Can I Take Magnesium Glycinate And Melatonin Together

Sleepless nights plague millions, driving many to explore over-the-counter remedies. Two popular contenders, magnesium glycinate and melatonin, are often touted for their sleep-enhancing properties. The question on many minds: Is it safe, and more importantly, is it effective to take them together?
This article delves into the science behind combining magnesium glycinate and melatonin, examining potential benefits, risks, and expert opinions. It navigates the nuances of dosage, individual variations, and potential interactions, providing a comprehensive guide for those seeking a better night's rest.
Understanding Magnesium Glycinate and Melatonin
Magnesium glycinate is a form of magnesium where magnesium is bound to the amino acid glycine. This chelated form is known for its high bioavailability and gentle impact on the digestive system, making it a preferred choice for supplementation.
Magnesium plays a crucial role in hundreds of bodily functions, including muscle relaxation, nerve function, and blood sugar control. Magnesium deficiency has been linked to sleep disturbances, anxiety, and muscle cramps.
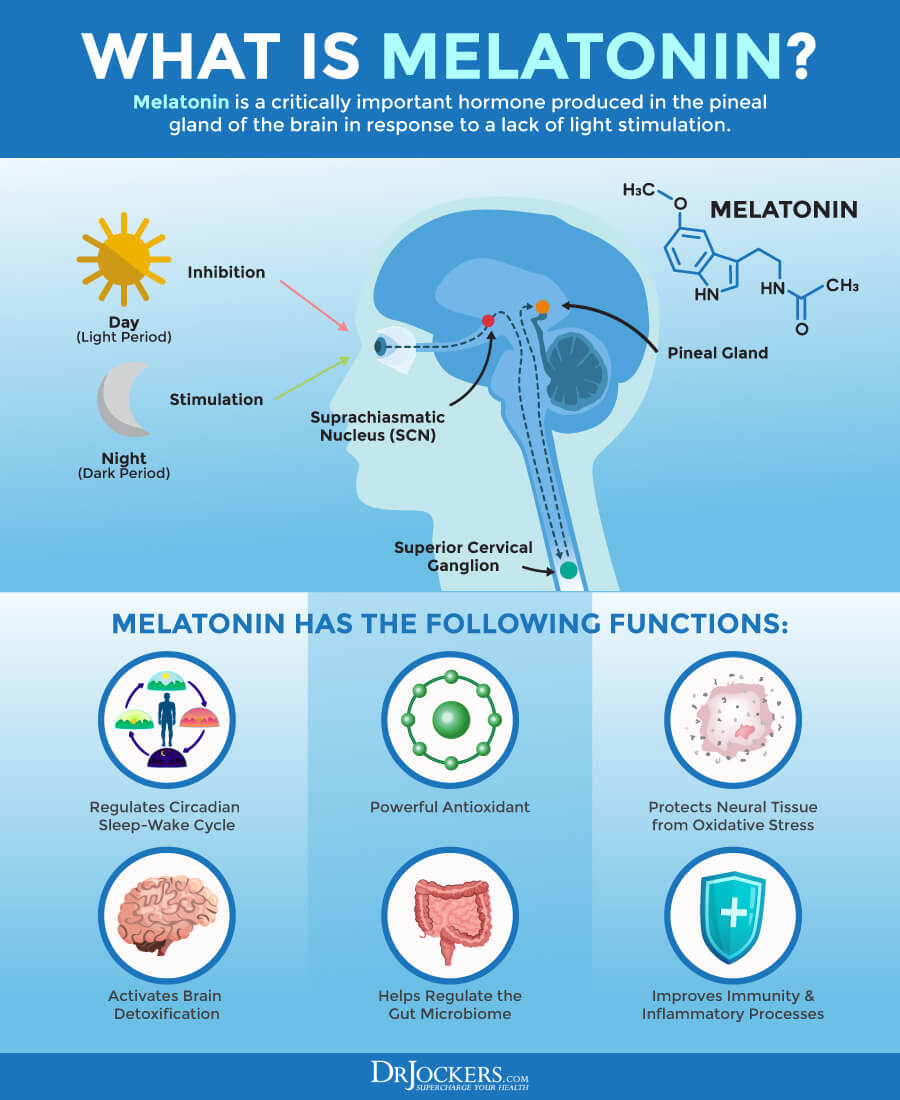
Melatonin, on the other hand, is a hormone naturally produced by the pineal gland in the brain. It regulates the sleep-wake cycle, signaling to the body when it's time to sleep.
Melatonin supplements are commonly used to address jet lag, insomnia, and other sleep disorders. It works by mimicking the body's natural melatonin production, promoting drowsiness and improving sleep quality.
Potential Benefits of Combining Magnesium Glycinate and Melatonin
The rationale behind combining magnesium glycinate and melatonin lies in their complementary mechanisms of action. Magnesium helps to calm the nervous system and relax muscles, while melatonin signals to the brain that it's time to sleep.
Some individuals find that this combination leads to a more restful and deeper sleep. The synergistic effect may be particularly beneficial for those experiencing sleep disturbances due to stress, anxiety, or muscle tension.
Preliminary research suggests that magnesium supplementation can improve sleep quality and reduce insomnia symptoms. Similarly, melatonin has been shown to shorten sleep latency (the time it takes to fall asleep) and increase total sleep time.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While generally considered safe, both magnesium glycinate and melatonin can have side effects. Magnesium glycinate, especially at high doses, can cause diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping.
Melatonin side effects are typically mild and may include drowsiness, headache, dizziness, and nausea. Some individuals also report experiencing vivid dreams or nightmares.
Combining the two substances could potentially amplify these side effects. It's crucial to start with low doses and gradually increase them as needed, monitoring for any adverse reactions.
Expert Opinions and Recommendations
Many healthcare professionals acknowledge the potential benefits of combining magnesium glycinate and melatonin for sleep. However, they emphasize the importance of individual assessment and personalized recommendations.
Dr. Anya Sharma, a sleep specialist, states, "Magnesium glycinate and melatonin can be a helpful combination for some patients struggling with sleep. However, it's essential to rule out underlying medical conditions and address any lifestyle factors that may be contributing to sleep problems."
She further adds, "It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have any pre-existing medical conditions or are taking other medications."
Always remember to inform your doctor about all supplements you are taking.
Registered Dietitian, Sarah Chen, highlights the importance of dietary sources of magnesium. "Before reaching for supplements, prioritize magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Supplementation should be considered only when dietary intake is insufficient."
Dosage and Timing Considerations
The optimal dosage of magnesium glycinate and melatonin varies depending on individual needs and tolerance. A common starting dose for magnesium glycinate is 200-400mg taken 30-60 minutes before bedtime.
Melatonin dosages typically range from 0.3mg to 5mg, also taken 30-60 minutes before bed. It's crucial to start with the lowest effective dose and gradually increase if needed.
It's generally recommended to take both supplements at the same time, approximately 30-60 minutes before bedtime. This allows both substances to work synergistically to promote relaxation and sleepiness.
Potential Interactions and Contraindications
Magnesium can interact with certain medications, including antibiotics, diuretics, and proton pump inhibitors. Melatonin may interact with blood thinners, antidepressants, and immunosuppressants.
Individuals with kidney problems should exercise caution when taking magnesium supplements, as their kidneys may not be able to efficiently excrete excess magnesium. Melatonin is generally not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women due to insufficient research on its safety in these populations.
Always consult with a healthcare professional or pharmacist to check for potential drug interactions before combining magnesium glycinate and melatonin.
The Importance of Lifestyle Factors
While magnesium glycinate and melatonin can be helpful tools for improving sleep, they are not a substitute for healthy sleep habits. Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing the sleep environment are essential for promoting restful sleep.
Avoid caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime, as these substances can interfere with sleep. Regular exercise, stress management techniques, and a balanced diet can also contribute to better sleep quality.
If sleep problems persist despite implementing healthy sleep habits and trying over-the-counter remedies, it's crucial to seek professional help. A healthcare provider can evaluate underlying medical conditions and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Looking Ahead: Future Research
Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of combining magnesium glycinate and melatonin. Clinical trials specifically designed to assess the efficacy and safety of this combination are warranted.
Studies exploring the optimal dosage and timing of these supplements, as well as their potential benefits for specific populations (e.g., older adults, individuals with insomnia), would be valuable.
Ultimately, the decision to take magnesium glycinate and melatonin together should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional, considering individual needs, medical history, and potential risks. The goal is to achieve sustainable and restful sleep through a holistic approach that encompasses both lifestyle modifications and, when appropriate, targeted supplementation.