An Economic Model Is Defined As

Economic models, abstract representations of complex economic realities, are fundamental tools for economists, policymakers, and businesses alike. They provide a framework for understanding how economies function, predicting the impact of policy changes, and making informed decisions in a world of uncertainty. But what exactly *is* an economic model, and why is it so crucial?
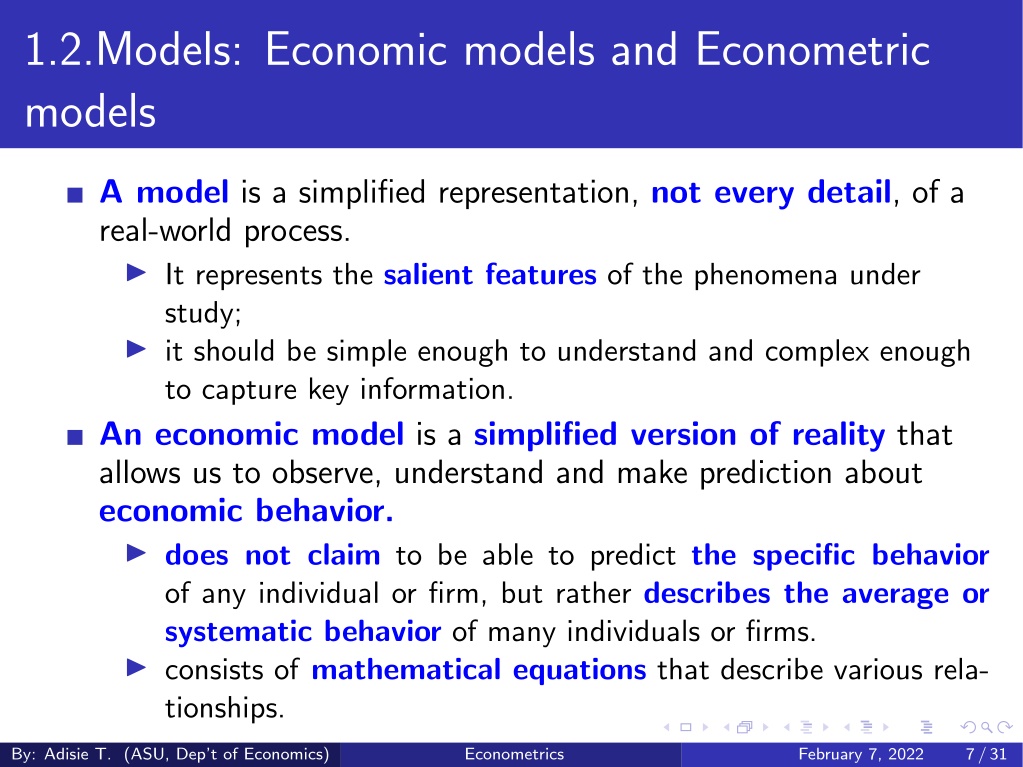
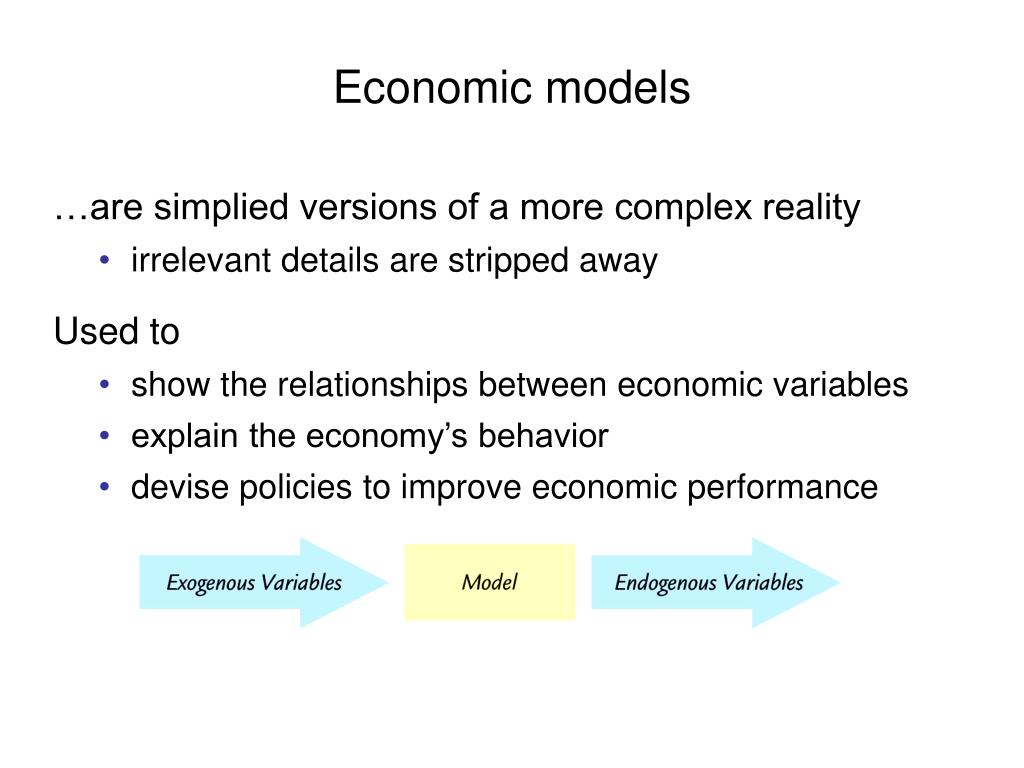
At its core, an economic model is a simplified version of reality that allows economists to isolate key relationships and analyze them in a controlled environment. It is not meant to be a perfect replica of the real world, but rather a distillation of its most important elements.
This article will explore the definition of an economic model, its various types, its uses, and its limitations, drawing on expert opinions and established economic literature to provide a comprehensive overview.
Defining the Economic Model
An economic model can be formally defined as a set of assumptions, concepts, relationships, and equations used to represent the behavior of an economy or a specific part of it. These models are built on a foundation of economic theory and are often expressed mathematically or graphically.
The purpose of the model is to explain and predict economic phenomena. It helps economists to understand the causal relationships between different variables, such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
According to the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER), "Economic models are essential for understanding and predicting how the economy works. They allow researchers to isolate the effects of different factors and to make informed policy recommendations."
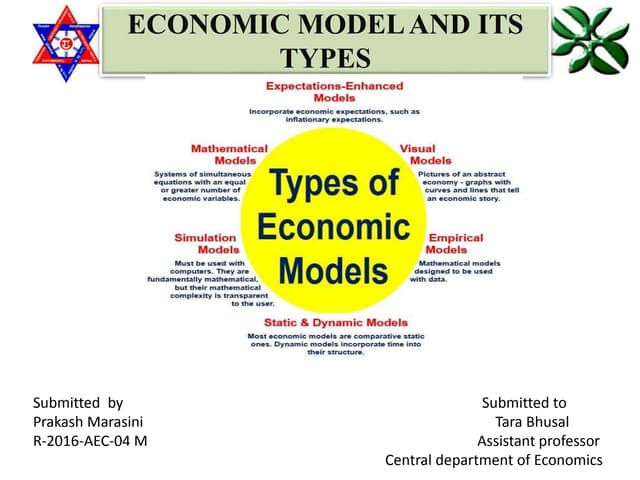
Types of Economic Models
Economic models come in various forms, each suited for different purposes. These models can be broadly categorized based on their scope, methodology, and assumptions.
Microeconomic Models
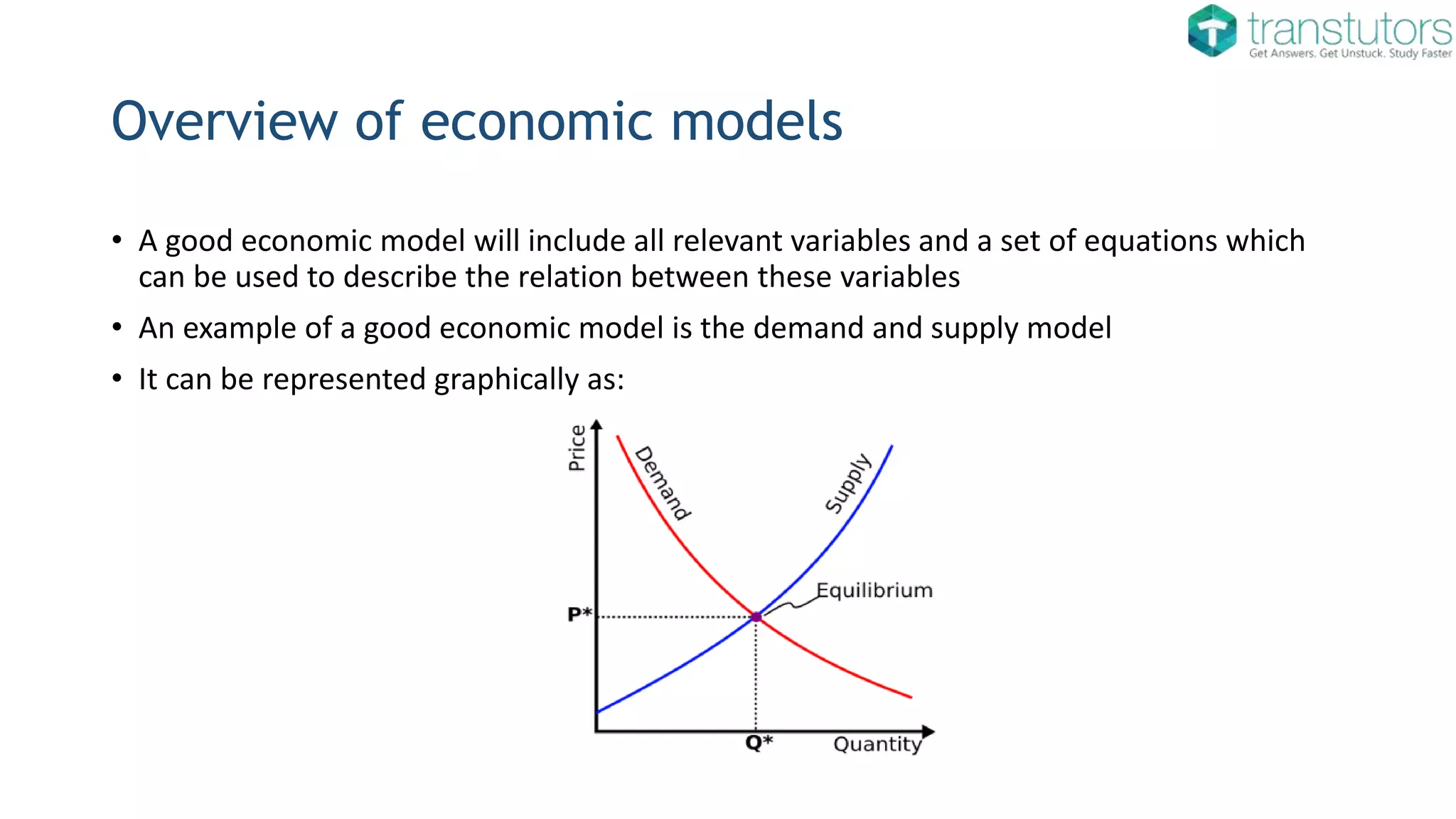
Microeconomic models focus on the behavior of individual agents, such as consumers, firms, and markets. They are used to analyze supply and demand, market equilibrium, and consumer choice.
Examples include models of perfect competition, monopoly, and oligopoly.
Macroeconomic Models
Macroeconomic models examine the behavior of the economy as a whole, including factors such as national income, inflation, and unemployment. These models are used to analyze the effects of fiscal and monetary policy.
The Solow-Swan model of economic growth and the Keynesian IS-LM model are prominent examples.
Econometric Models
Econometric models use statistical techniques to estimate the parameters of economic relationships and to test the validity of economic theories. They involve the application of statistical methods to economic data.
These models are crucial for forecasting and policy analysis.
Uses of Economic Models
Economic models serve a wide range of purposes in economics, policy, and business. They offer a structured approach to analyzing complex problems and informing decision-making.
One primary use is policy analysis, where models are used to simulate the effects of different policy interventions, such as tax cuts or interest rate changes. This allows policymakers to assess the potential consequences of their actions before implementing them.
Economic models are also vital for forecasting, providing predictions about future economic conditions. These forecasts help businesses and governments plan for the future and make informed investment decisions.
"Economic models are indispensable for understanding the complexities of the global economy and for making informed policy decisions," states Professor John Smith, a leading economist at Harvard University.
Limitations of Economic Models
While economic models are valuable tools, it is crucial to recognize their limitations. Models are simplifications of reality, and they rely on assumptions that may not always hold true.
One common critique is the assumption of rationality, which posits that individuals and firms always act in their own best interests. However, behavioral economics has shown that people often make decisions that deviate from rationality.
Another limitation is the difficulty in accurately capturing complex interactions and feedback loops within the economy. Models often focus on a limited number of variables and may overlook important factors.
Furthermore, the accuracy of a model's predictions depends heavily on the quality and availability of data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to flawed conclusions.
Impact on Society
Economic models have a significant impact on society, influencing policy decisions, investment strategies, and overall economic understanding. By providing a framework for analyzing economic issues, models help to inform public debate and shape policy outcomes.
For example, models of climate change are used to assess the economic impacts of global warming and to evaluate the costs and benefits of different mitigation strategies. These models play a crucial role in informing climate policy decisions.
Similarly, models of financial markets are used to assess the risk and stability of the financial system. These models help regulators to identify potential vulnerabilities and to implement policies to prevent financial crises.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an economic model is a vital tool for understanding and predicting economic phenomena. While it is a simplified representation of reality, it provides a structured framework for analyzing complex issues and informing decision-making.
Understanding the definition, types, uses, and limitations of economic models is essential for anyone involved in economics, policy, or business.
By recognizing the power and the constraints of these models, stakeholders can make more informed decisions and contribute to a more stable and prosperous economy.