Bv And Yeast At The Same Time

Experiencing symptoms like itching, burning, and unusual discharge in the vaginal area can be unsettling. Many women are familiar with either bacterial vaginosis (BV) or yeast infections, but the possibility of experiencing both simultaneously raises concerns and questions. Understanding the intricacies of this co-occurrence is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
This article explores the phenomenon of co-existing BV and yeast infections, examining the potential causes, diagnostic challenges, and appropriate management strategies. It aims to provide clear, factual information based on current medical understanding and research.
Understanding Bacterial Vaginosis and Yeast Infections
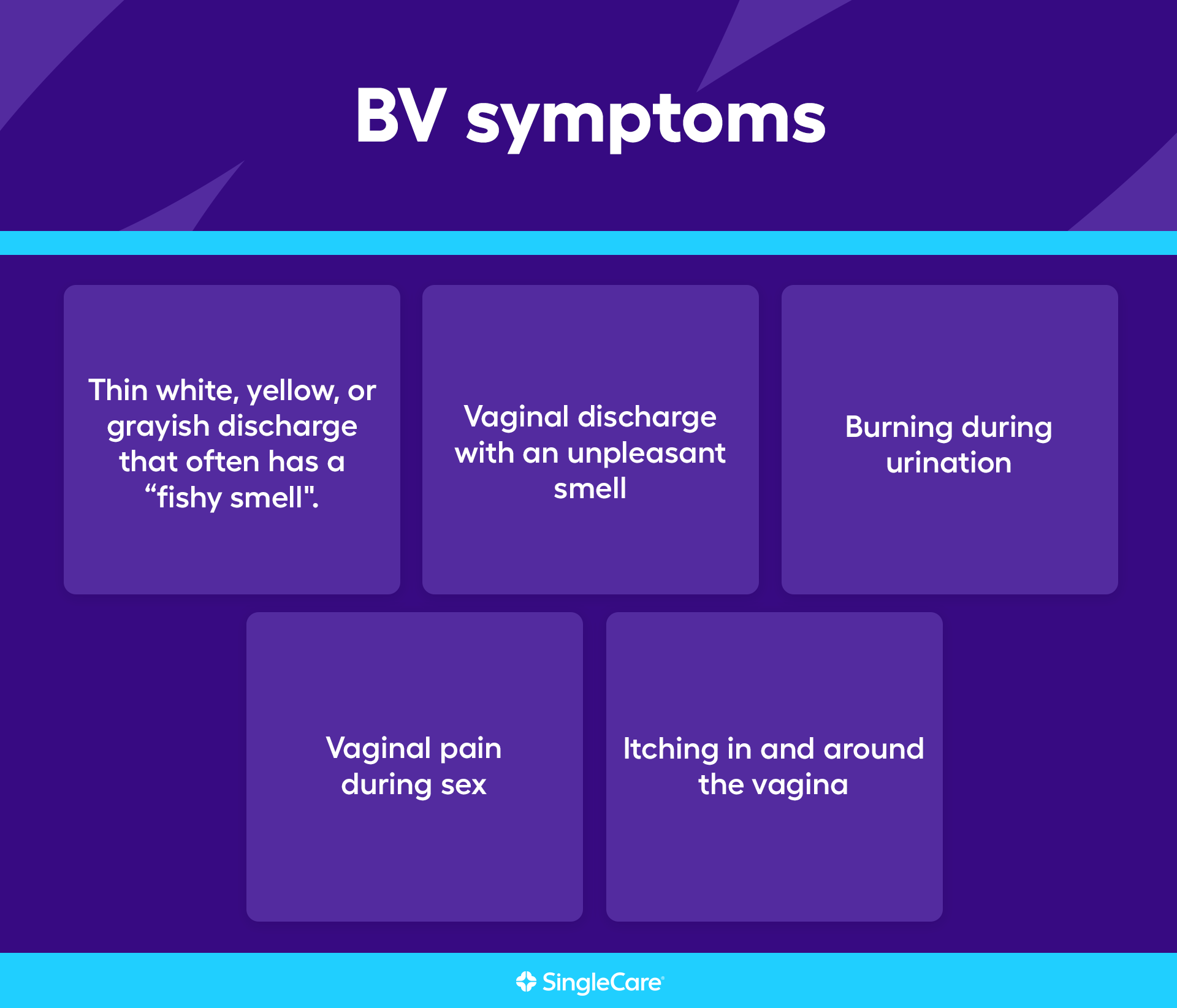
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a common vaginal condition caused by an imbalance in the vaginal bacteria. Normally, lactobacilli, "good" bacteria, dominate the vaginal environment. In BV, these are replaced by other bacteria, leading to an overgrowth of anaerobic bacteria.
Yeast infections, on the other hand, are typically caused by an overgrowth of a fungus called Candida, most commonly Candida albicans. These infections cause inflammation and irritation in the vagina and vulva.
The Potential for Co-occurrence
While seemingly distinct, BV and yeast infections can, in fact, occur together. Several factors can contribute to this co-occurrence.
Changes in the vaginal environment can disrupt the balance, potentially creating conditions favorable for both BV and Candida. These changes can be triggered by various factors, including antibiotic use, douching, and hormonal fluctuations, like those associated with menstruation or pregnancy.
Antibiotics, while targeting specific bacterial infections, can inadvertently kill beneficial bacteria, like lactobacilli. This can create an opportunity for both the bacteria associated with BV and Candida to proliferate.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), BV increases a woman's susceptibility to other infections. This can include sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and potentially also create a more hospitable environment for Candida overgrowth.
Diagnostic Challenges
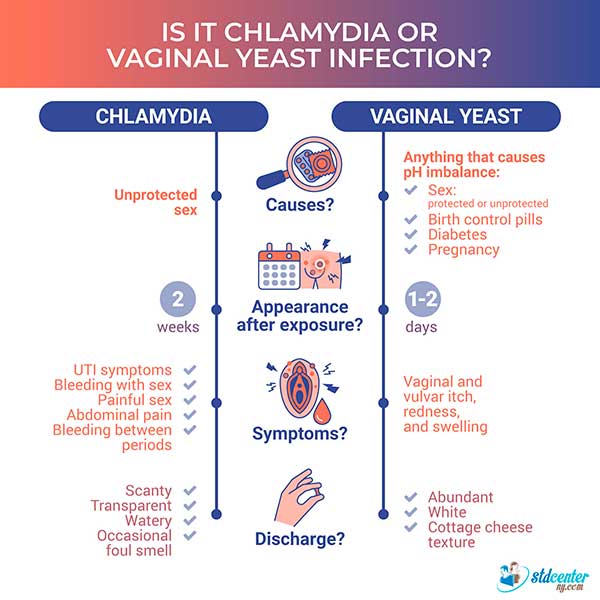
Diagnosing both BV and a yeast infection simultaneously can be challenging because the symptoms can overlap. Both conditions can cause vaginal itching, burning, and discharge.
The discharge associated with BV is typically thin, watery, and grayish-white with a distinct fishy odor. A yeast infection discharge is more often thick, white, and resembles cottage cheese.
Given the potential for confusion, it's crucial to seek professional medical evaluation for accurate diagnosis. A healthcare provider can perform a pelvic exam and lab tests, such as a vaginal fluid sample analysis, to identify the specific organisms involved.
"Self-diagnosing and treating vaginal infections can be problematic, as it may lead to incorrect treatment and potentially worsen the condition," warns Dr. Jane Doe, a gynecologist at University Hospital.
Treatment Strategies
Treating co-existing BV and yeast infections requires a targeted approach that addresses both conditions separately. Typically, this involves using different medications simultaneously or sequentially.
BV is often treated with antibiotics, such as metronidazole or clindamycin, which can be administered orally or as a vaginal gel or cream. Yeast infections are typically treated with antifungal medications, such as fluconazole (oral) or clotrimazole (topical cream or suppository).
It's essential to follow the healthcare provider's instructions carefully and complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve. Failure to do so can lead to recurrence or antibiotic resistance.
Prevention and Management
While preventing the simultaneous occurrence of BV and yeast infections can be challenging, certain lifestyle modifications can help maintain a healthy vaginal environment. Avoiding douching is crucial, as it disrupts the natural balance of bacteria.
Using unscented soaps and avoiding harsh feminine hygiene products can also help prevent irritation. Wearing breathable cotton underwear and avoiding tight-fitting clothing can improve airflow and reduce moisture.
Some studies suggest that probiotics, particularly those containing lactobacilli, may help restore and maintain a healthy vaginal flora. However, more research is needed to determine the effectiveness of specific probiotic strains and dosages.
Impact and Significance
The concurrent occurrence of BV and yeast infections can significantly impact a woman's quality of life. The persistent symptoms can cause discomfort, anxiety, and disruption of daily activities.
Untreated BV can increase the risk of more serious complications, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and preterm labor in pregnant women. Therefore, prompt and accurate diagnosis and treatment are essential.
Raising awareness about the possibility of co-existing infections and encouraging women to seek professional medical advice can improve outcomes and prevent potential complications.
In conclusion, experiencing both BV and a yeast infection at the same time is possible and requires careful diagnosis and tailored treatment. By understanding the factors contributing to this co-occurrence and adopting preventive measures, women can take proactive steps to maintain vaginal health and well-being.
.jpg)