Can You Eat In A Calorie Deficit While Breastfeeding

Breastfeeding mothers often grapple with the question: Can I lose weight while nourishing my baby? Navigating a calorie deficit during lactation requires careful consideration and expert guidance.
This article explores the safe and effective ways to manage calorie intake while ensuring optimal milk production and maternal well-being.
Understanding Calorie Needs During Breastfeeding
Lactation increases a woman's daily calorie requirements. Generally, breastfeeding mothers need an extra 300-500 calories per day, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics.
This additional energy supports milk production, which is a demanding physiological process. Failing to meet these needs can compromise milk supply and maternal health.
The Calorie Deficit Dilemma
Creating a calorie deficit involves consuming fewer calories than the body expends. While effective for weight loss, it poses challenges during breastfeeding.
A drastic calorie reduction can lead to fatigue, nutrient deficiencies, and a potential decrease in milk production. It is essential to approach this cautiously and under professional supervision.
Expert Recommendations: The Who, What, When, Where, and How
Healthcare professionals, including lactation consultants and registered dietitians, are key resources. They can provide personalized guidance based on individual needs and circumstances.
What to do: aim for a modest calorie deficit of no more than 500 calories per day. When to start: wait until breastfeeding is well-established, typically around 6-8 weeks postpartum.
Where to seek guidance: consult with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian. How to achieve a deficit: focus on nutrient-dense foods and regular, moderate exercise.
Safe Weight Loss Strategies
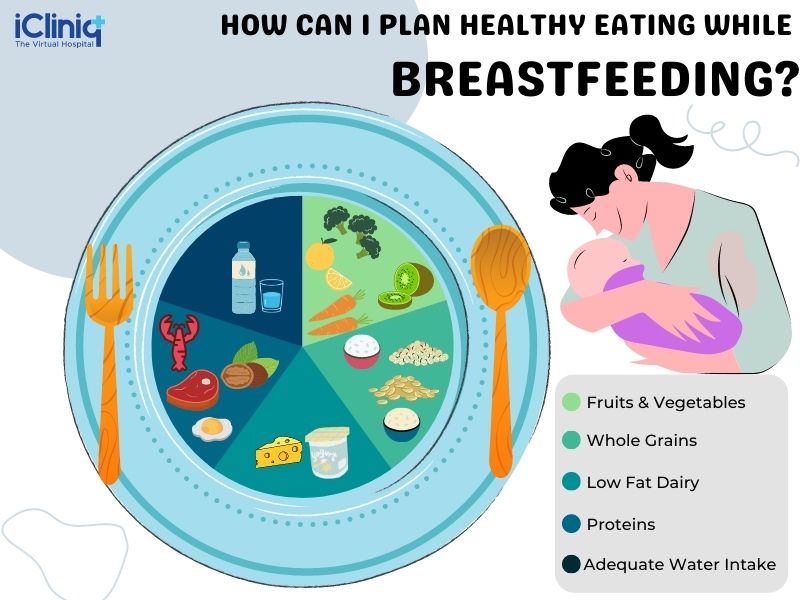
Prioritize nutrient-rich foods: focus on fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. These foods provide essential vitamins and minerals for both mother and baby.
Stay hydrated: drink plenty of water throughout the day to support milk production. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily.
Engage in moderate exercise: regular physical activity can help burn calories and improve overall health. Choose activities like walking, swimming, or postpartum yoga.
Avoid restrictive diets: fad diets and extreme calorie restriction are not recommended during breastfeeding. They can be harmful to both mother and baby.
Potential Risks of Excessive Calorie Restriction
A significant calorie deficit can lead to several adverse effects. These include reduced milk supply, nutrient deficiencies, and increased fatigue and irritability.
Maternal malnutrition can also impact the quality of breast milk, potentially affecting infant growth and development. It's crucial to prioritize a balanced and adequate diet.
Studies suggest that severe calorie restriction can release toxins stored in fat tissue into the breast milk. This could pose risks to the baby's health, according to research published in the Journal of Human Lactation.
Monitoring Milk Supply and Infant Growth
Regularly monitor your milk supply to ensure your baby is getting enough. Signs of adequate milk intake include consistent weight gain, frequent wet diapers, and contented behavior after feedings.
Consult with a pediatrician to track your baby's growth and development. They can assess whether your baby is thriving on breast milk alone.
If you notice a decrease in milk supply or signs of poor infant growth, reassess your calorie intake and consult with a lactation consultant.
The Importance of Professional Guidance
Every woman's body responds differently to calorie restriction during breastfeeding. Personalized guidance is essential to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Registered dietitians can help you create a balanced meal plan that meets your individual calorie and nutrient needs. They can also provide support and encouragement throughout your weight loss journey.
Lactation consultants can assess your milk supply and provide strategies to optimize breastfeeding. Their expertise can help you overcome challenges and achieve your goals.
Debunking Common Myths
Myth: Breastfeeding automatically leads to weight loss. While breastfeeding burns calories, it doesn't guarantee weight loss. Diet and exercise still play crucial roles.
Myth: You need to eat for two while breastfeeding. While calorie needs increase, you don't need to double your food intake. Focus on nutrient-dense foods.
Myth: Exercise will harm your milk supply. Moderate exercise is safe and beneficial during breastfeeding. Avoid strenuous activity that could lead to fatigue.
Moving Forward: What to Do Next
Consult with your healthcare provider to discuss your weight loss goals. Get personalized recommendations based on your individual circumstances.
Consider working with a registered dietitian to create a balanced meal plan. Focus on nutrient-dense foods and moderate calorie restriction.
Monitor your milk supply and your baby's growth closely. Adjust your calorie intake as needed to ensure both your health and your baby's well-being. Remember, gradual and sustainable changes are key.