The Term Jurisdiction As Used In Your Text Means

Critical legal interpretations are shifting. The definition of "jurisdiction", as used in specific legal texts, is undergoing intense scrutiny, potentially reshaping legal proceedings and international agreements.
Defining Jurisdiction: A Core Legal Principle
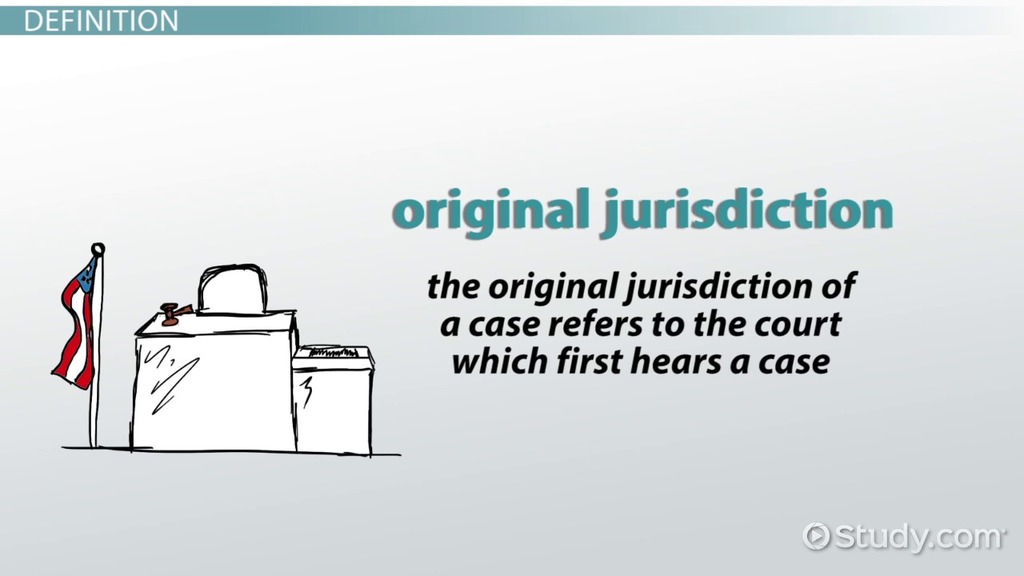
The term jurisdiction, broadly defined, refers to the authority of a court or other governing body to hear and decide a case. However, its specific application varies dramatically depending on the context of the legal document.
The specific interpretation hinges on several elements, including the explicit wording of the document, the legislative history, and relevant case law precedents. It’s not a one-size-fits-all definition.
Key Components of Jurisdictional Authority
Jurisdiction can be categorized in several ways, each carrying distinct implications. Understanding these categories is vital for interpreting the term accurately.
Territorial jurisdiction defines authority based on geographical boundaries. A court typically has jurisdiction over events occurring within its defined territory.
Subject matter jurisdiction limits a court's power to hear only certain types of cases. For instance, bankruptcy courts only handle bankruptcy matters.
Personal jurisdiction (also known as in personam jurisdiction) concerns the court's power over specific individuals or entities. This requires sufficient contacts with the jurisdiction.
Appellate jurisdiction refers to the authority of a higher court to review decisions made by lower courts. This ensures legal oversight and consistency.
Contextual Variations and Their Impact
The meaning of jurisdiction within a specific legal text is rarely self-evident. Analyzing the surrounding clauses and the document's overall purpose is crucial.
Consider a treaty governing international trade. Jurisdiction might refer to the authority of an international tribunal to resolve disputes between signatory nations.
In a domestic statute, jurisdiction could define the power of a federal agency to regulate businesses within a specific industry. This directly affects corporate compliance.
Furthermore, conflict of laws principles come into play when disputes involve multiple jurisdictions. Courts must determine which jurisdiction's laws apply to the case.
Recent Developments and Ongoing Debates
Recent legal challenges have highlighted the ambiguity surrounding the term jurisdiction. Judges are actively debating its scope in new and complex situations.
The rise of the internet has created novel jurisdictional questions. Determining where an online transaction occurs for jurisdictional purposes is a growing challenge.
Cybercrime presents unique difficulties. Establishing jurisdiction over hackers operating from foreign countries is a persistent hurdle for law enforcement.
Moreover, the enforcement of international judgments depends on recognizing the jurisdiction of foreign courts. This recognition is not always guaranteed.
Implications for Legal Practice and Policy
A clear understanding of jurisdiction is paramount for legal professionals. It dictates where a lawsuit can be filed and what laws will govern the outcome.
Businesses must consider jurisdictional issues when expanding into new markets. Failure to do so can result in unexpected legal liabilities.
Policymakers should carefully consider the jurisdictional implications of new legislation. Vague or poorly defined jurisdictional provisions can lead to costly litigation.
Next Steps and Monitoring the Evolution
Legal experts are closely monitoring upcoming court decisions that will further shape the definition of jurisdiction. These cases could set new precedents.
Continued analysis of legislative intent and historical context is essential for interpreting existing laws. The term is dynamic, not static.
Ongoing dialogues between legal scholars, practitioners, and policymakers are crucial. These discussions will help ensure that the concept of jurisdiction remains relevant and effective in the modern era.