Australia Adult Feeding Tubes And Formula Market

The subtle hum of medical equipment has become a constant for a growing number of Australians who rely on adult feeding tubes and specialized formulas. Behind the clinical settings and prescribed diets lies a complex and evolving market, one grappling with increasing demand, supply chain vulnerabilities, and ethical considerations surrounding accessibility and quality of life.
This article delves into the Australian adult feeding tube and formula market, examining its current state, the key players involved, the driving forces behind its expansion, the challenges it faces, and the outlook for the future. Understanding this market is crucial for healthcare providers, policymakers, patients, and their families as they navigate the intricacies of nutritional support.
Market Overview and Growth Drivers
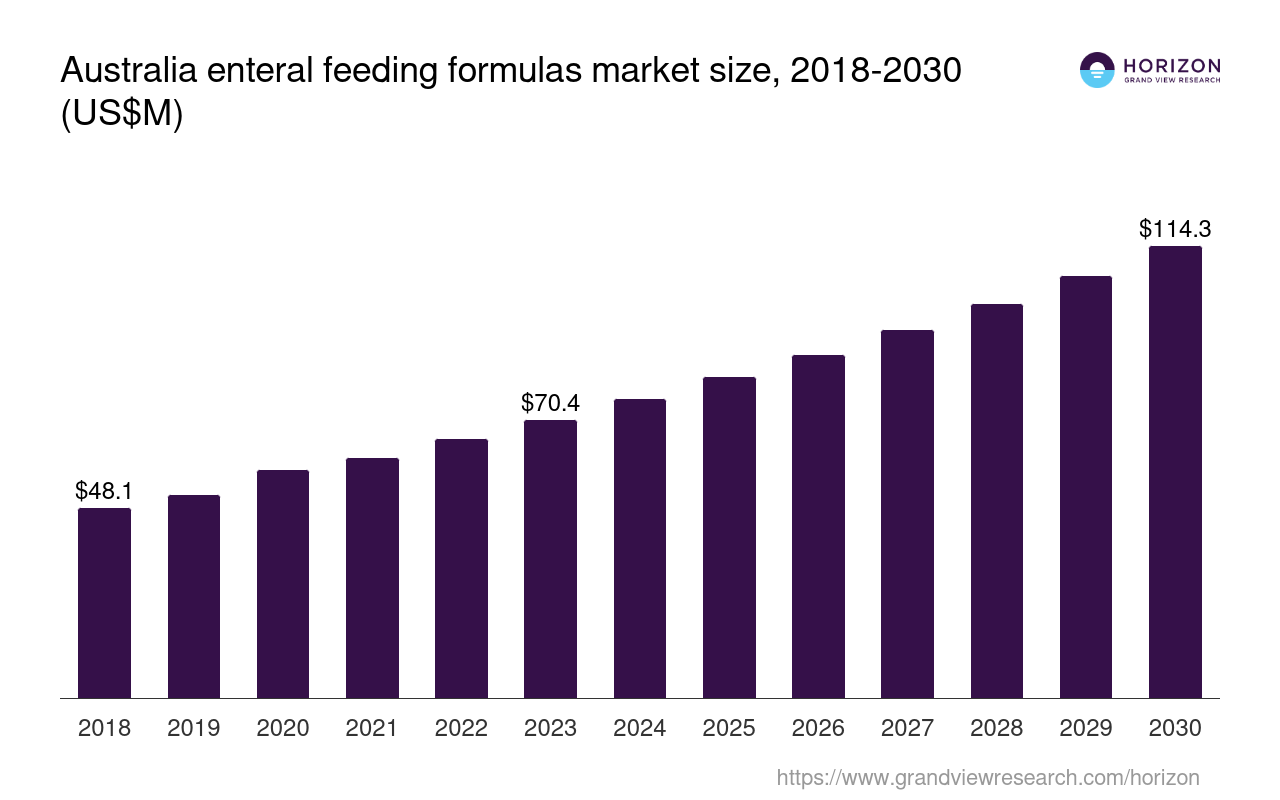
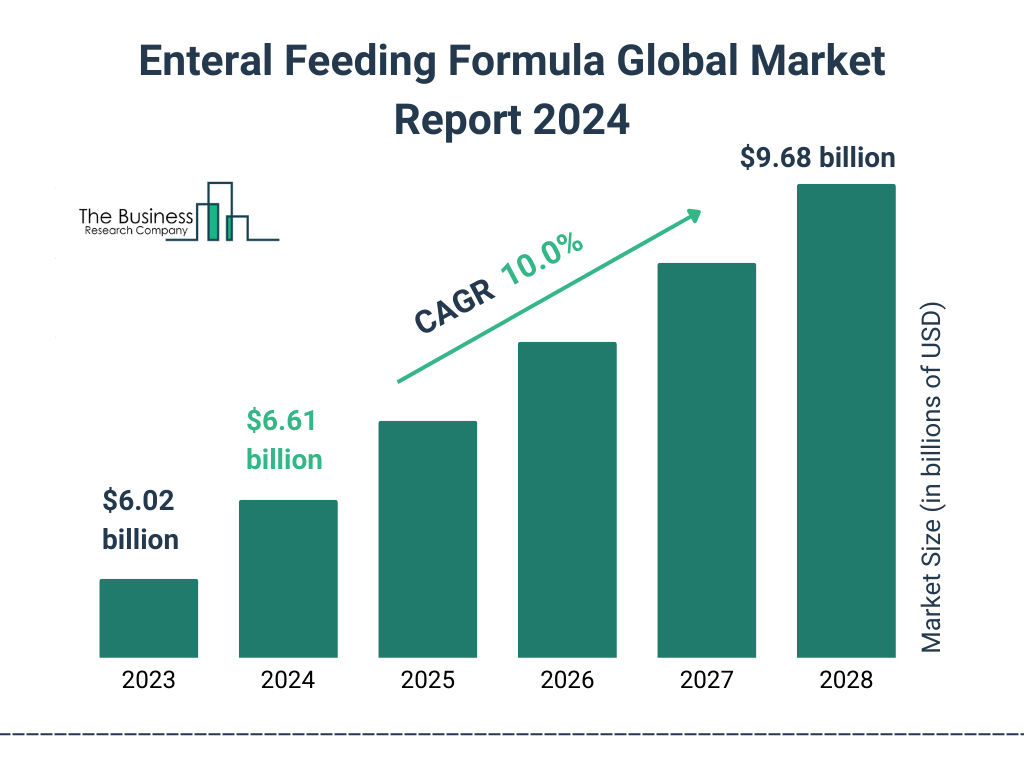
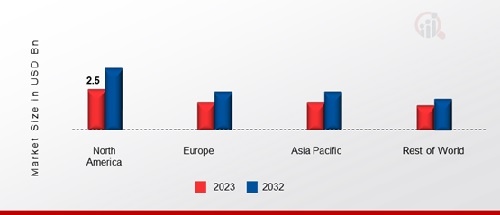
The Australian adult feeding tube and formula market is experiencing consistent growth, fueled by an aging population, increased prevalence of chronic diseases, and advancements in medical technology that extend life expectancy. Conditions such as dysphagia, cancer, stroke, and neurological disorders often necessitate the use of enteral nutrition to ensure adequate caloric and nutrient intake.
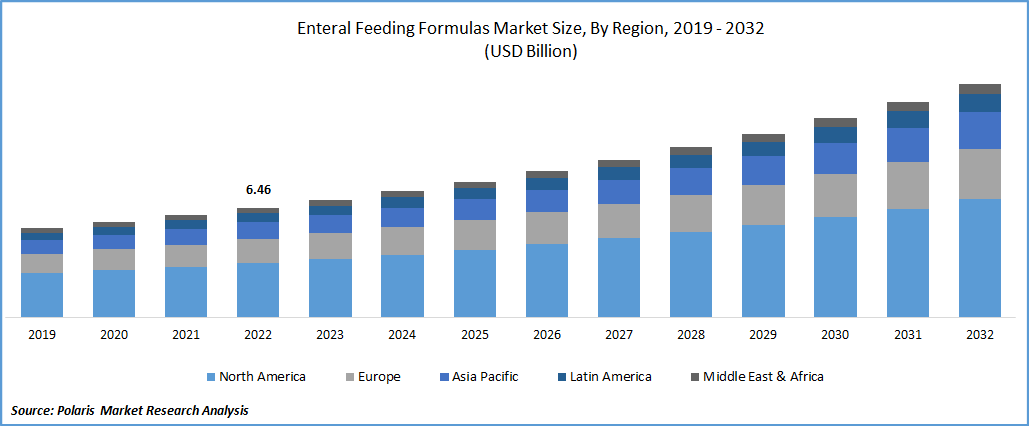
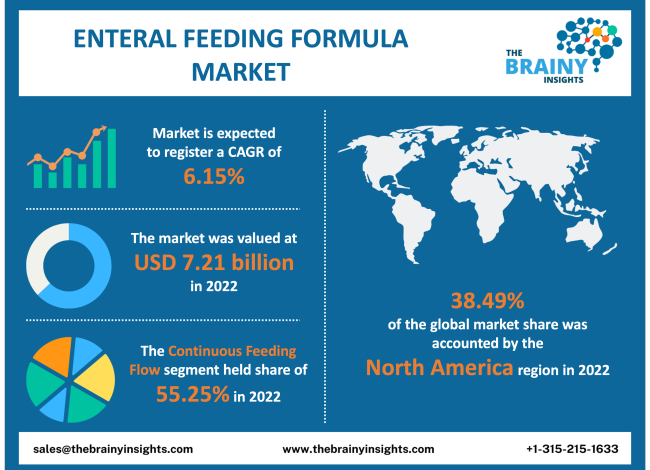
According to a report by IBISWorld, the market size is substantial, with revenue generated through the sale of feeding tubes, specialized formulas, and related medical devices. Nestlé Health Science and Abbott Nutrition are major players, dominating the market with a wide range of products catering to diverse dietary needs and medical conditions.
Technological advancements in feeding tube design, such as smaller bore tubes and improved insertion techniques, contribute to patient comfort and ease of use. The development of more sophisticated formulas, tailored to specific medical conditions like diabetes or renal failure, further drives market growth by offering targeted nutritional solutions.
Key Market Segments
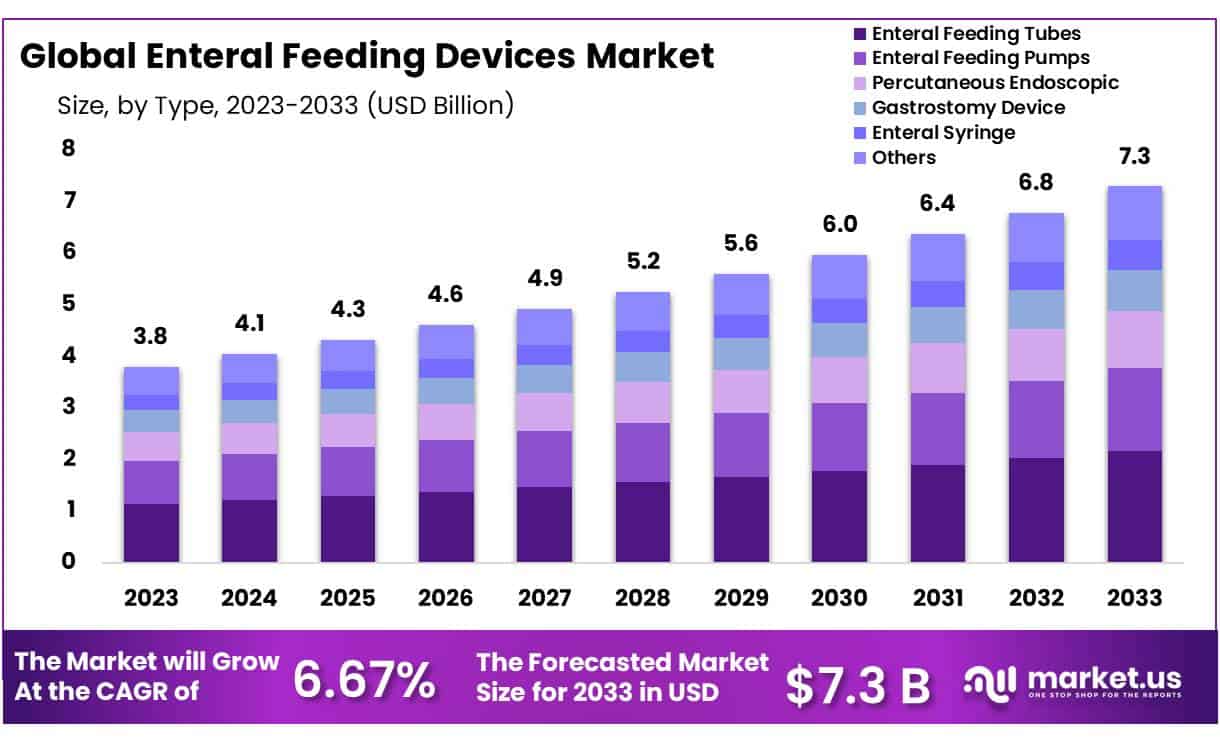
The market can be segmented based on several factors, including the type of feeding tube, the route of administration, and the type of formula. Nasogastric (NG) tubes and percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes are the most common types of feeding tubes used in adults.
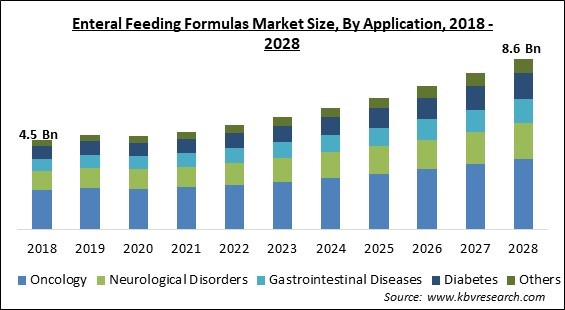
Formulas are broadly categorized into standard polymeric formulas, semi-elemental formulas, and elemental formulas, each designed to meet different levels of digestive capacity. Specialized formulas, such as those for patients with diabetes, renal disease, or immune deficiencies, represent a significant and growing segment.
Home enteral nutrition (HEN) is an increasingly important segment, allowing patients to receive nutritional support in the comfort of their own homes. This trend is driving demand for user-friendly feeding pumps, portable formulas, and comprehensive support services.
Challenges and Concerns
Despite its growth, the Australian adult feeding tube and formula market faces several challenges. Supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by global events, can lead to shortages of essential products and increased costs.
Accessibility and affordability are significant concerns, particularly for patients who rely on HEN and may face financial barriers to obtaining the necessary supplies. The cost of specialized formulas can be substantial, and coverage under the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) or private health insurance may be limited.
Ethical considerations surrounding the use of feeding tubes, particularly in end-of-life care, are also a subject of ongoing debate. Balancing the benefits of nutritional support with the potential burden on patients and their families requires careful consideration.
Regulatory Landscape and Quality Assurance
The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) regulates the safety and efficacy of feeding tubes and formulas in Australia. Manufacturers must comply with stringent quality standards and labeling requirements to ensure patient safety.
Hospitals and healthcare providers adhere to established clinical guidelines for the prescription and administration of enteral nutrition. These guidelines emphasize the importance of individualized assessments, appropriate formula selection, and ongoing monitoring to optimize patient outcomes.
There is a growing emphasis on improving the quality of life for individuals receiving enteral nutrition. This includes providing comprehensive education and support to patients and their caregivers, as well as promoting patient autonomy and decision-making.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
Technology plays a crucial role in advancing the adult feeding tube and formula market. Telehealth consultations and remote monitoring devices enable healthcare providers to track patient progress and adjust treatment plans remotely.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being used to develop personalized nutritional recommendations based on individual patient characteristics and needs. This has the potential to optimize formula selection and improve patient outcomes.
Research and development efforts are focused on creating more biocompatible feeding tubes, developing more palatable and nutritious formulas, and improving the delivery methods for enteral nutrition.
Future Outlook
The Australian adult feeding tube and formula market is expected to continue its growth trajectory in the coming years. This growth will be driven by an aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and advancements in medical technology.
Personalized nutrition and targeted therapies are likely to become more prevalent, allowing for more individualized and effective treatment strategies. The integration of technology, such as telehealth and remote monitoring, will further enhance patient care and improve outcomes.
Addressing the challenges of accessibility, affordability, and ethical considerations will be crucial to ensuring that all Australians have access to the nutritional support they need. Ongoing collaboration between healthcare providers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders is essential to shaping the future of this vital market and improving the lives of individuals who rely on feeding tubes and formulas. Ensuring equitable access and focusing on patient-centered care will define success in this evolving landscape.