Are 15 Minute Breaks Required By Law In Michigan

The question of whether 15-minute breaks are mandated by law in Michigan is a common source of confusion for both employees and employers. Many believe that such breaks are legally required, but the reality is more nuanced. Understanding the legal landscape surrounding break times is crucial for ensuring compliance and fostering a fair work environment.
This article delves into the specifics of Michigan's labor laws, clarifying the requirements for meal and rest breaks. It will also address common misconceptions and provide resources for those seeking further information. The information is intended to provide clarity on this important aspect of employment law.
Federal Law: The Baseline
It's important to first understand the federal context. The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), a federal law, does *not* require employers to provide rest or meal breaks. However, it does regulate how certain breaks are treated in terms of compensation.
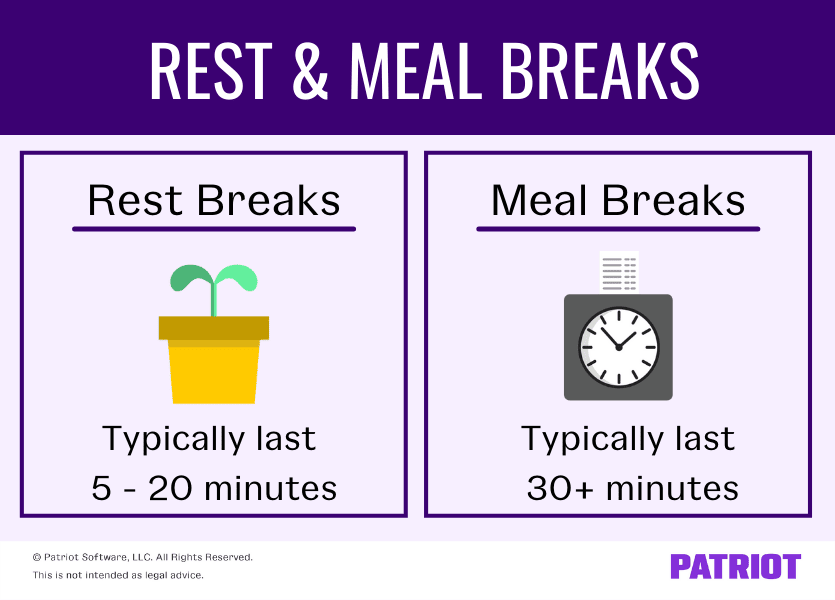
Specifically, if an employer chooses to offer short breaks, usually lasting from 5 to 20 minutes, they must be paid. These breaks are considered part of the work day.
Longer breaks, typically 30 minutes or more, taken for meals, do *not* need to be paid, provided the employee is completely relieved of their duties during that time.
Michigan Law: Following the Federal Lead
Michigan labor law largely mirrors the federal stance on break times. The state does *not* have a law requiring employers to provide either rest or meal breaks to employees aged 16 and older.
This means that, generally speaking, adult employees in Michigan are *not* legally entitled to any breaks during their workday. The provision of breaks is typically left to the discretion of the employer.
However, there are exceptions to this general rule. Specific regulations apply to certain industries and age groups.
Exceptions: Minors and Certain Industries
One notable exception concerns minor employees. Michigan law stipulates that employers must provide a 30-minute meal break to employees under the age of 18 who work more than five consecutive hours.
This provision aims to protect young workers and ensure they have adequate time to rest and eat during longer shifts. Failure to provide this break is a violation of Michigan's youth employment standards.
Furthermore, collective bargaining agreements or specific industry regulations may dictate break policies. It's essential to consult these agreements or regulations to determine if they include provisions regarding break times.
The Impact on Employees and Employers
The absence of a state law mandating breaks has a significant impact on employees. Many workers may find themselves working long hours without any guaranteed time to rest or eat.
This can lead to decreased productivity, increased stress, and potential health issues. Some argue that mandatory break times would improve employee well-being and boost overall morale.
For employers, the lack of a state mandate offers flexibility in managing their operations. They can tailor break policies to suit their specific needs and circumstances. However, this flexibility also places a greater responsibility on employers to treat their employees fairly and provide adequate opportunities for rest and recuperation.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
A common misconception is that a 15-minute break is legally required every few hours. This belief often stems from a misunderstanding of federal guidelines or word-of-mouth information.
In Michigan, there is *no* general legal requirement for a 15-minute break. Employers are free to set their own break policies, provided they comply with federal regulations regarding compensation for short breaks.
Another misconception is that all employees are entitled to a lunch break. While many employers offer lunch breaks as a standard practice, it is *not* legally mandated for adult employees in Michigan, unless specified in a contract or collective bargaining agreement.
Seeking Further Information and Resources
Employees and employers seeking clarification on Michigan's break time laws can consult the Michigan Department of Labor and Economic Opportunity (LEO). The LEO website provides valuable information on employment standards, including youth employment regulations.
Additionally, individuals can seek legal advice from an employment attorney. An attorney can provide personalized guidance based on specific circumstances and help navigate complex legal issues.
Understanding your rights and responsibilities is crucial for fostering a fair and compliant workplace. Proper research and consultation with relevant resources can help ensure that both employees and employers are aware of their legal obligations.
Conclusion: Understanding the Current Landscape
In conclusion, Michigan law *does not* require employers to provide 15-minute breaks to employees aged 16 and older. While federal law dictates how short breaks are compensated, the state leaves the decision of whether or not to offer breaks largely to the employer’s discretion.
The exception is for employees under the age of 18, who are entitled to a 30-minute meal break after five consecutive hours of work. It is important for both employers and employees to be aware of these regulations.
Navigating the complexities of labor law requires careful attention to detail and access to reliable information. By staying informed and consulting relevant resources, individuals can ensure compliance and promote a fair and productive work environment in Michigan.