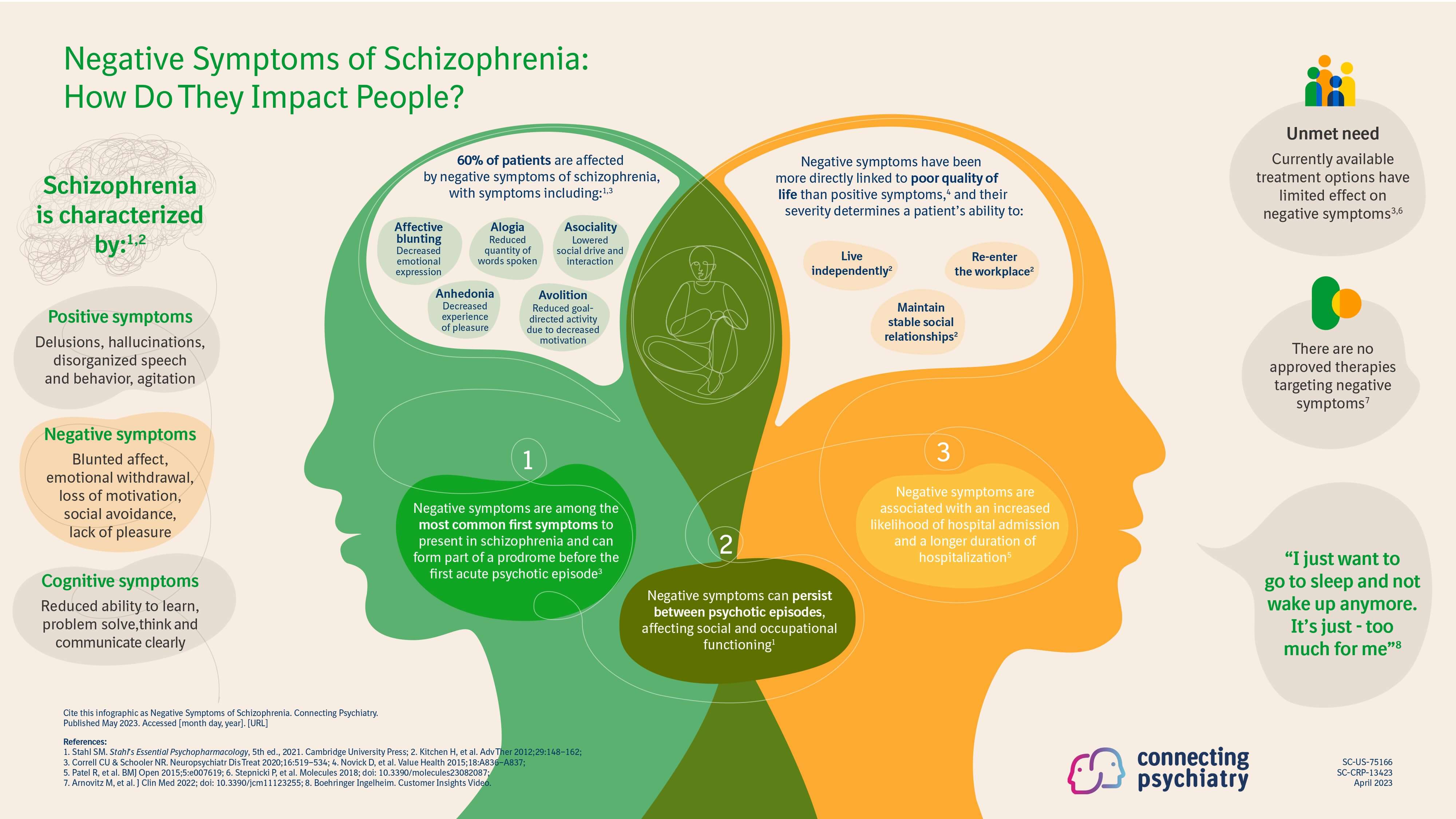
Negative symptoms, on the other hand, represent a *loss* or reduction of normal functions. Common negative symptoms include blunted affect (reduced emotional expression), alogia (poverty of speech), avolition (lack of motivation), and anhedonia (inability to experience pleasure).
These symptoms can be particularly debilitating as they impact a person's ability to engage in daily activities, maintain relationships, and experience joy.
Cognitive symptoms involve difficulties with thinking processes. These include problems with attention, memory, and executive functions (planning, organization, and decision-making). Cognitive deficits can significantly impair a person's ability to function at work or school.
The Misconception: Multiple Personality Disorder
A common misconception is that schizophrenia involves multiple personality disorder, now known as dissociative identity disorder (DID). This is *incorrect*. Schizophrenia is *not* characterized by having multiple distinct personalities.
DID is a separate and distinct mental disorder, typically stemming from severe trauma experienced in childhood. While both conditions are serious and complex, their underlying causes and symptom presentations are vastly different.
Delving Deeper: The Reality of Schizophrenia
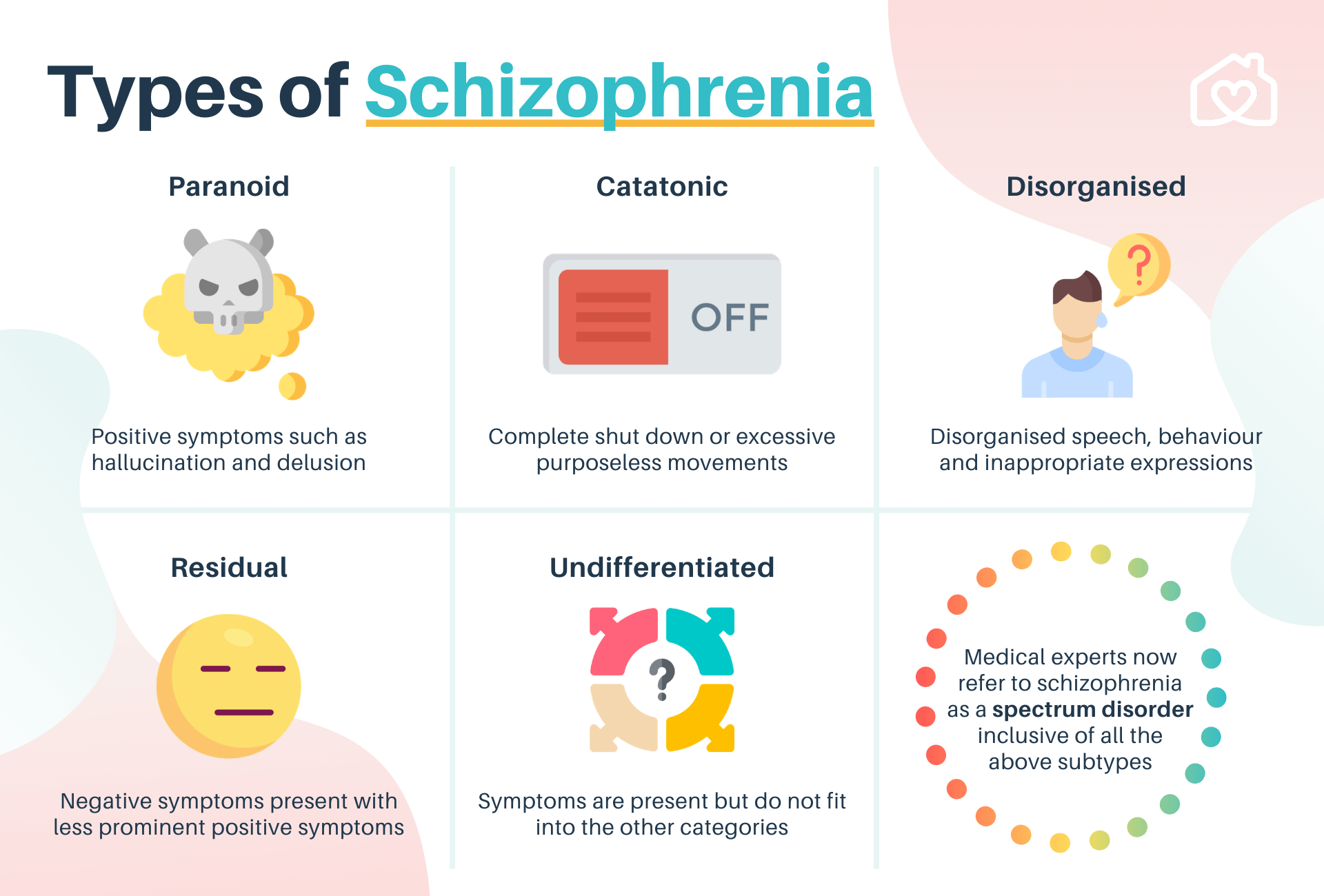
Individuals with schizophrenia experience a fragmented sense of reality. Their thoughts, perceptions, and behaviors may be disorganized and disconnected.
This disorganization can manifest as disorganized speech (e.g., incoherent rambling) or disorganized behavior (e.g., unpredictable or inappropriate actions). Catatonia, a state of immobility or excessive purposeless movement, can also occur, though it's less common with modern treatment approaches.
According to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), schizophrenia typically emerges in late adolescence or early adulthood. While there is no single cause, a combination of genetic predisposition, brain chemistry, and environmental factors are believed to play a role.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for schizophrenia, effective treatments are available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Antipsychotic medications are the cornerstone of treatment, helping to reduce positive symptoms like hallucinations and delusions.
Psychosocial therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and social skills training, can also be beneficial. These therapies help individuals develop coping strategies, manage stress, and improve social functioning.
Early intervention is crucial for improving outcomes. Individuals who receive prompt diagnosis and treatment are more likely to experience better symptom control and improved long-term functioning.
Combating Stigma and Promoting Understanding
One of the biggest challenges faced by individuals with schizophrenia is stigma. Negative stereotypes and misconceptions can lead to discrimination and social isolation.
It's essential to promote accurate information about schizophrenia and challenge harmful stereotypes. This can help create a more supportive and inclusive environment for those affected.
The World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes the importance of reducing stigma and discrimination associated with mental illness. Education and awareness campaigns are vital tools in combating these issues.
Looking Ahead: Research and Innovation
Ongoing research is focused on gaining a deeper understanding of the brain mechanisms underlying schizophrenia. Scientists are exploring new and innovative treatment approaches.
Advances in genetics, neuroimaging, and pharmacology hold promise for developing more targeted and effective therapies. The goal is to improve outcomes and enhance the lives of individuals with schizophrenia.
Ultimately, continued research and a commitment to evidence-based care are essential for improving the lives of individuals affected by this complex disorder. By fostering a greater understanding of schizophrenia, we can create a more compassionate and supportive society for those living with this condition.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/schizophrenia-spectrum-and-types-5193053-FINAL-ff64839e31a64ca293f12f168d488302.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-symptoms-of-schizophrenia-2953120-e15ca22957ec44ff8969cf9b8ac24568.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/schizophrenia-brain-5193049-Final-3b46cd3867aa47acb15f736551a87dac.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/positive-symptoms-in-schizophrenia-2953124-5d9769edb6ae4fa38284442f850315e1.png)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-Schizo-BLUE-horiz-aa2fec20cc164683913d92293f4c9540.jpg)