An Allowance For Doubtful Accounts Is Established.
The financial landscape for small businesses is undergoing a significant shift. Recent economic uncertainties and fluctuating market conditions have prompted a surge in concerns about uncollectible accounts receivable.
In response, regulators and industry experts are increasingly recommending, and in some cases mandating, the establishment of an Allowance for Doubtful Accounts. This allowance is a crucial accounting practice aimed at providing a more realistic picture of a company's financial health by accounting for the potential non-payment of debts.
The Essence of the Allowance: This article delves into the reasons behind the growing adoption of this allowance, its implications for businesses, and the methods used to calculate and implement it effectively. We'll explore the perspectives of accountants, business owners, and regulatory bodies, offering a comprehensive understanding of this evolving financial necessity.
Understanding the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
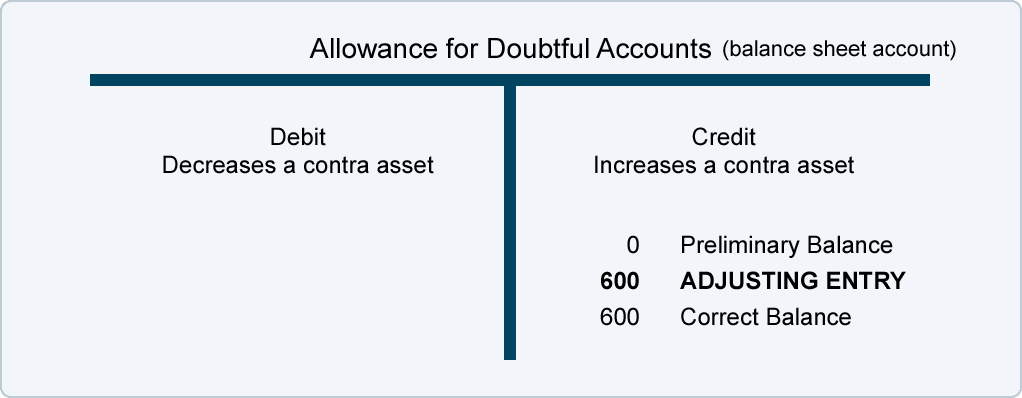
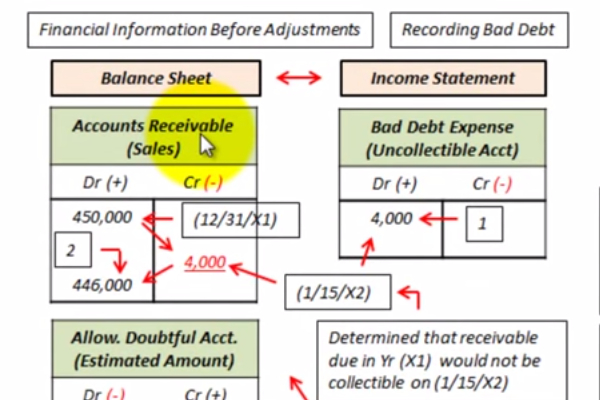
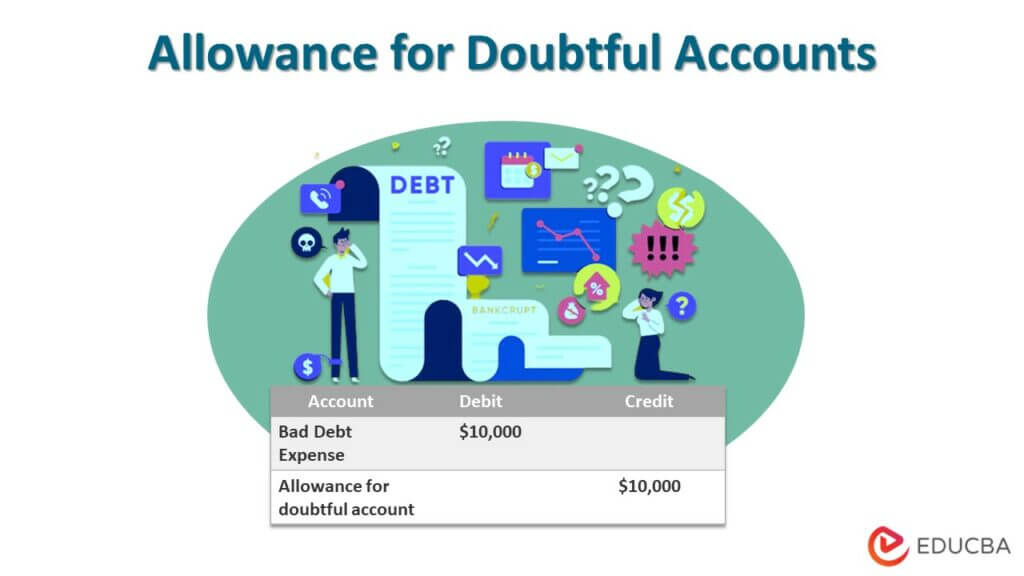
An Allowance for Doubtful Accounts, also known as a bad debt reserve, is a contra-asset account. This account reduces the total amount of accounts receivable reported on a company's balance sheet.
It represents management's estimate of the amount of accounts receivable that will ultimately prove uncollectible. This practice adheres to the matching principle in accounting.
The matching principle requires that expenses be recognized in the same period as the revenues they help to generate.
Why is it becoming more important?
The increased focus on the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts stems from several key factors. Economic downturns and periods of high inflation have historically led to a rise in business failures and bankruptcies.
This, in turn, increases the likelihood that companies will be unable to collect on outstanding invoices. Moreover, stricter regulatory scrutiny and the desire for greater financial transparency are pushing businesses to adopt more conservative accounting practices.
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), for example, has emphasized the importance of accurate and reliable financial reporting, particularly during times of economic uncertainty.
Calculating the Allowance: Methods and Considerations
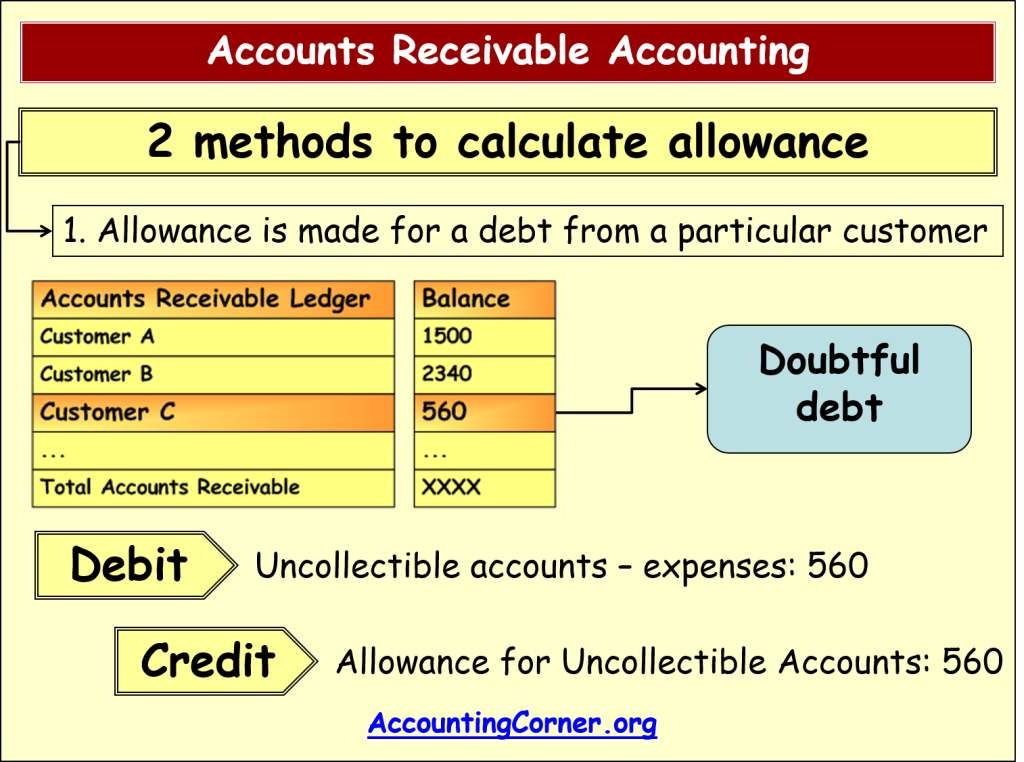
Several methods exist for calculating the appropriate amount for the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts. The most common are the percentage of sales method and the aging of accounts receivable method.
The percentage of sales method involves estimating bad debts based on a percentage of total credit sales. This percentage is typically derived from historical data and industry benchmarks.
The aging of accounts receivable method is considered more accurate. It categorizes accounts receivable by the length of time they have been outstanding.
The Aging Method in Detail
Under the aging method, a higher percentage of uncollectibility is applied to older receivables. For instance, receivables that are 30 days past due might be assigned a 5% uncollectibility rate.
Those that are 90 days past due might be assigned a 20% rate, and those over 120 days might be assigned a 50% or higher rate. This method allows for a more nuanced assessment of risk.
It also provides a clearer picture of the potential impact on a company's financial position.
Impact on Businesses: Opportunities and Challenges
Implementing an Allowance for Doubtful Accounts presents both opportunities and challenges for businesses. On the one hand, it provides a more realistic view of a company's financial health.
It enhances investor confidence and improves the accuracy of financial statements. This can be especially important for companies seeking financing or attracting investors.
On the other hand, establishing and maintaining the allowance requires careful analysis and ongoing monitoring. It can also result in a reduction of reported profits, which may be perceived negatively by some.
The Perspective of Small Business Owners
Many small business owners express concerns about the complexity and cost of implementing the allowance. "It's another layer of accounting that we have to manage," says Sarah Miller, owner of a local retail store.
"It takes time and resources that could be used elsewhere." However, financial advisors argue that the long-term benefits of the allowance outweigh the initial costs.
They emphasize that accurate financial reporting is essential for sustainable growth and stability.
Regulatory Landscape and Best Practices
Regulatory bodies are increasingly emphasizing the importance of accurate and transparent financial reporting. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) provides guidance on accounting for credit losses, including the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts.
Companies are expected to adhere to these standards and provide adequate disclosures about their credit risk exposures. Best practices include regularly reviewing and updating the allowance based on current economic conditions and historical data.
It is also important to maintain detailed documentation of the methods and assumptions used in calculating the allowance.
Expert Opinions and Recommendations
Dr. David Chen, a professor of accounting at a leading university, stresses the importance of professional judgment in determining the appropriate level of the allowance. "It's not just about crunching numbers," he says.
"It's about understanding the specific risks and challenges that a company faces." He recommends that companies seek guidance from qualified accounting professionals to ensure that their allowance is reasonable and supportable.
Industry experts also advise companies to invest in robust credit management systems and processes to minimize the risk of bad debts.
Looking Ahead: The Future of the Allowance
As economic uncertainty persists, the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts will likely remain a critical accounting practice. Technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, may offer new ways to improve the accuracy and efficiency of bad debt estimation.
Businesses that proactively address the issue of uncollectible accounts will be better positioned to navigate economic challenges and maintain long-term financial stability. Embracing transparency and adopting sound accounting practices is not just a matter of compliance.
It's a strategic imperative for building trust and fostering sustainable growth.



.jpg)