Magnesium Absorption Is Enhanced By The Presence Of
The silent epidemic of magnesium deficiency continues to plague populations worldwide, impacting everything from cardiovascular health to cognitive function. While awareness of magnesium's importance is growing, understanding how to optimize its absorption remains a critical challenge. Recent research sheds light on key synergistic relationships that significantly enhance magnesium uptake, offering hope for more effective supplementation strategies.
The key to unlocking magnesium's benefits lies not just in consuming enough, but in maximizing its bioavailability. This article delves into the science behind magnesium absorption, highlighting the crucial role of specific nutrients and compounds that act as facilitators. We examine the evidence supporting the enhanced absorption of magnesium in the presence of certain vitamins, minerals, and other dietary components, exploring the implications for dietary recommendations and supplement formulation.
The Science of Magnesium Absorption
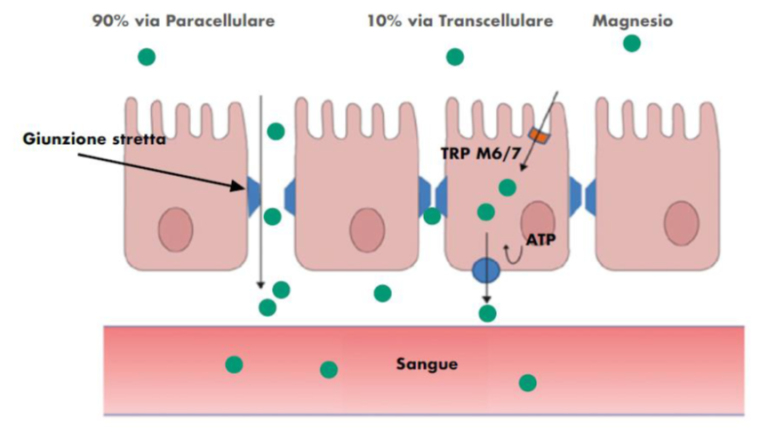
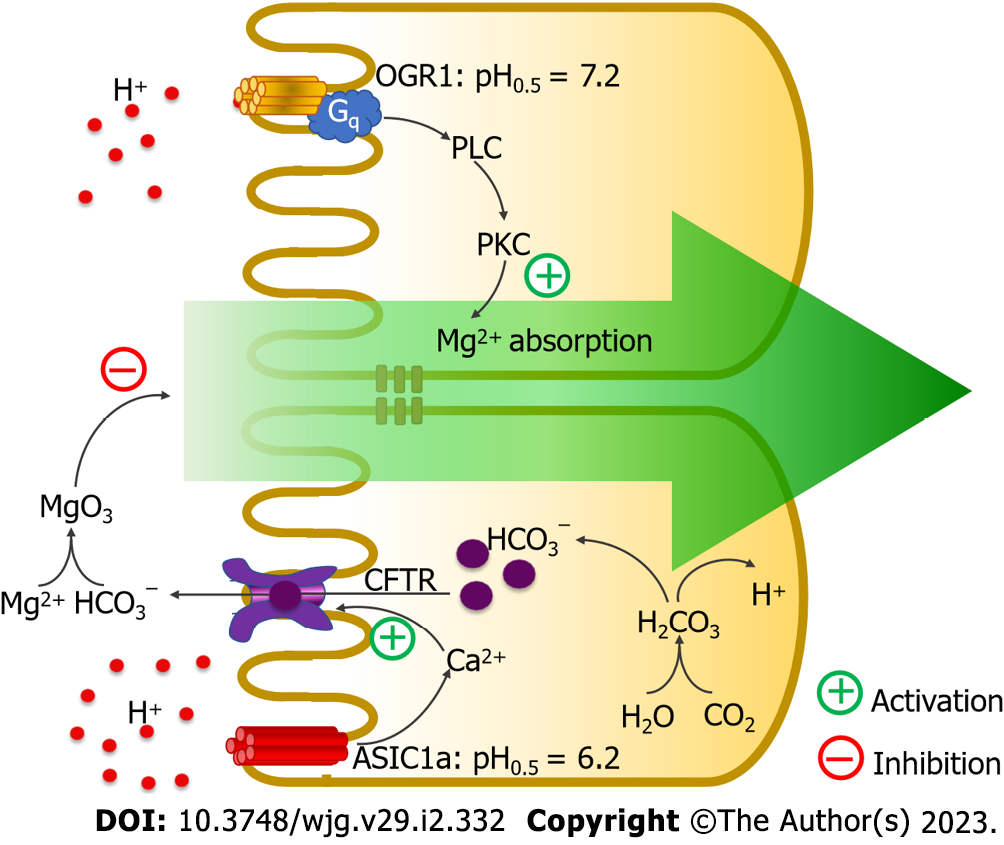
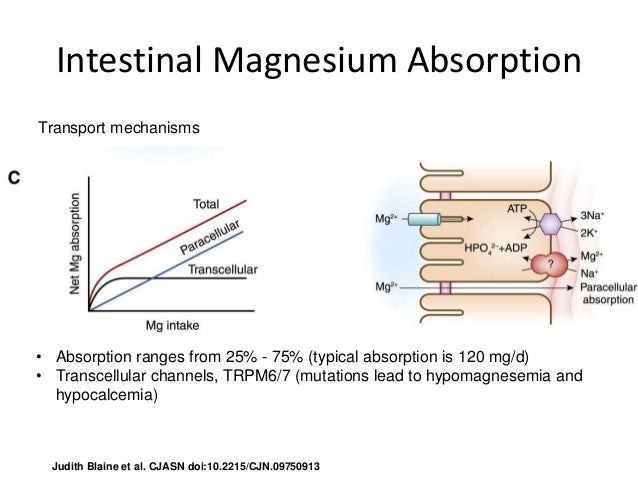
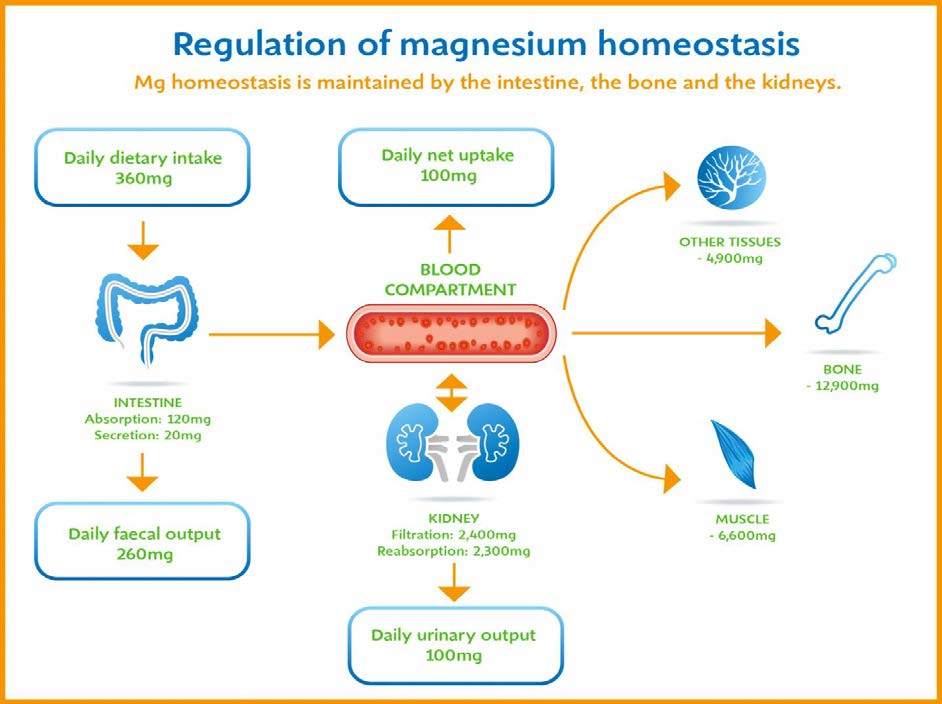
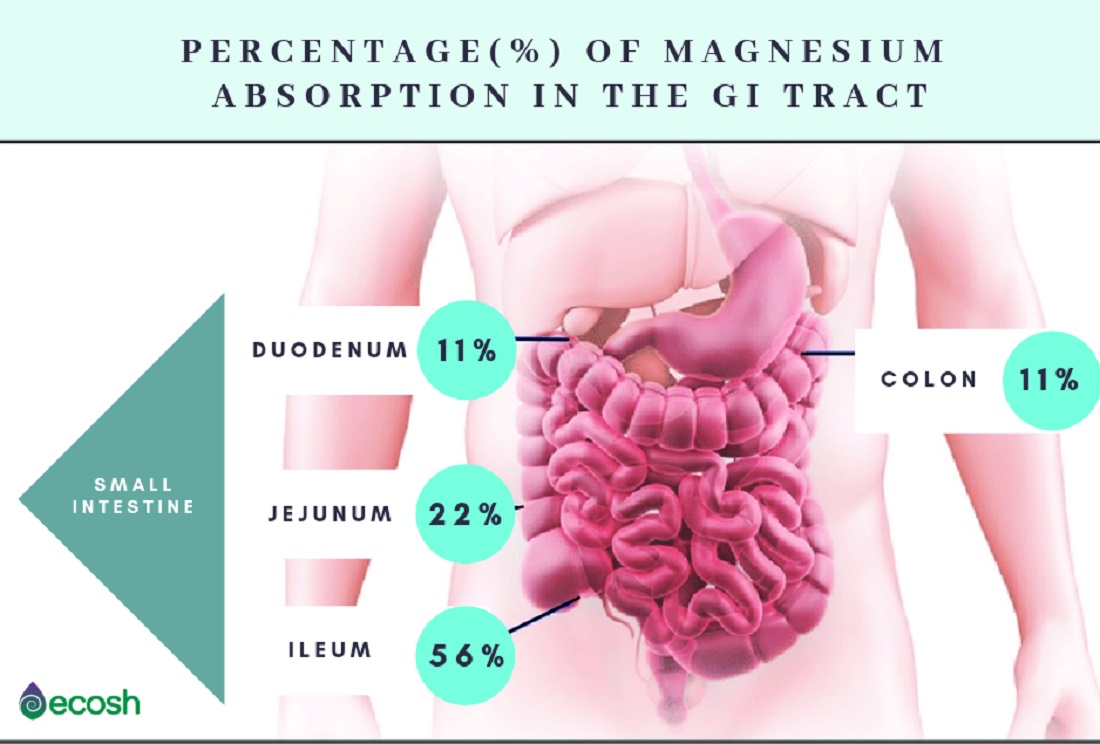
Magnesium absorption primarily occurs in the small intestine, a complex process influenced by various factors. These factors include the form of magnesium ingested, the individual's gut health, and the presence of other nutrients in the digestive tract. Understanding these interactions is essential for optimizing magnesium status.
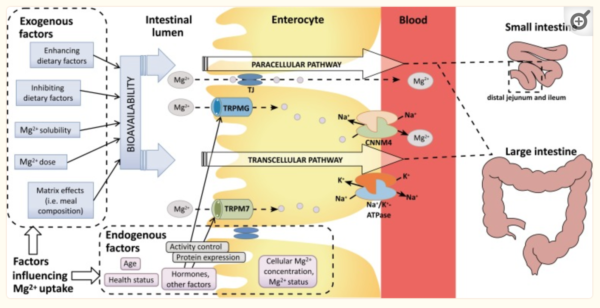
Passive diffusion and active transport are the two main mechanisms involved in magnesium uptake. Passive diffusion occurs when magnesium moves across the intestinal wall from an area of high concentration to low concentration, without requiring energy. Active transport, on the other hand, involves specialized protein transporters that actively shuttle magnesium across the cell membrane, requiring energy expenditure.
Vitamin D's Crucial Role
Vitamin D is arguably the most significant enhancer of magnesium absorption. Vitamin D stimulates the production of calbindin, a protein that binds to calcium and magnesium in the intestinal cells. This binding facilitates the transport of both minerals across the cell membrane and into the bloodstream.
Studies have shown a direct correlation between adequate vitamin D levels and improved magnesium absorption. Individuals with vitamin D deficiency often exhibit lower magnesium levels, even with sufficient dietary intake. Supplementation with both vitamin D and magnesium can be particularly beneficial for those with deficiencies in both nutrients.
The Synergistic Relationship with Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, plays a vital role in cellular magnesium uptake. It assists in transporting magnesium across cell membranes, improving its utilization within the body's cells. This synergy is particularly important for muscle function and nerve transmission.
The combination of magnesium and vitamin B6 has been shown to be effective in managing conditions like premenstrual syndrome (PMS), where magnesium deficiency is often implicated. The enhanced intracellular magnesium levels achieved through this combination contribute to improved mood and reduced symptoms.
Carbohydrates and Insulin's Influence
The presence of carbohydrates, particularly glucose, can influence magnesium absorption through insulin secretion. Insulin stimulates the uptake of magnesium into cells, effectively reducing magnesium levels in the bloodstream. This effect can be both beneficial and detrimental.
While insulin facilitates magnesium uptake into cells, excessive carbohydrate consumption can lead to increased magnesium excretion through the kidneys. This can contribute to magnesium depletion, particularly in individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes. Therefore, a balanced carbohydrate intake is crucial for maintaining optimal magnesium levels.
The Impact of Other Minerals: Calcium and Potassium
The interplay between magnesium and other minerals, such as calcium and potassium, is complex and can affect magnesium absorption. High doses of calcium can compete with magnesium for absorption in the intestines. Maintaining a proper calcium-to-magnesium ratio is essential for preventing interference.
Potassium, like magnesium, is an intracellular cation, and their levels are often interconnected. Adequate potassium intake is necessary for maintaining proper magnesium balance within cells. However, the precise mechanisms by which potassium influences magnesium absorption are still under investigation.
The Role of Gut Health
A healthy gut microbiome is essential for optimal nutrient absorption, including magnesium. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in gut bacteria, can impair magnesium absorption. Conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can also significantly reduce magnesium uptake.
Probiotics and prebiotics can improve gut health and potentially enhance magnesium absorption. By promoting a balanced gut microbiome, these supplements can create a more favorable environment for nutrient uptake. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the specific strains and dosages that are most effective for enhancing magnesium absorption.
Future Directions and Implications
The ongoing research into magnesium absorption is paving the way for more targeted and effective supplementation strategies. Understanding the synergistic relationships between magnesium and other nutrients can lead to improved supplement formulations and dietary recommendations. This includes combining magnesium with vitamin D, vitamin B6, and optimizing carbohydrate intake.
Personalized nutrition approaches, taking into account individual factors like gut health, vitamin D status, and dietary habits, are likely to become increasingly important in addressing magnesium deficiency. Tailoring supplementation and dietary recommendations to individual needs can maximize magnesium absorption and utilization.
Ultimately, enhancing magnesium absorption requires a holistic approach that considers the complex interplay of various factors. By focusing on synergistic nutrient combinations and promoting gut health, individuals can optimize their magnesium status and reap the full benefits of this essential mineral. As research continues to unravel the intricacies of magnesium absorption, we can anticipate even more effective strategies for combating magnesium deficiency and improving overall health.