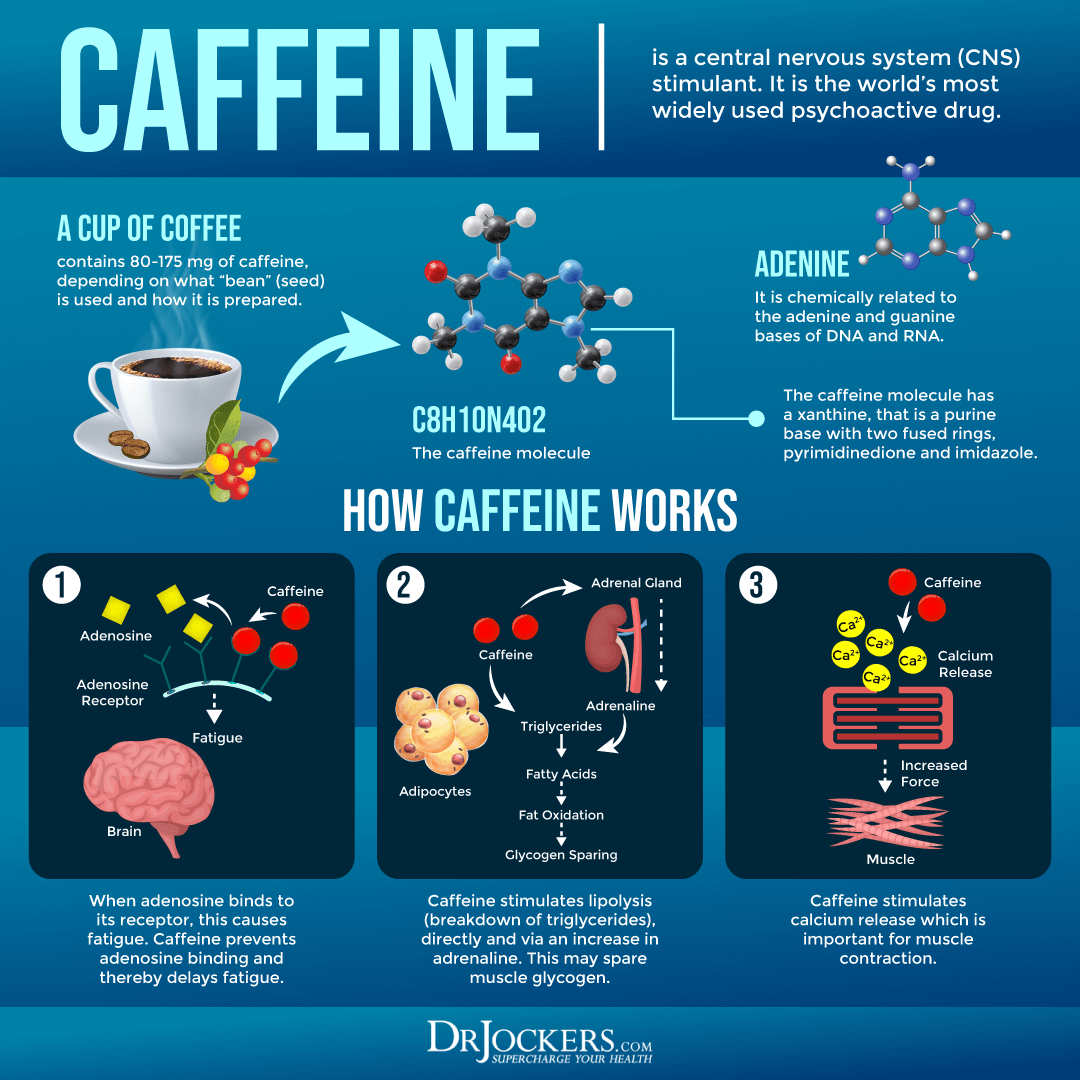
Caffeine Anhydrous Vs Green Coffee Bean Extract
Imagine stepping into a bustling coffee shop, the aroma of freshly brewed beans filling the air. Sunlight streams through the window, illuminating the swirling steam rising from a cup. A woman sits near the window. She is typing away at her laptop. She takes a sip of her latte. It fuels her focus as she tackles her work. This scene, so familiar to many, speaks to the widespread appeal of caffeine. However, the world of caffeine is far more complex than your average morning cup, branching into various forms with different origins and effects. We will explore the difference between caffeine anhydrous and green coffee bean extract.
Caffeine anhydrous and green coffee bean extract are two caffeine sources frequently found in dietary supplements and energy drinks. While both aim to deliver the stimulating effects of caffeine, their composition, processing, and potential health impacts differ significantly. Understanding these nuances is crucial for consumers seeking to make informed choices about their caffeine intake.
The Buzz Behind Caffeine Anhydrous
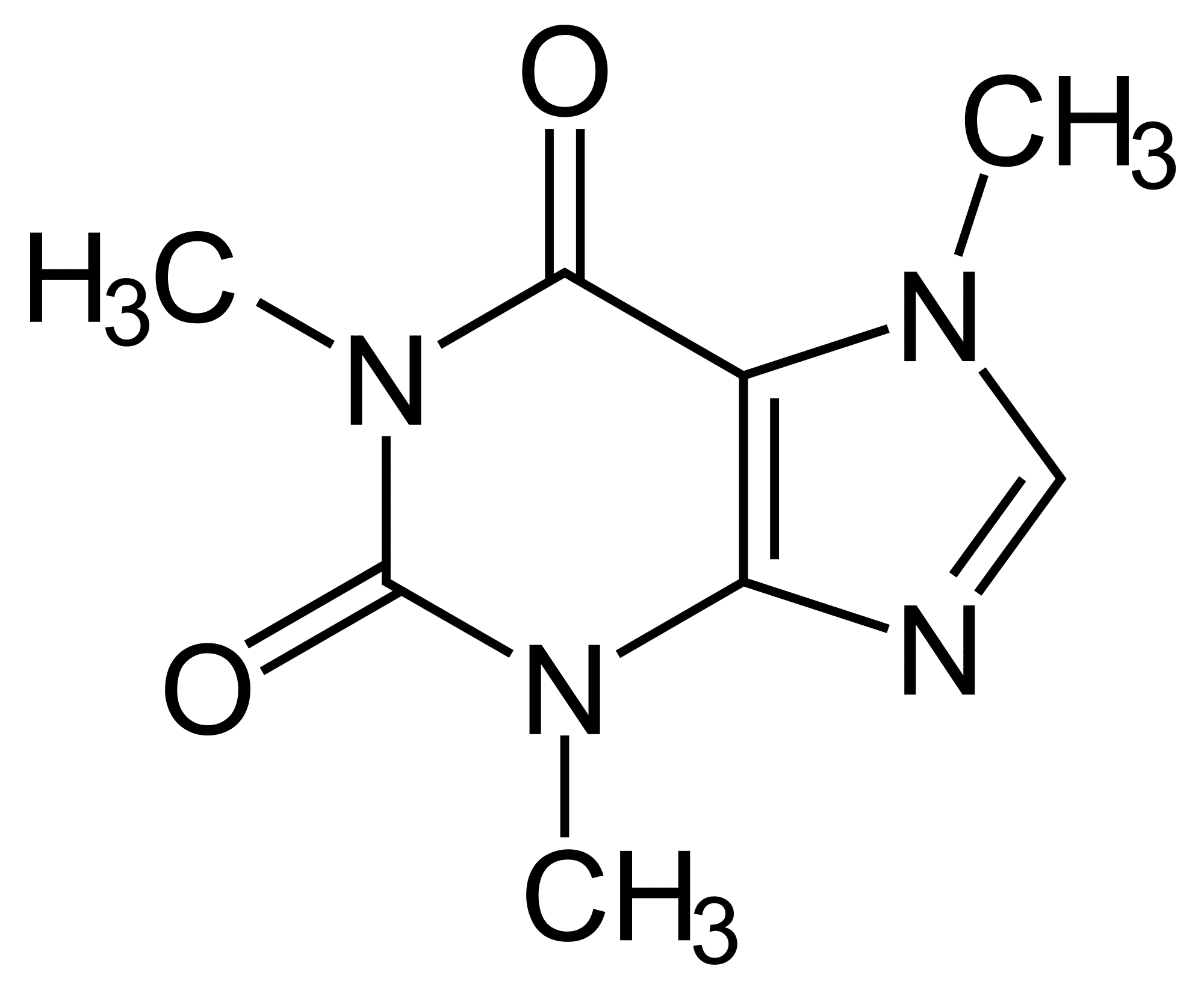
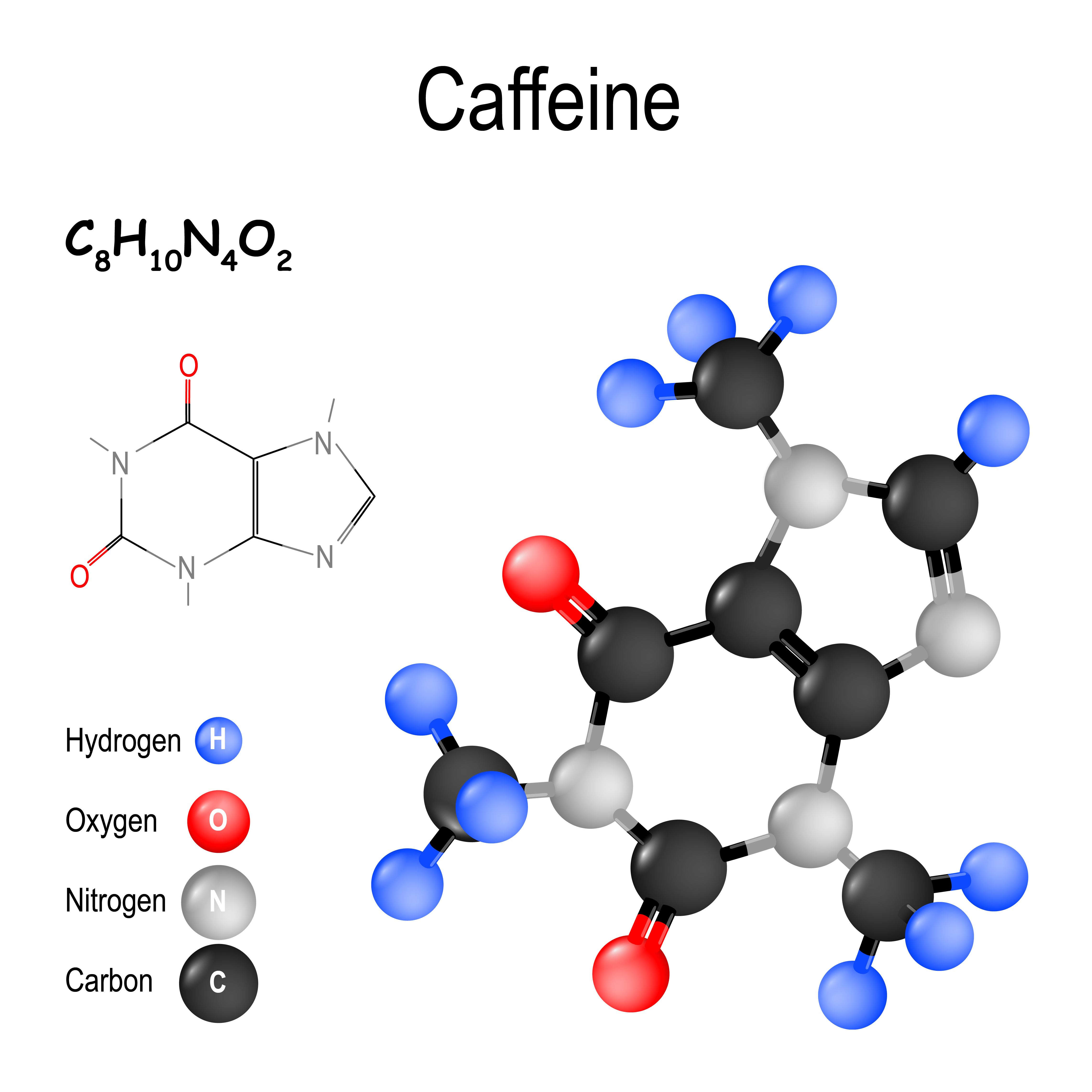
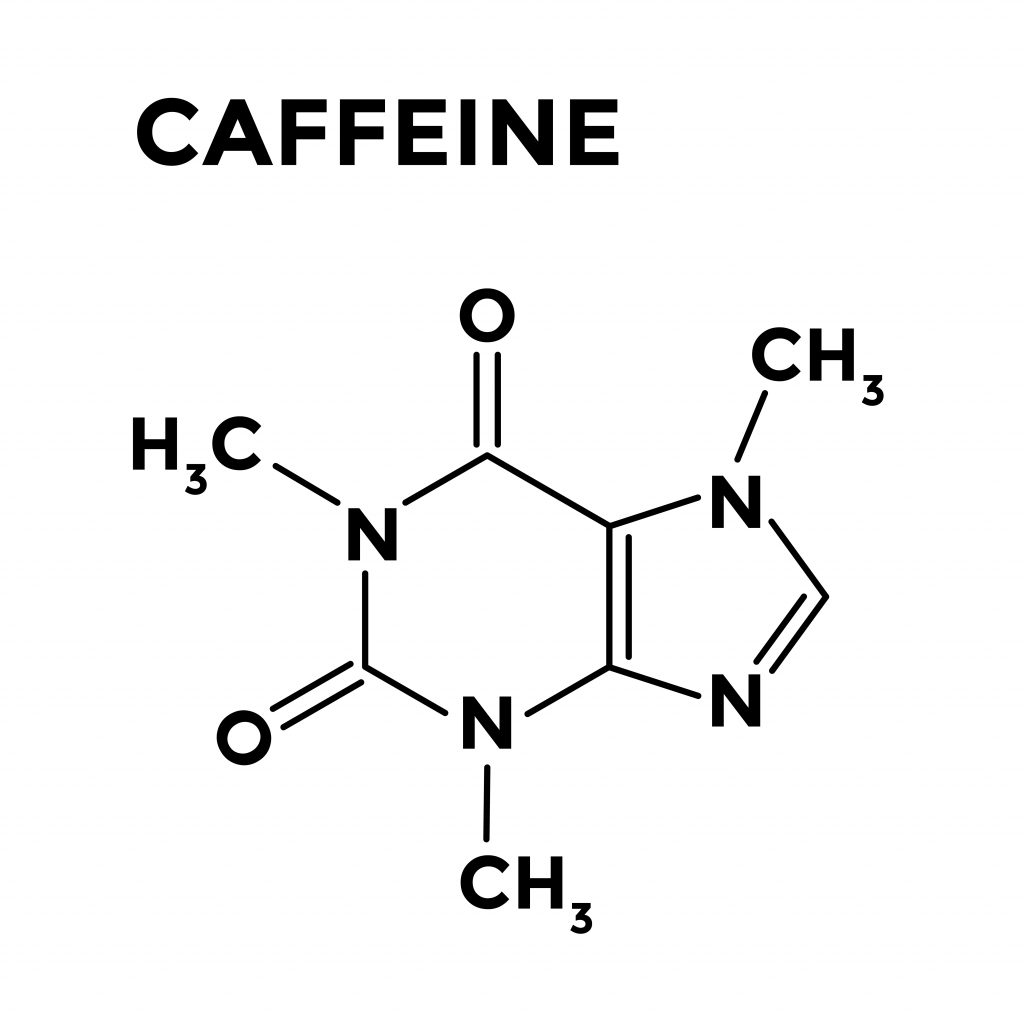
Caffeine anhydrous is a dehydrated form of caffeine. It is derived from various sources, including coffee beans and tea leaves. It means "without water." The dehydration process concentrates the caffeine, resulting in a potent, pure powder.
This concentrated form is favored for its consistent dosage and rapid absorption rate. It is widely used in pre-workout supplements, energy drinks, and weight loss pills. The speed and potency of caffeine anhydrous provide a quick energy boost and enhanced alertness.
The creation of caffeine anhydrous involves extracting caffeine from its natural sources and then dehydrating it to remove any remaining water. This process creates a highly concentrated powder, typically around 99% pure caffeine. The extraction methods can vary, including using solvents like ethyl acetate or supercritical carbon dioxide.
Because it's so potent, accurately measuring dosage is crucial when using caffeine anhydrous. The lack of water allows for a more precise caffeine content per serving. This makes it easier for manufacturers to formulate products with specific energy-boosting effects. A single gram of caffeine anhydrous contains approximately 1000mg of caffeine.
Unveiling Green Coffee Bean Extract
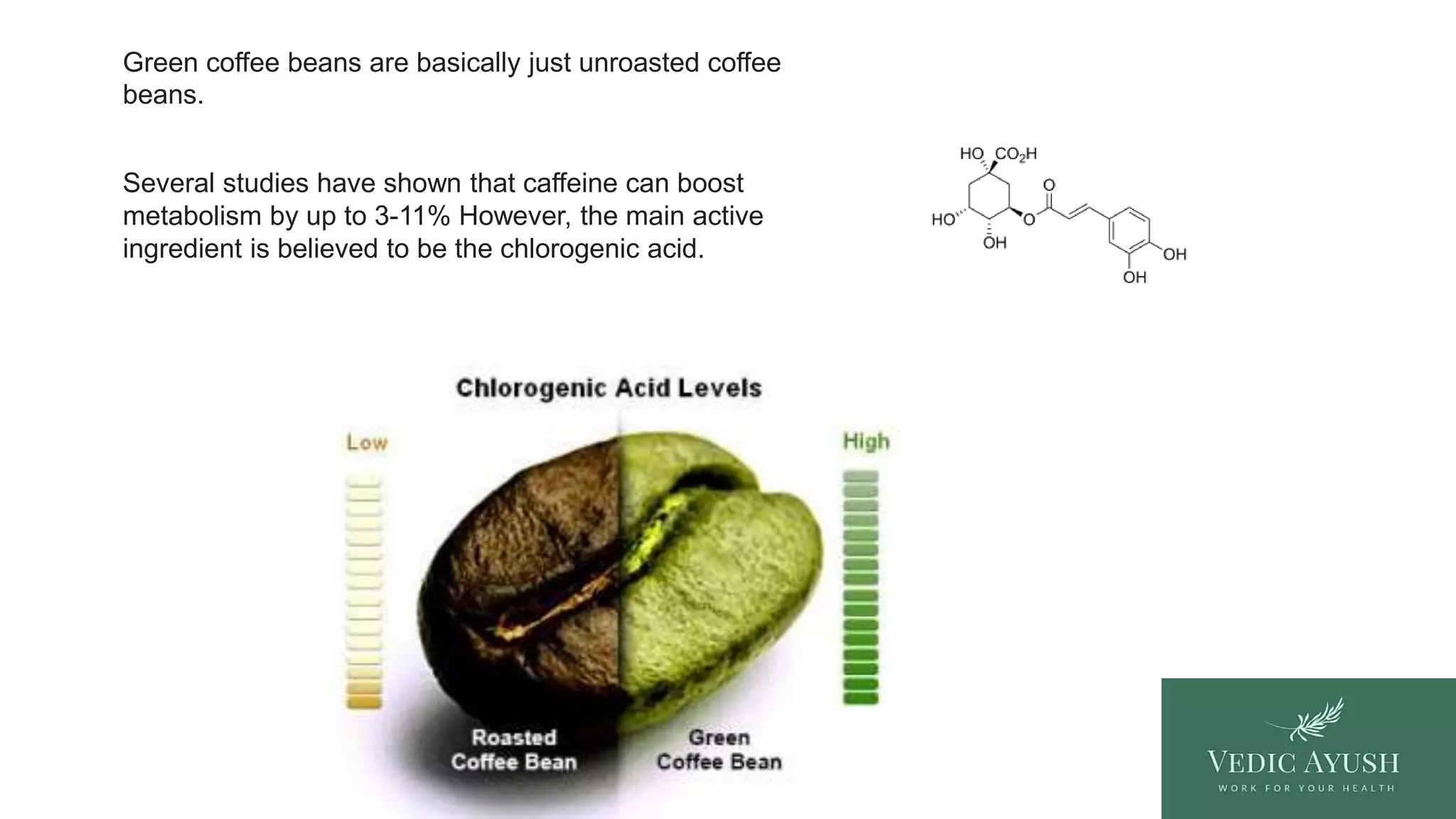
Green coffee bean extract is derived from unroasted coffee beans. These beans contain a wealth of chlorogenic acids. These are powerful antioxidants that are believed to have numerous health benefits. The unroasted state is vital to preserving these acids, which are largely lost during the roasting process.
Unlike the immediate energy surge associated with caffeine anhydrous, green coffee bean extract offers a more sustained and gradual release of caffeine. It often promoted for its potential weight management benefits and antioxidant properties.
The extraction process for green coffee bean extract typically involves soaking the unroasted beans in water or other solvents to draw out the desired compounds, including caffeine and chlorogenic acids. The extract is then concentrated and dried to create a powder or liquid form.
Green coffee bean extract's caffeine content is naturally lower than that of caffeine anhydrous. This means the stimulating effects are often milder and more sustained. The presence of chlorogenic acids adds another layer of complexity. These acids have been studied for their potential to impact glucose metabolism and fat absorption.
Comparing Effects and Benefits
The primary similarity between caffeine anhydrous and green coffee bean extract is their caffeine content. Both provide the stimulating effects that caffeine is known for, such as increased alertness, reduced fatigue, and enhanced cognitive function. However, the ways in which they deliver these effects differ considerably.
Caffeine anhydrous delivers a rapid and powerful energy surge, making it ideal for activities that require intense focus and physical exertion. Its quick absorption rate means users often feel the effects within minutes. It is a popular choice for athletes, students, and anyone needing an immediate boost.
Green coffee bean extract offers a more gradual and sustained release of caffeine. This can be beneficial for those seeking a gentler energy boost without the jitters or crash associated with high doses of caffeine. The chlorogenic acids may also contribute to its health benefits. These benefits include improved blood sugar control and antioxidant protection.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While both caffeine anhydrous and green coffee bean extract are generally considered safe for consumption, they can cause side effects, particularly when taken in high doses. The side effects include anxiety, insomnia, digestive issues, and increased heart rate.
Caffeine anhydrous's potency increases the risk of adverse effects. Overconsumption can lead to more severe issues, such as heart palpitations, high blood pressure, and even caffeine toxicity. It is important to adhere strictly to recommended dosages to minimize these risks.
Green coffee bean extract, with its lower caffeine concentration, generally poses a lower risk of severe side effects. However, some individuals may still experience digestive discomfort or allergic reactions. The long-term effects of chlorogenic acids are still being studied.
Making Informed Choices
Choosing between caffeine anhydrous and green coffee bean extract depends on individual needs and preferences. If you seek a rapid and potent energy boost for workouts or intense focus, caffeine anhydrous might be the better option. However, it's vital to approach it with caution and adhere to recommended dosages.
If you prefer a gentler, more sustained energy lift and are interested in the potential antioxidant benefits, green coffee bean extract could be a more suitable choice. Its lower caffeine content and additional health-promoting compounds make it an appealing alternative for those sensitive to caffeine or seeking broader health benefits.
Ultimately, the key is to research thoroughly, consult with a healthcare professional if needed, and listen to your body's response. Understanding the nuances of each form of caffeine allows consumers to make informed decisions that align with their health goals and lifestyle.
The Future of Caffeine Consumption
As research continues to uncover the complexities of caffeine and its various forms, we can expect to see further innovation in the way caffeine is extracted, processed, and consumed. New delivery methods, personalized dosages, and combinations with other beneficial compounds may become more prevalent. It is important to stay informed and adapt our understanding as new findings emerge.
The conversation surrounding caffeine is continually evolving. As consumers become more health-conscious, the demand for natural and sustainable sources of caffeine is likely to grow. Green coffee bean extract, with its antioxidant properties and gentler energy profile, could see increased popularity.
Whether you're reaching for a cup of coffee, a pre-workout supplement, or a dietary aid, understanding the different forms of caffeine empowers you to make informed choices. It allows for a better overall wellness. By embracing knowledge and staying mindful of our bodies' responses, we can harness the benefits of caffeine while minimizing the potential risks.










:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-Lines-Caffeine-Sources-green-horiz-edit-4-32b42be237b84827bf205f003cd0a8dc.jpg)