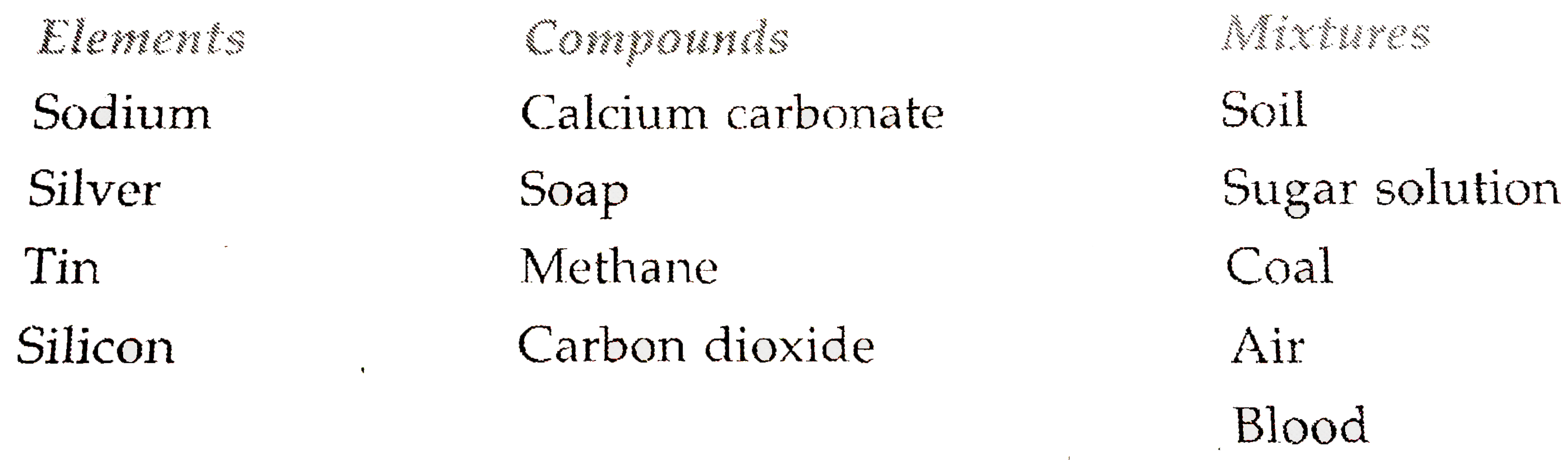Blood Is A Compound Or Mixture

Urgent reports confirm a critical re-evaluation of blood's fundamental classification. Scientific consensus is shifting: blood, long considered a compound, is definitively a mixture.
This paradigm shift, affecting fields from medicine to forensics, necessitates immediate adjustments in research, diagnostics, and educational curricula. The implications are far-reaching, demanding swift action from scientific bodies and healthcare institutions globally.
The Defining Evidence
For decades, blood was often simplified in textbooks and introductory materials as a compound, particularly in the context of basic chemistry. This was due to its seemingly uniform composition and vital role in biological systems.
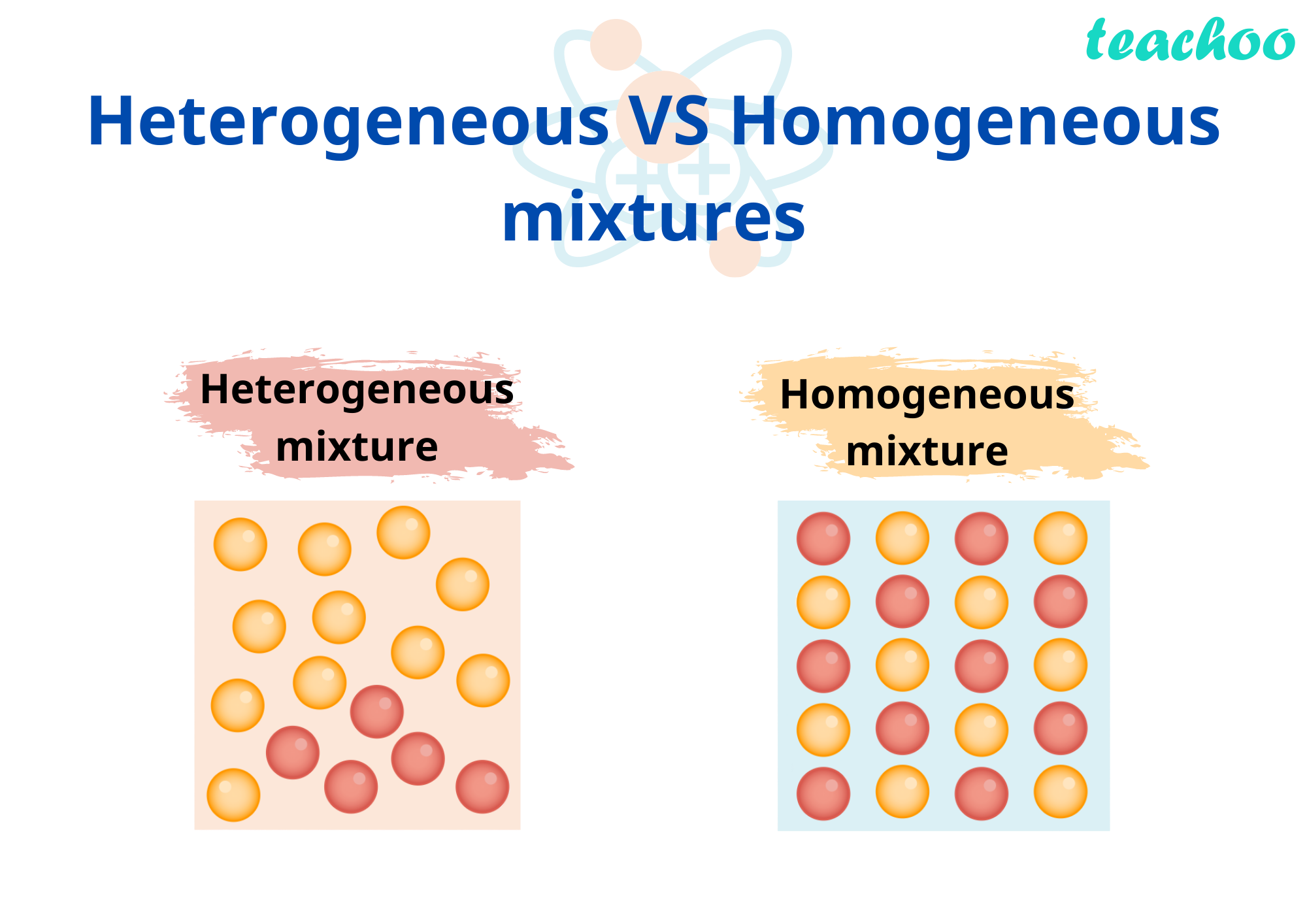
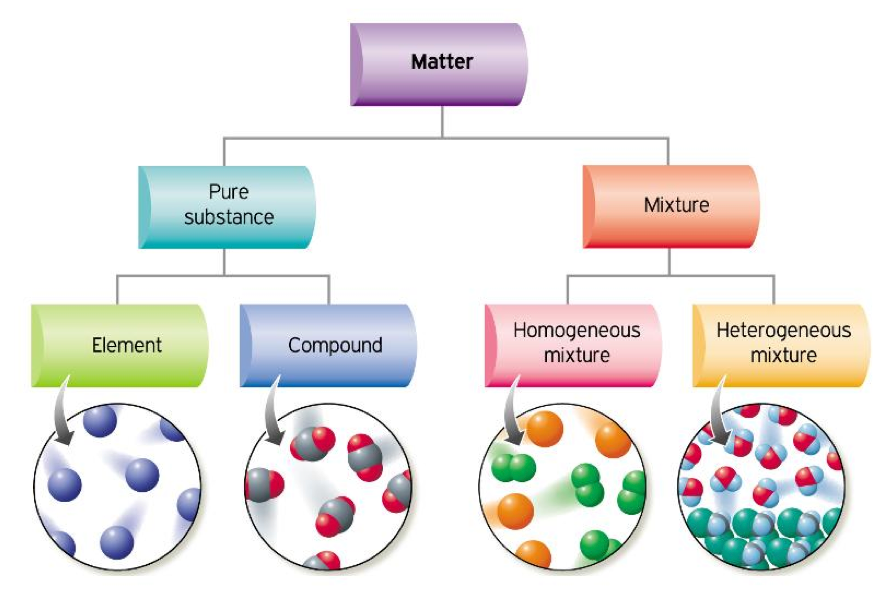
However, increasingly sophisticated analytical techniques have proven this to be inaccurate. Blood is demonstrably a complex mixture composed of distinct components that retain their individual properties.
What are the components?
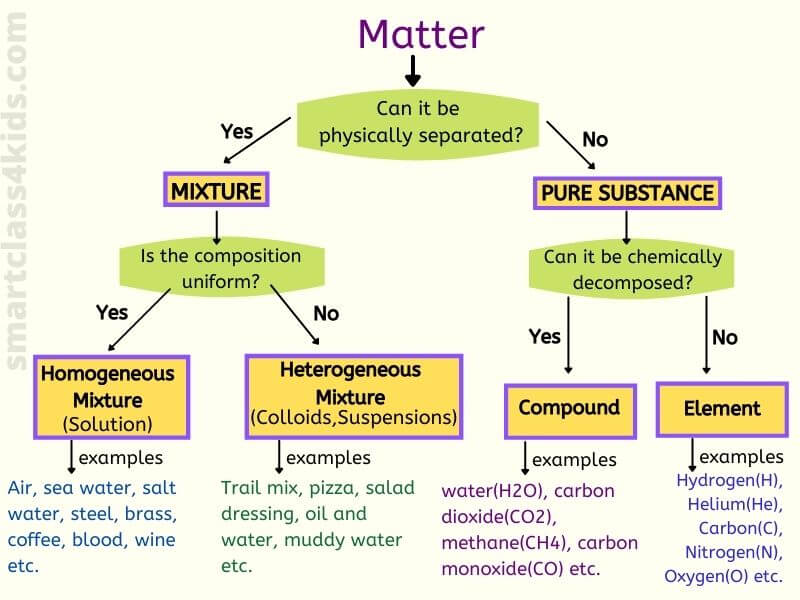
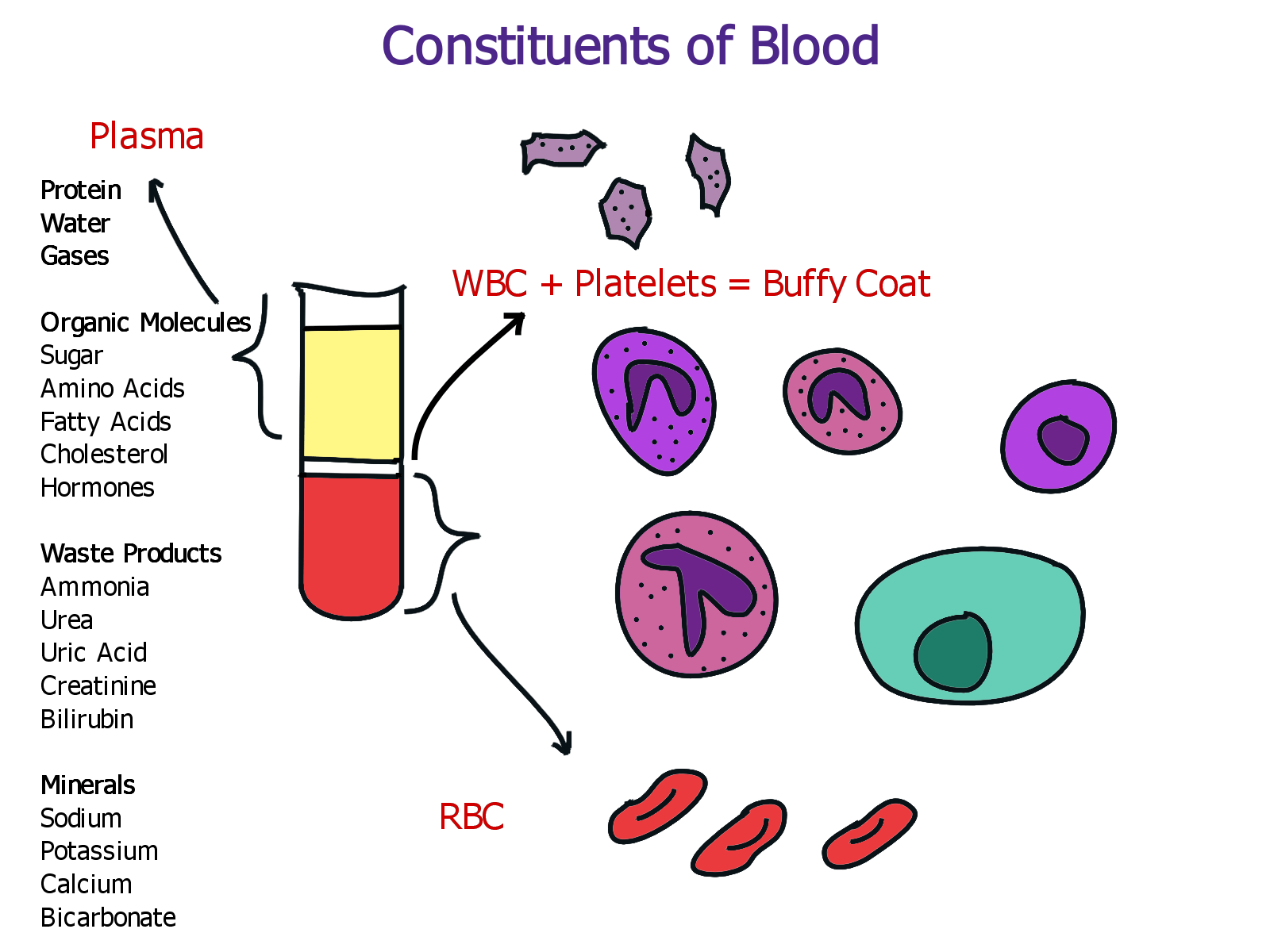
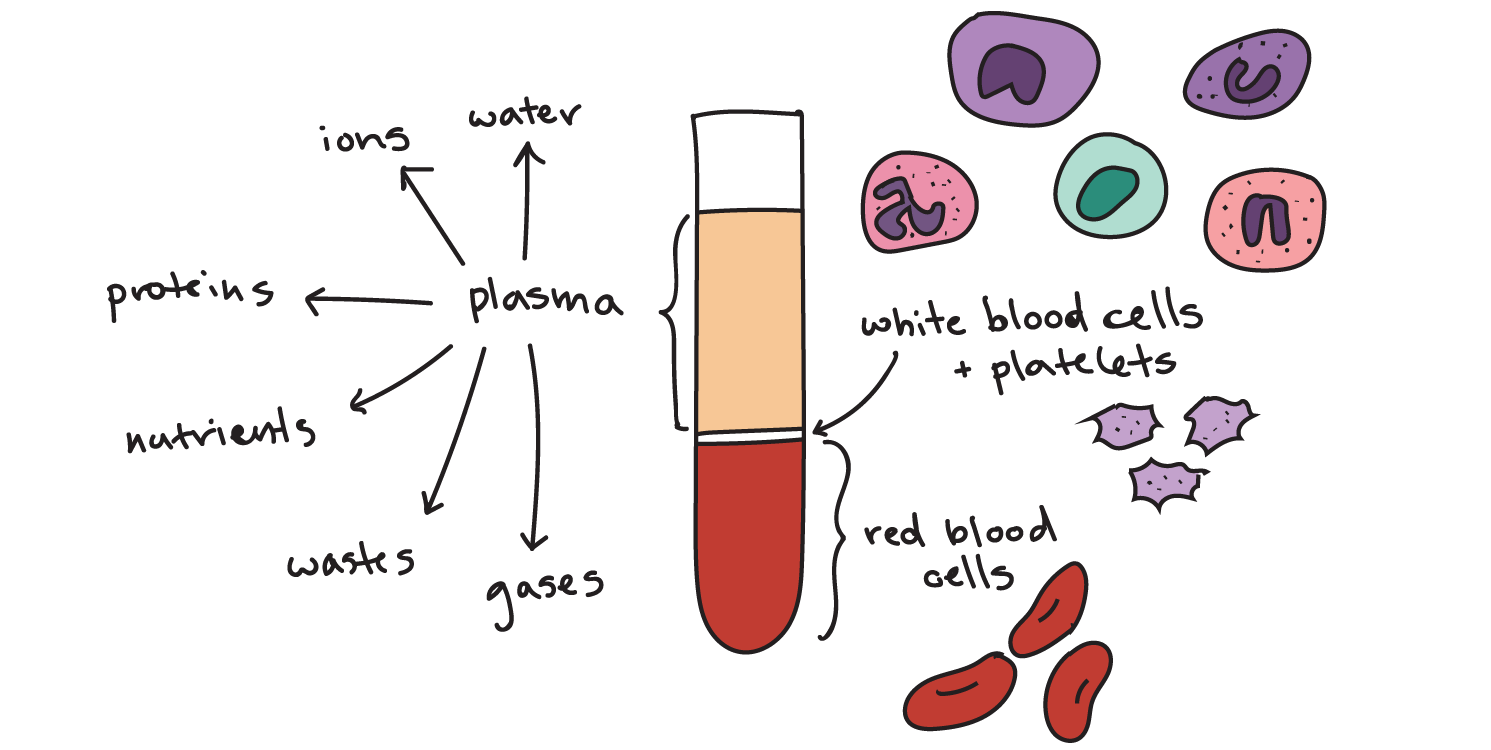
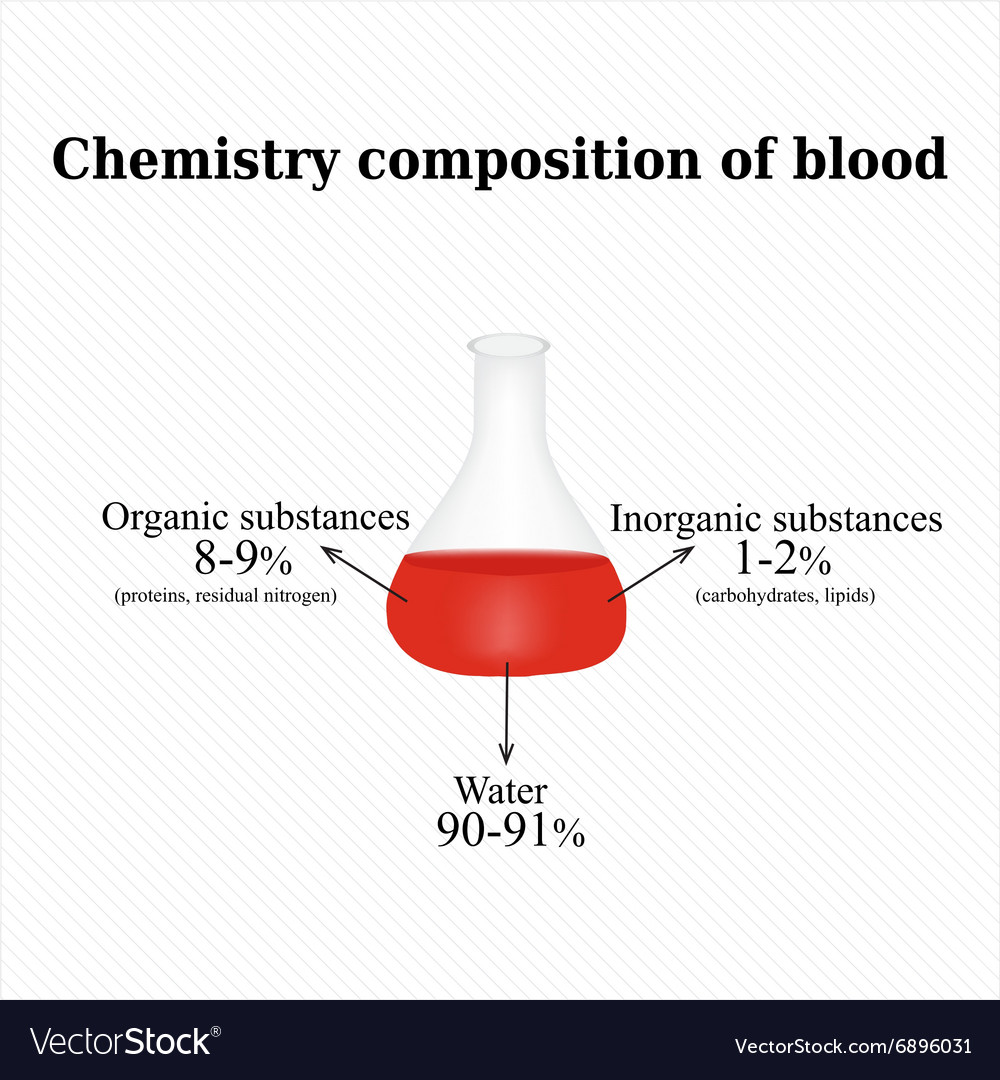
Blood is a heterogeneous mixture composed of various components. These include plasma, red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes).
Each component has a specific function and can be physically separated without altering the fundamental nature of the substances involved.
Plasma, the liquid component, is itself a mixture of water, salts, proteins, and dissolved substances. Red blood cells transport oxygen, while white blood cells are crucial for immune function. Platelets are responsible for blood clotting.
Why the Misconception?
The initial misclassification likely stemmed from the relative homogeneity of blood upon visual inspection. Unlike visibly heterogeneous mixtures like sand and water, blood appears uniform to the naked eye.
Furthermore, early chemical analyses were limited in their ability to differentiate between the complex array of substances present. Improved technology has allowed scientists to isolate and characterize each component with greater precision.
Advanced techniques like mass spectrometry and flow cytometry can now identify and quantify the different cells and molecules within blood, clearly demonstrating its mixed nature.
Impact on Medical Practices
The reclassification has immediate relevance to medical practices. Blood transfusions rely on the ability to separate and administer specific blood components to patients based on their individual needs.
This process is only effective because blood is a mixture, allowing for the selective delivery of red blood cells, platelets, or plasma without altering the fundamental properties of the transfused material.
Diagnostic tests also depend on this understanding. Complete blood counts (CBCs) measure the quantities of different blood cells to identify abnormalities indicative of various diseases.
Forensic Science Implications
The forensic science community is also affected by this clarification. Blood spatter analysis and DNA profiling are critical tools in criminal investigations, relying on the distinct characteristics of blood's components.
The ability to isolate and analyze DNA from blood samples depends on the fact that DNA remains intact within the white blood cells. This separation would be impossible if blood were a true compound.
The understanding that blood is a mixture allows forensic scientists to accurately interpret evidence and reconstruct events at crime scenes.
Global Response and Future Directions
Scientific organizations are now urging educational institutions to update their curricula to reflect the accurate classification of blood. Textbooks and online resources need to be revised to reflect the updated understanding.
International scientific conferences are planning dedicated sessions to discuss the implications of this reclassification and to explore new research avenues. Funding agencies are expected to prioritize research projects that leverage the understanding of blood as a mixture to develop novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) is reviewing the current definitions of compounds and mixtures to ensure consistency and clarity across scientific disciplines.
Further research will focus on developing more sophisticated methods for analyzing blood components. This will lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses of diseases and improved treatments for a wide range of medical conditions.
Immediate steps include widespread dissemination of the updated information to healthcare professionals, educators, and the general public. Transparency and accuracy are critical to ensure that this fundamental shift in understanding translates into tangible benefits for society.


/GettyImages-185085872-58a07ebc5f9b58819cba33ba.jpg)

![Blood Is A Compound Or Mixture Examples of Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures [ANSWERED] – Dear Learners](https://dearlearners.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/is-blood-an-element-compound-or-mixture_-1-768x480.jpg)