Best Sleeping Position To Reduce Eye Pressure

Imagine waking up, the sun gently kissing your face, but instead of feeling refreshed, you're greeted by a persistent throbbing behind your eyes. It's a subtle discomfort, a nagging pressure that seems to dull the vibrancy of the world. While many factors can contribute to this sensation, one surprisingly simple aspect of your daily routine—your sleeping position—might be playing a larger role than you realize.
The position you adopt for those precious hours of sleep can significantly impact the pressure within your eyes, also known as intraocular pressure (IOP). Understanding the relationship between sleep posture and IOP could be a key to alleviating discomfort and potentially safeguarding your vision.
Understanding Intraocular Pressure (IOP)
Intraocular pressure is the fluid pressure inside the eye. It's maintained by a delicate balance of fluid production and drainage.
When this balance is disrupted, the IOP can increase, potentially leading to damage to the optic nerve, the crucial pathway that transmits visual information from your eye to your brain.
This damage is the hallmark of glaucoma, a leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide, according to the World Health Organization. Maintaining a healthy IOP is therefore vital for preserving vision.
The Link Between Sleep Position and IOP
During sleep, our bodies undergo various physiological changes, including shifts in blood flow and fluid distribution. These changes can be influenced by our sleeping posture.
Research suggests that certain sleeping positions can elevate IOP, especially in individuals already susceptible to eye pressure issues or those diagnosed with glaucoma.
Studies have shown a correlation between sleeping positions and fluctuations in IOP, highlighting the importance of considering this factor in managing eye health.
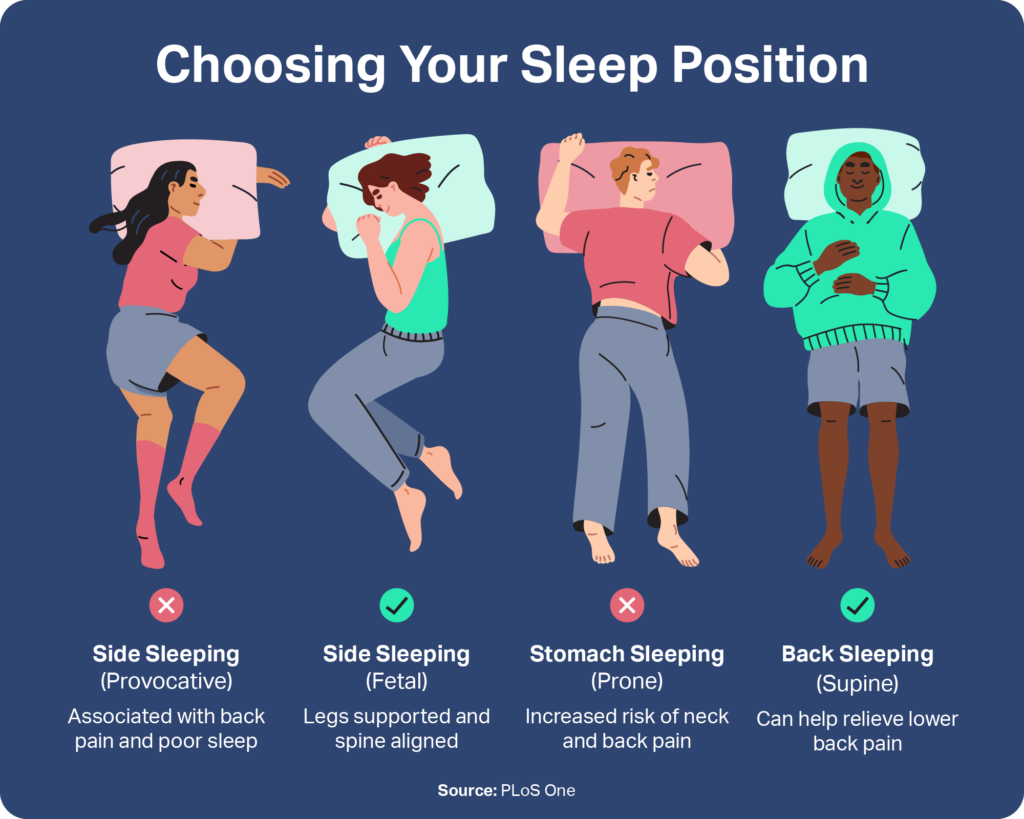
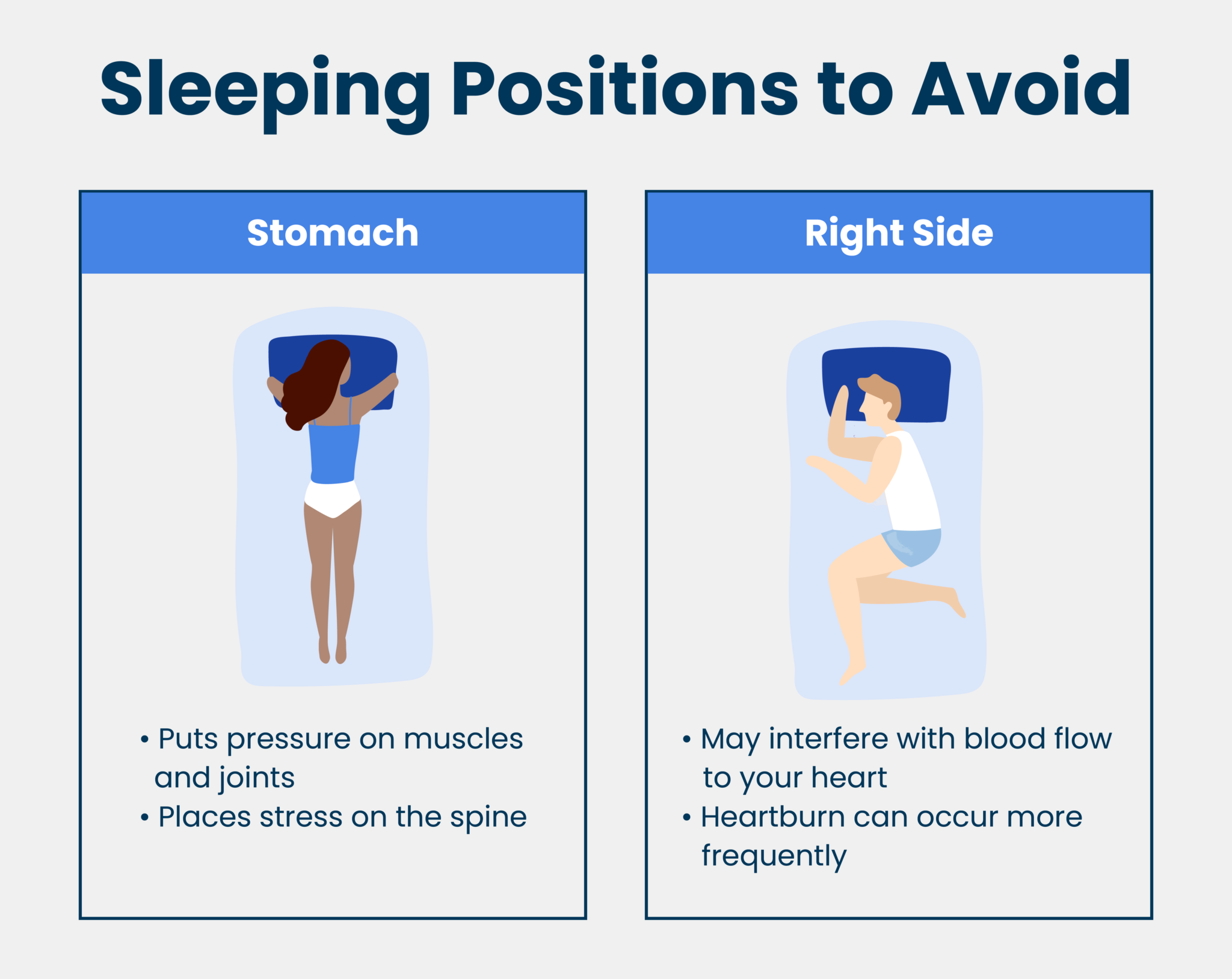
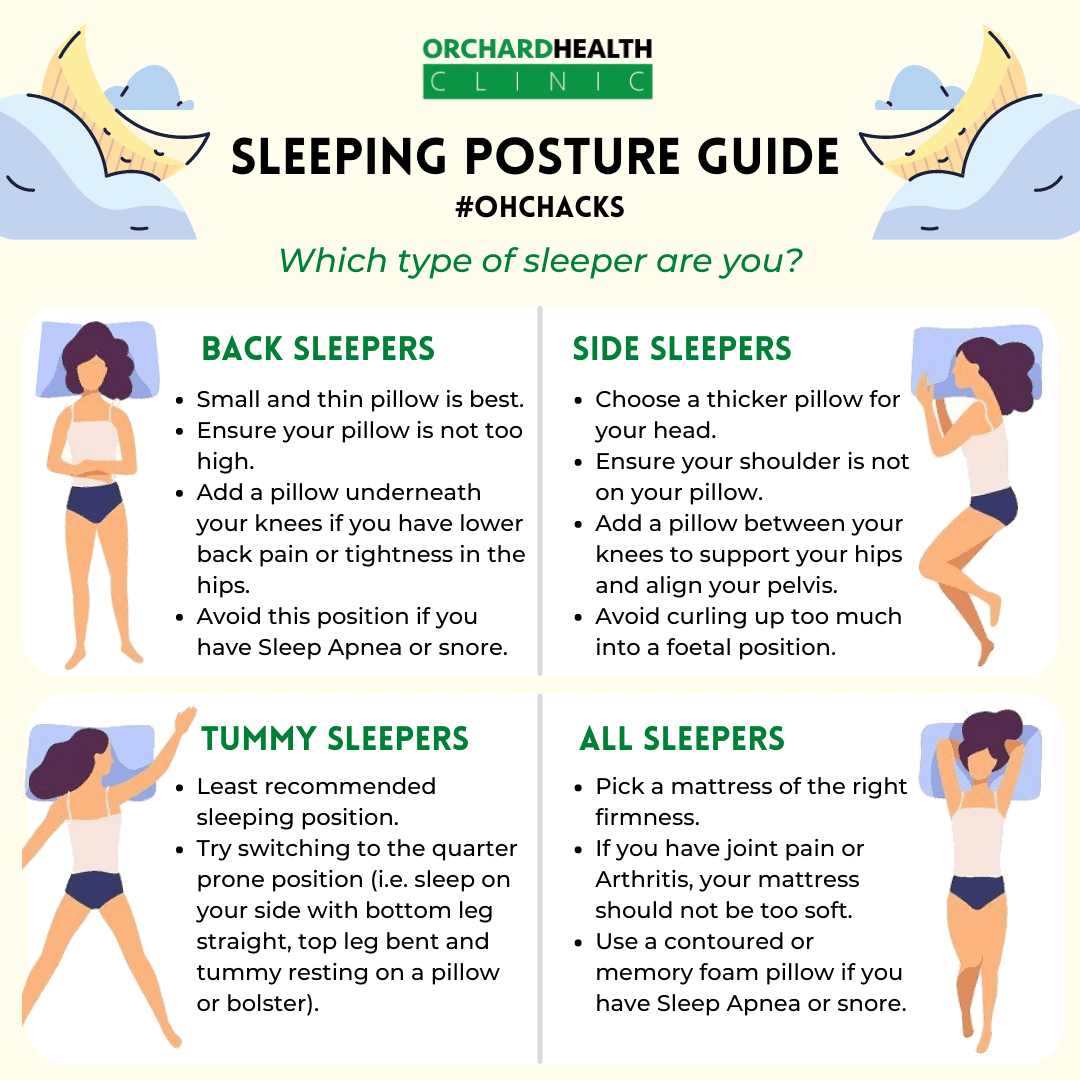
Side Sleeping: The Dominant Eye Dilemma
Sleeping on your side, while generally considered comfortable by many, can have asymmetrical effects on your eyes. Studies have shown that the eye in contact with the pillow often experiences a higher IOP compared to the eye facing upwards.
This increased pressure is thought to be due to the external compression exerted on the eye by the pillow. Over time, this consistent pressure could potentially contribute to or exacerbate eye conditions.
A study published in the Journal of Glaucoma indicated a statistically significant increase in IOP in the dependent eye (the eye closer to the pillow) in participants who habitually slept on their side.
Sleeping on Your Stomach: A Potentially Problematic Posture
Sleeping on your stomach is generally discouraged by eye health professionals due to the pressure it exerts on both eyes. When lying face down, both eyes are subjected to prolonged compression against the pillow.
This can lead to a significant increase in IOP and may worsen existing eye conditions or contribute to the development of new ones. Stomach sleeping might also exacerbate facial puffiness and other issues.
While less common than side sleeping, stomach sleeping poses a higher risk due to the direct and sustained pressure on both eyes.
Sleeping on Your Back: A Preferred Position
Sleeping on your back is often considered the most beneficial posture for maintaining healthy IOP. In this position, the weight of your body is evenly distributed, and there is minimal external pressure on the eyes.
This reduces the risk of elevating IOP during sleep and can contribute to better overall eye health. It also promotes better spinal alignment.
While individual comfort levels vary, adopting a supine (back-sleeping) position could be a proactive step toward protecting your vision.
Practical Tips for Optimizing Your Sleep Position
While changing deeply ingrained sleep habits can be challenging, here are some practical tips to help you optimize your sleeping position and potentially reduce eye pressure.
First, try gradually transitioning to sleeping on your back. You can use pillows to support your head and neck and prevent you from rolling onto your side or stomach.
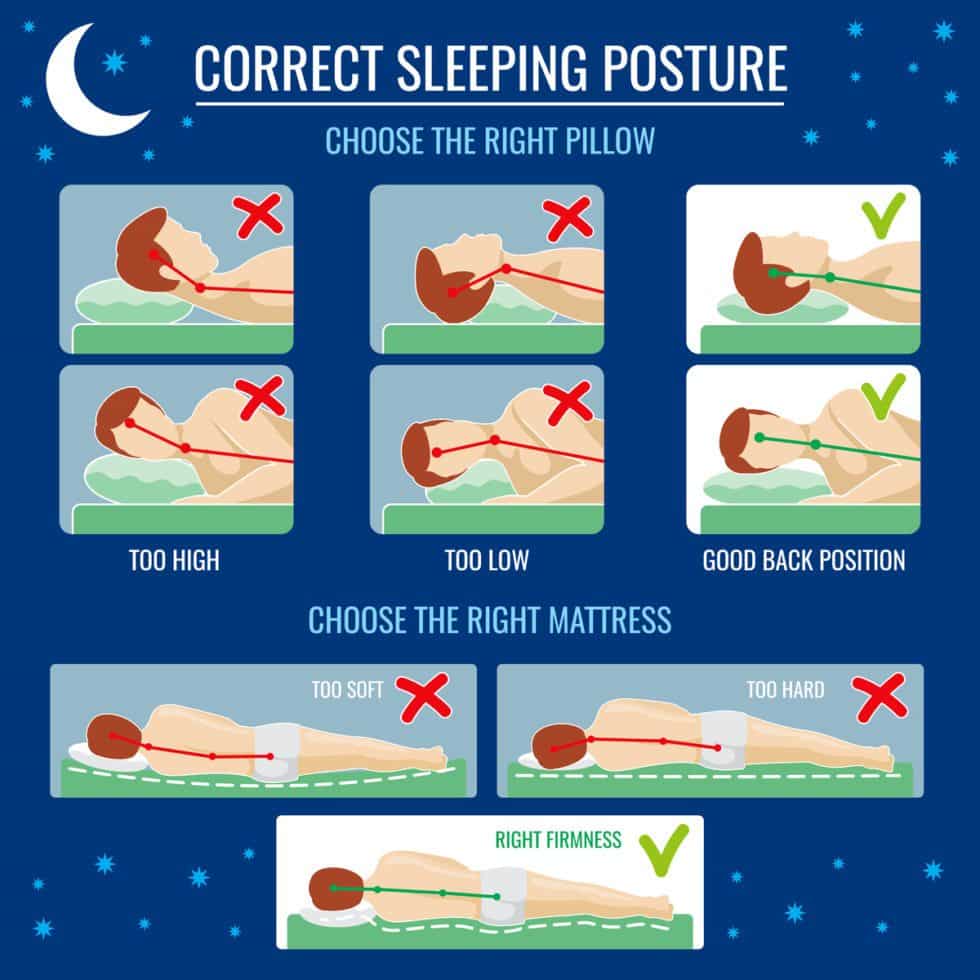
Second, if you find it difficult to sleep on your back, consider using a firmer pillow. A firmer pillow can help reduce the amount of pressure exerted on your eyes when sleeping on your side.
Third, make sure your pillow is at the right height. An improperly positioned pillow can strain your neck and potentially affect blood flow, indirectly impacting IOP.
Fourth, be mindful of your sleeping position throughout the night. If you wake up on your side or stomach, gently roll back onto your back.
Fifth, consult with your eye doctor if you have concerns about your IOP or your risk of glaucoma. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your individual needs and circumstances.
The Role of Lifestyle and Overall Health
While sleep position is an important factor, it's crucial to remember that it's just one piece of the puzzle. Overall lifestyle and health habits play a significant role in maintaining healthy IOP.
Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, and avoiding smoking can all contribute to better eye health. Managing stress is also important, as stress can sometimes lead to increased IOP.
Regular eye exams are essential for early detection and management of any potential eye problems, including glaucoma. Early detection and treatment are key to preventing vision loss.
The Importance of Professional Consultation
The information provided here is for general knowledge and informational purposes only, and does not constitute medical advice. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or ophthalmologist for any concerns regarding your eye health or before making any decisions related to your treatment or care.
Self-treating can be dangerous, and a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan from a medical professional are always recommended. They can assess your individual risk factors and provide tailored recommendations for maintaining healthy IOP and preventing vision loss.
Don't hesitate to seek professional guidance if you have any concerns about your eye health. Your vision is precious, and taking proactive steps to protect it is always a worthwhile investment.
Conclusion
Our nightly slumber, often taken for granted, can be a hidden contributor to our eye health. By understanding the potential impact of sleeping positions on intraocular pressure, we can make informed choices to safeguard our vision.
Adopting a back-sleeping position, using a supportive pillow, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are simple yet powerful steps we can take to promote eye health. Remember, knowledge is power, especially when it comes to preserving our precious sight.
So, the next time you settle into bed, take a moment to consider your sleeping posture. It might just be the key to waking up to a brighter, clearer world.