Biopolymers Are Made Of Green Materials That Are Generated By

In a world increasingly concerned with sustainability, the development and adoption of biopolymers are gaining significant traction. These materials, derived from renewable biological sources, offer a promising alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics, addressing concerns about pollution and resource depletion.
This article explores the growing field of biopolymers, examining their composition, production methods, applications, and potential impact on various industries and the environment.
What are Biopolymers?
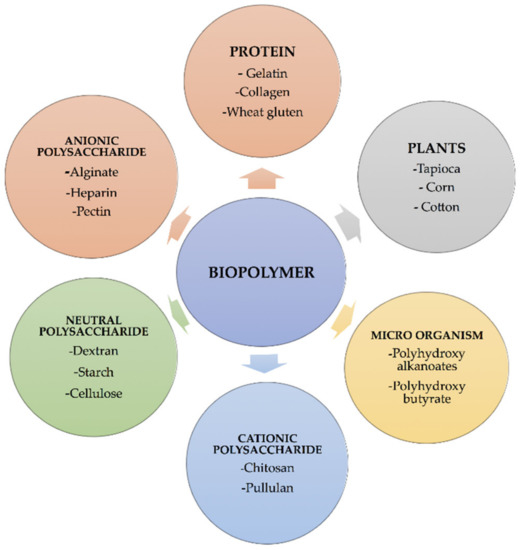
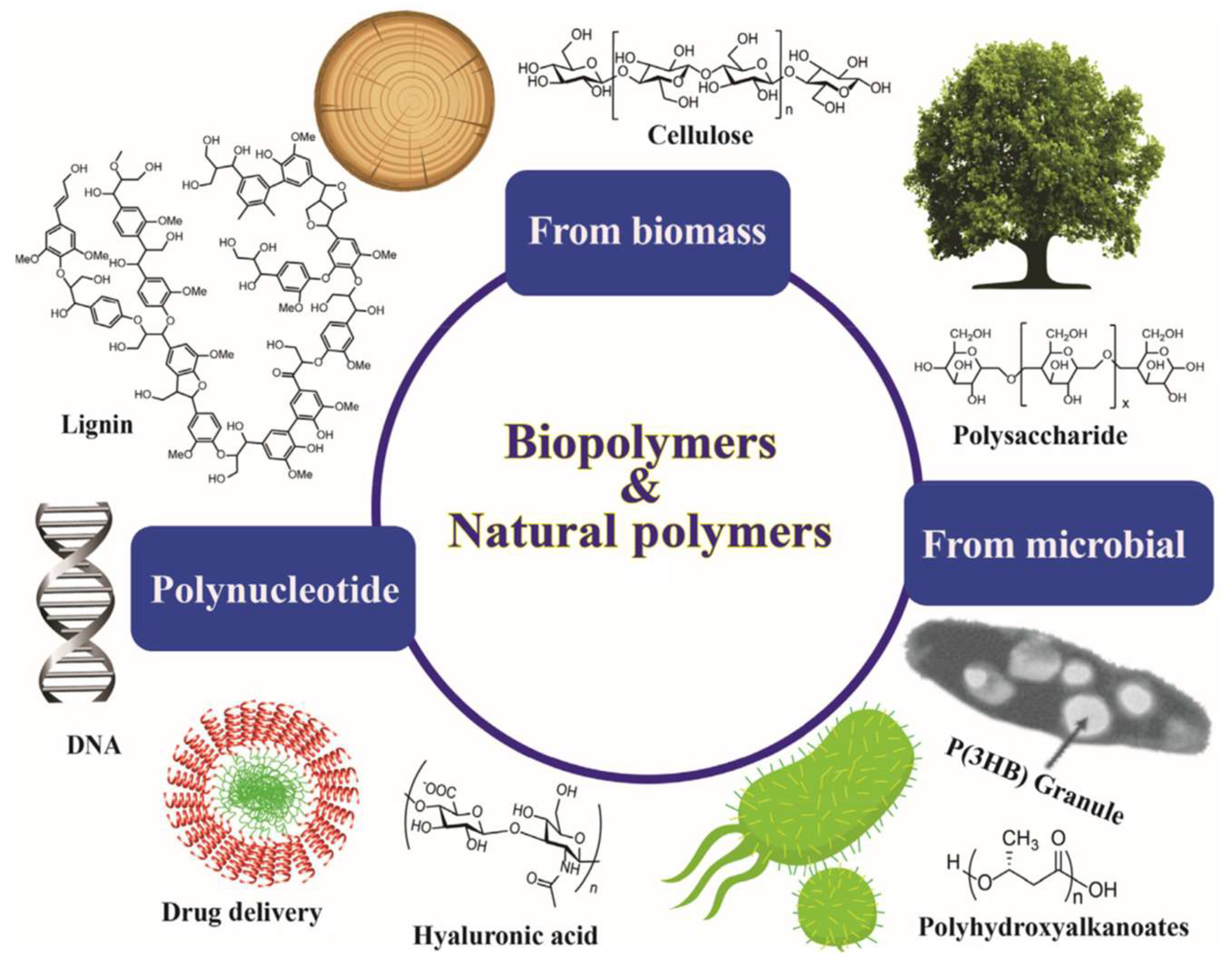
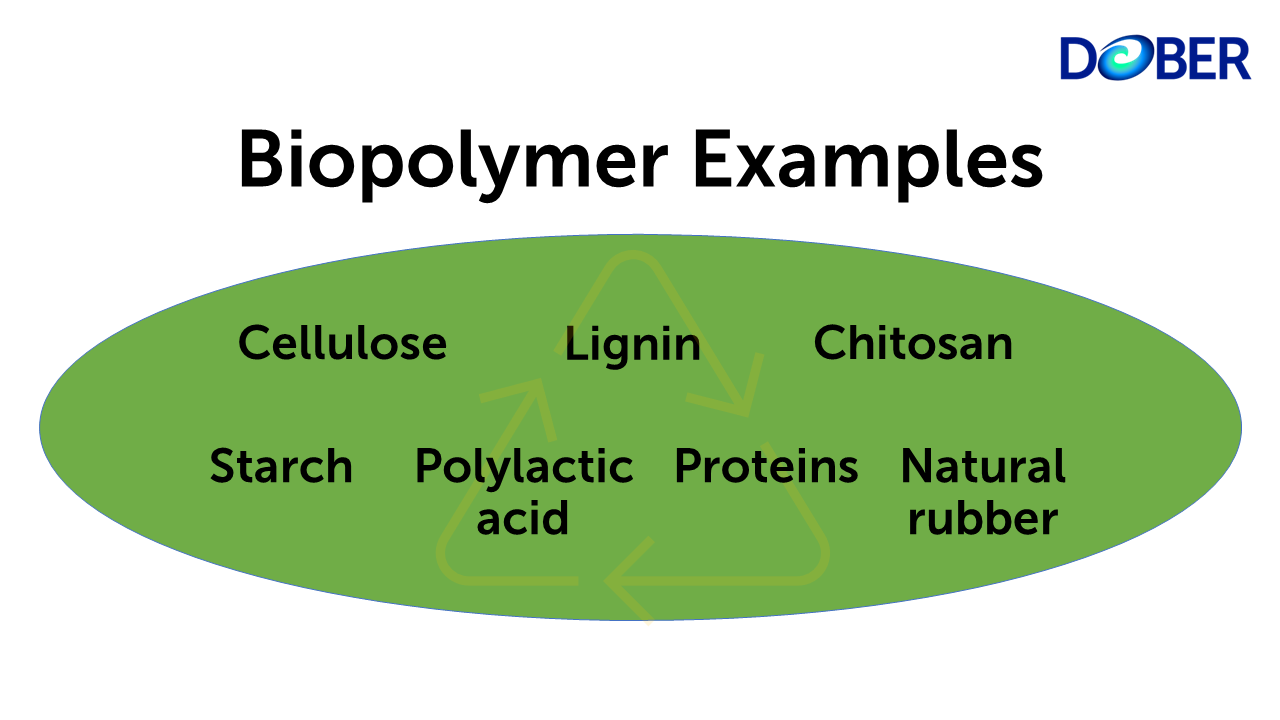
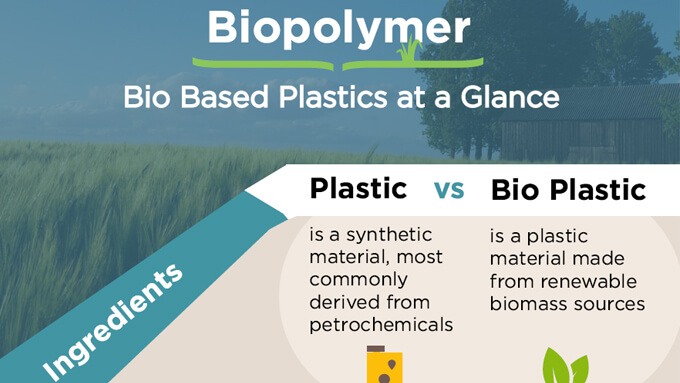
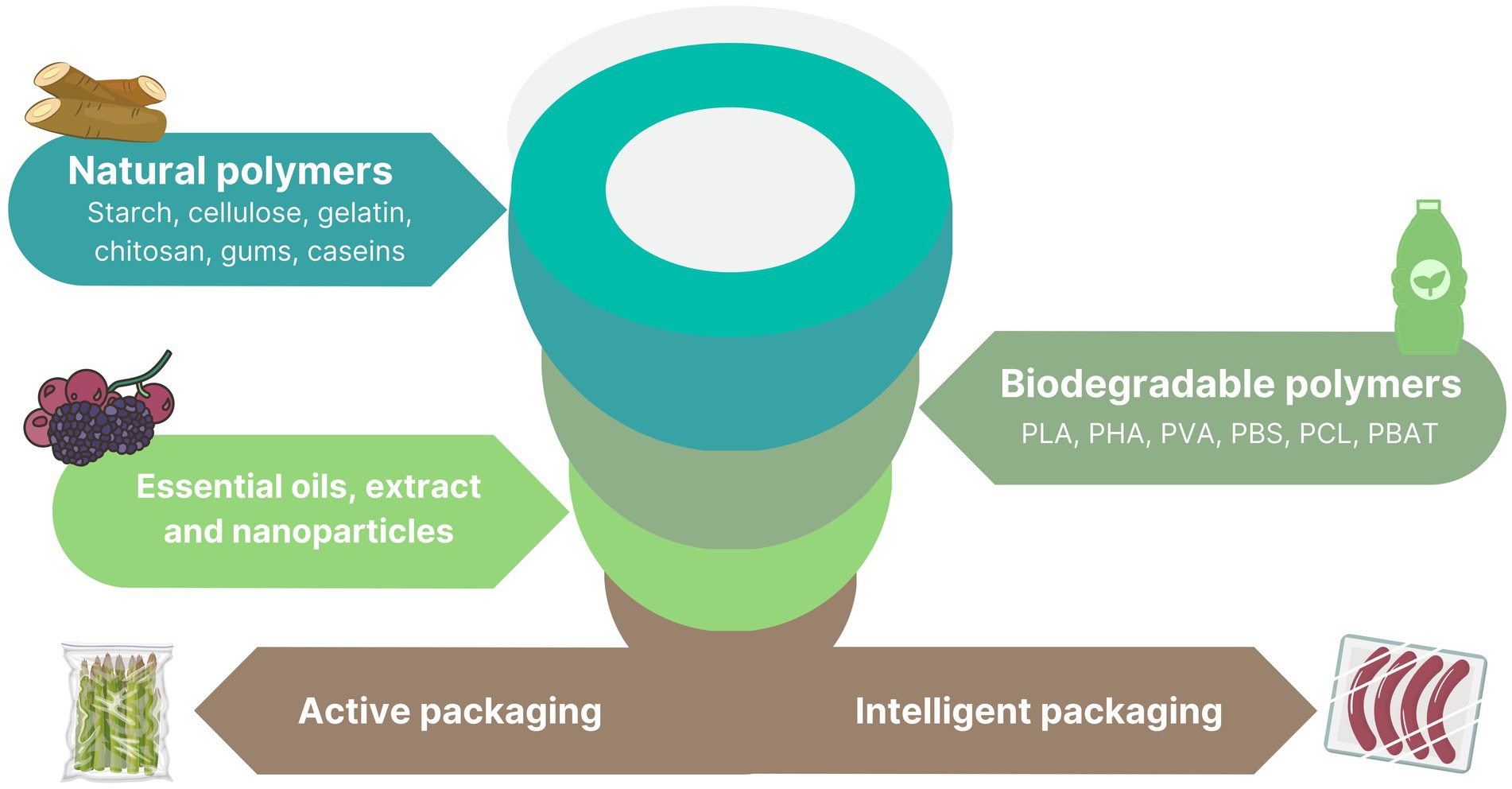
Biopolymers, simply put, are polymers produced by living organisms. They're generated from renewable biomass sources like corn starch, sugarcane, vegetable oils, and even microorganisms.
Unlike conventional plastics that rely on fossil fuels, biopolymers offer a pathway towards a more circular and sustainable economy. The appeal lies in their biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint.
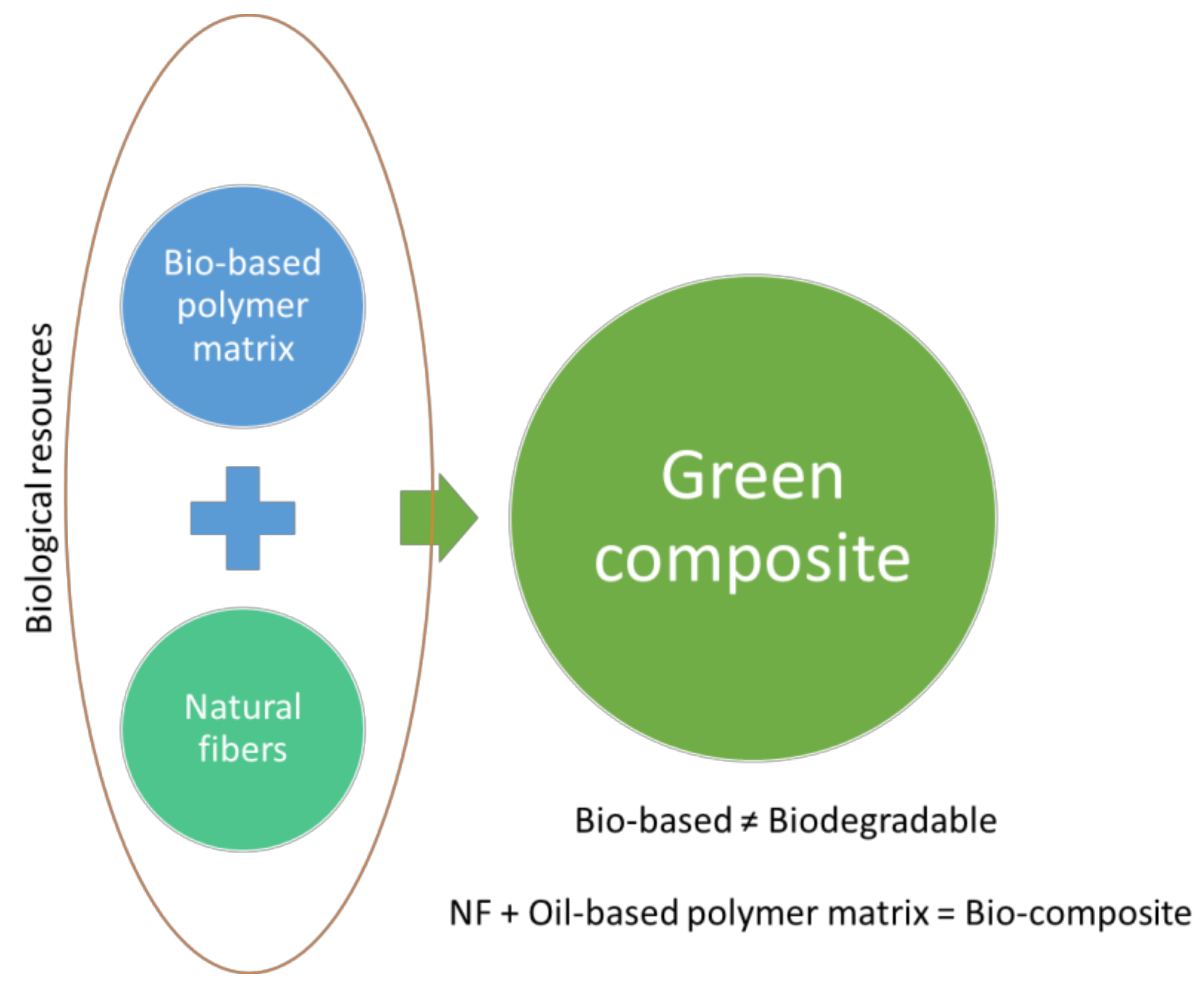
There are three main categories: Polymers directly extracted from biomass (e.g., starch, cellulose), polymers produced by fermentation processes (e.g., polyhydroxyalkanoates - PHAs), and polymers synthesized chemically from bio-based monomers (e.g., polylactic acid - PLA).
The Manufacturing Process
The production of biopolymers varies depending on the specific type. For example, PLA, one of the most common biopolymers, is typically produced through the fermentation of sugar to lactic acid.
This lactic acid is then polymerized into PLA, which can be further processed into various forms like films, fibers, and molded parts. Other biopolymers like PHAs are produced by bacteria through fermentation processes.
These bacteria accumulate PHAs as energy storage materials. The polymer is then extracted from the bacterial cells.
Applications Across Industries
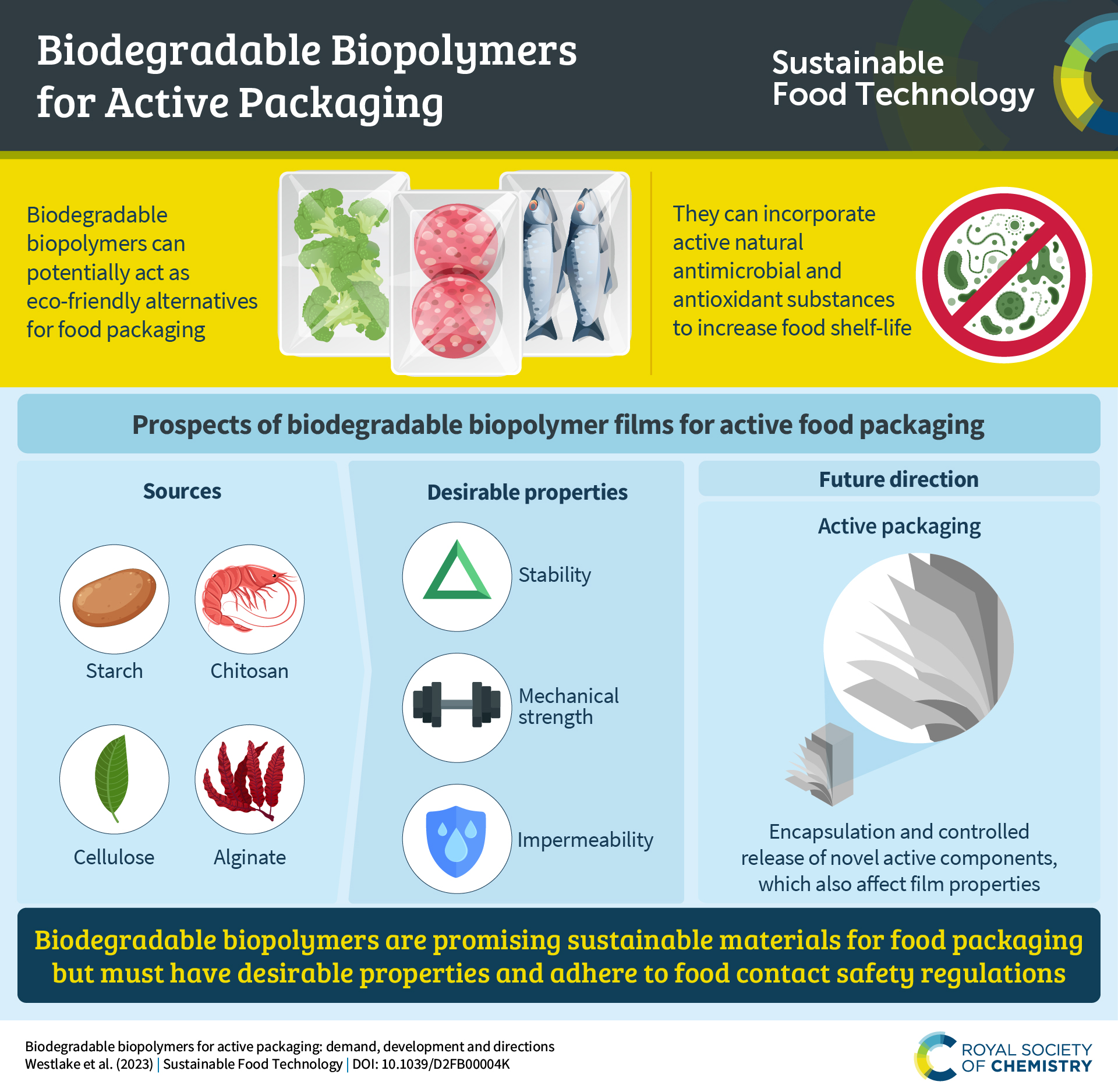
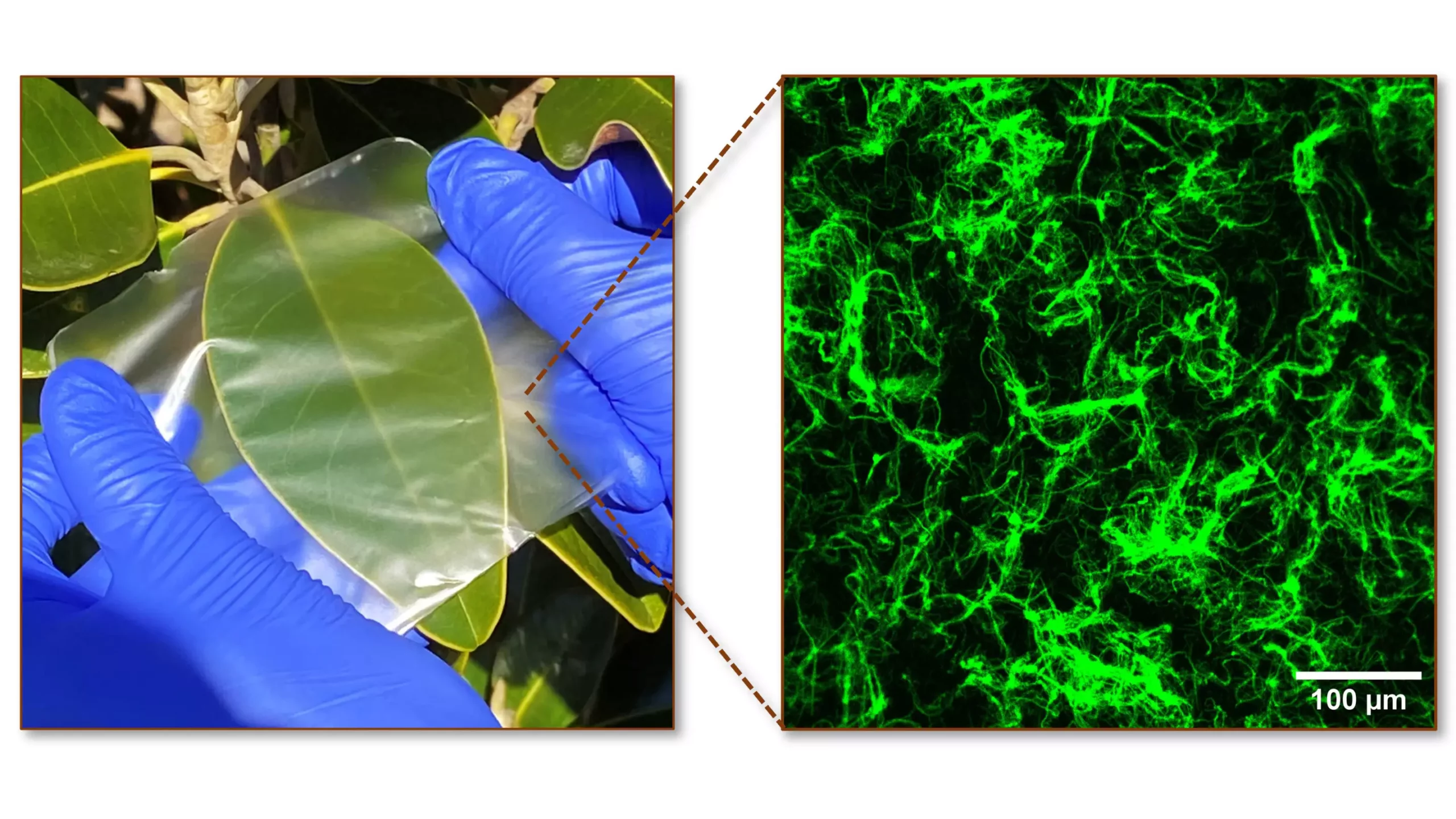
The versatility of biopolymers has led to their adoption in a wide range of industries. Packaging is a major application, with biopolymers being used to create compostable food containers, films, and bags.
In agriculture, they are used for mulch films and controlled-release coatings for fertilizers. The biomedical field utilizes biopolymers for drug delivery systems, sutures, and tissue engineering scaffolds.
Furthermore, the automotive and textile industries are exploring the use of biopolymers in components and fibers, respectively.
Environmental Benefits
The primary advantage of biopolymers is their potential to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. By utilizing renewable resources, they contribute to lowering greenhouse gas emissions associated with plastic production.
Many biopolymers are biodegradable or compostable under specific conditions. This offers a solution to the problem of plastic waste accumulation in landfills and oceans.
However, it's important to note that biodegradability depends on the specific type of biopolymer and the surrounding environmental conditions, like temperature and humidity.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite their potential, biopolymers face certain challenges. Production costs are often higher compared to conventional plastics, making them less competitive in some markets.
The performance characteristics of some biopolymers may not fully match those of traditional plastics, limiting their use in certain demanding applications. The infrastructure for proper composting and disposal of biodegradable biopolymers is still lacking in many regions.
However, ongoing research and development are addressing these challenges. Innovations in production processes are reducing costs, while advancements in material science are improving the performance of biopolymers.
The Future of Biopolymers
The market for biopolymers is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by increasing environmental awareness and stricter regulations on plastic waste. Governments and organizations worldwide are promoting the use of bio-based materials through incentives and policies.
Consumer demand for sustainable products is also fueling the growth of the biopolymer industry. Collaboration between researchers, manufacturers, and policymakers is crucial to overcome the existing challenges and unlock the full potential of biopolymers.
Ultimately, the widespread adoption of biopolymers represents a significant step towards a more sustainable and circular economy, reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigating the environmental impact of plastic waste.
Investing in research and infrastructure is crucial to facilitate this transition and ensure a future where biopolymers play a central role in a greener and more responsible world.