Can You Take Antidepressants In The Military

Military personnel battling depression face a complex reality regarding antidepressant use. Strict regulations govern who can take these medications and under what circumstances, impacting readiness and career prospects.
This article breaks down the current policy on antidepressant use in the military, highlighting who is affected, what the restrictions are, where these policies apply, when changes were implemented, and how service members navigate this challenging landscape.
Who is Affected?
All branches of the U.S. military—Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard—are subject to these regulations.
The policies impact both active-duty personnel and those in the reserves and National Guard.
Individuals diagnosed with depression, anxiety, or other mental health conditions requiring antidepressant medication are directly affected.
What are the Restrictions?
The military's primary concern is readiness. Specifically, the ability of service members to perform their duties effectively and safely.
While not an outright ban, the use of antidepressants is heavily scrutinized and can limit certain roles and assignments.
Individuals requiring long-term antidepressant treatment may face limitations on deployments, special duties, and even reenlistment.
Where do these Policies Apply?
These policies are enforced across all military installations and operational environments worldwide.
This includes both stateside bases and overseas deployments.
Medical evaluations and treatment protocols are standardized across the various branches to ensure consistent application.
When were these Changes Implemented?
The current policies have evolved over time, influenced by research on mental health, medication effectiveness, and operational demands.
Significant updates were made in the early 2000s as the military addressed the mental health needs of veterans returning from Iraq and Afghanistan. More recently, the Defense Health Agency (DHA) has played a key role in standardizing treatment protocols.
Ongoing reviews ensure policies reflect the latest medical knowledge and operational realities.
How do Service Members Navigate This?
Service members diagnosed with depression must undergo a thorough medical evaluation.
This includes a review of their medical history, a psychiatric assessment, and consideration of alternative treatment options.
If antidepressant medication is deemed necessary, the prescribing physician must document the rationale and monitor the individual's progress closely.
Medication and Deployments
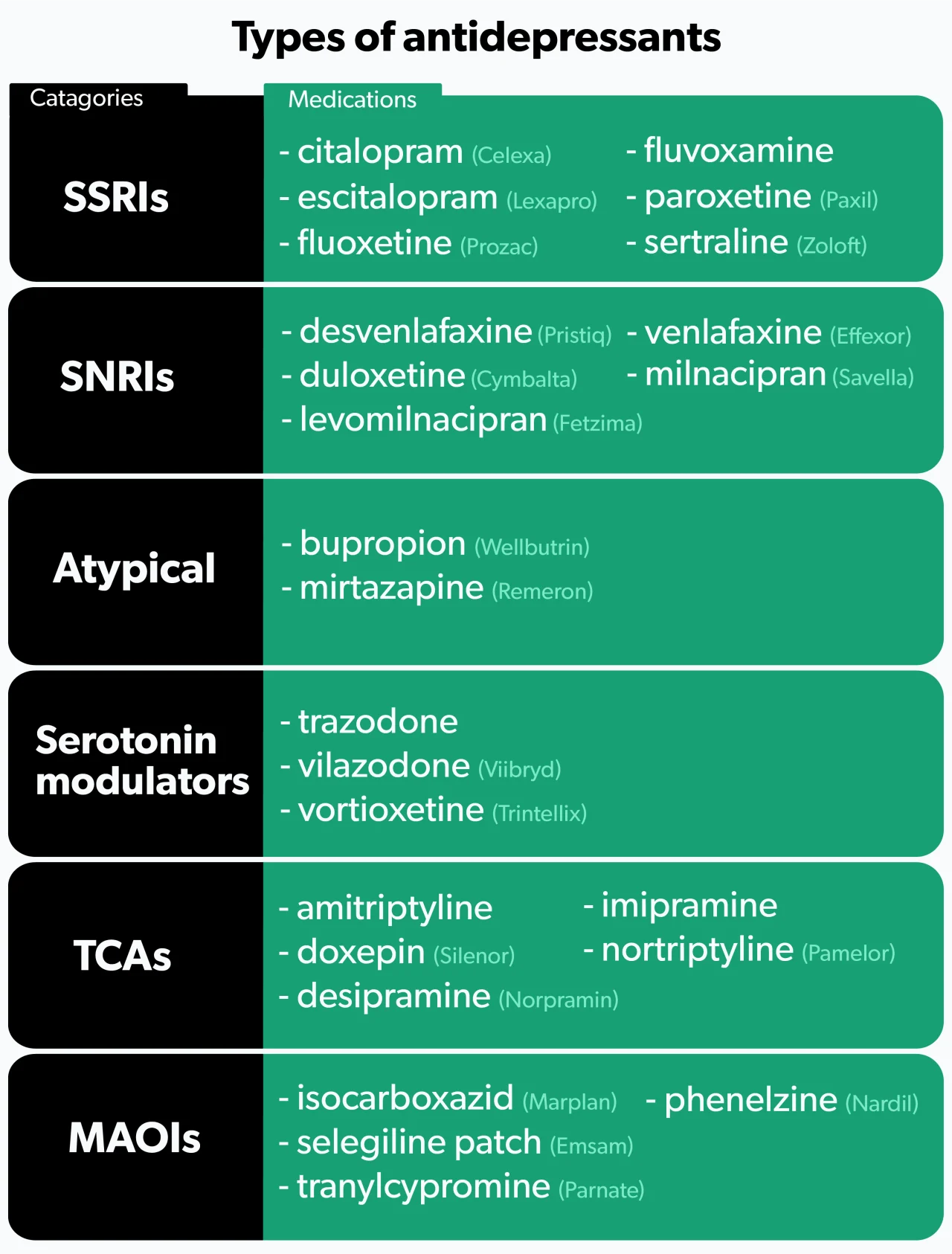
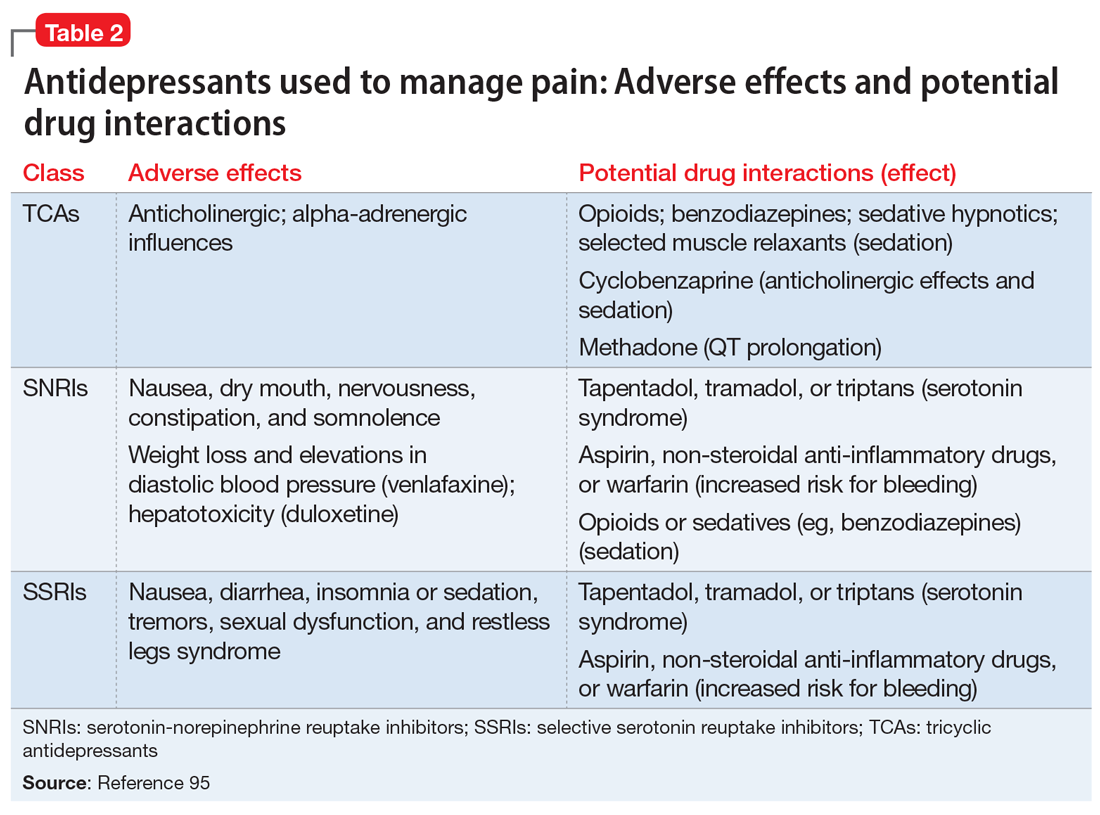
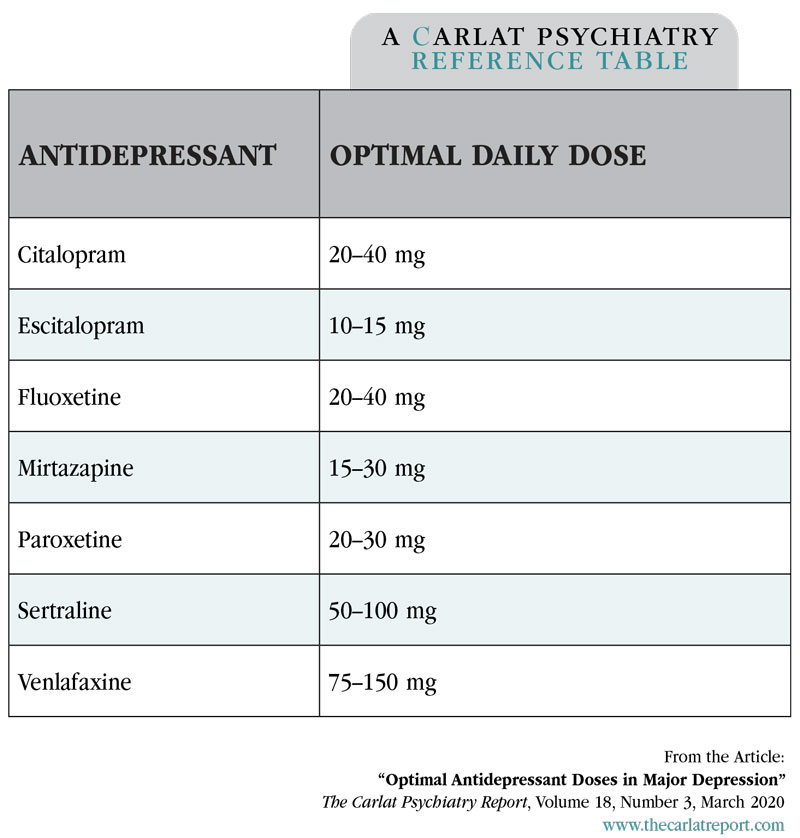
Specific antidepressants may be preferred over others due to their side effect profiles and potential impact on cognitive function.
During deployments, access to medication and mental health support can be limited, posing significant challenges for those requiring ongoing treatment.
Commanders play a crucial role in ensuring that service members receive the necessary care and support, but they also must consider mission requirements.
The Waiver Process
In some cases, individuals taking antidepressants may be eligible for a waiver to continue serving in specific roles or deploy to certain locations.
The waiver process is complex and involves a review by medical and operational authorities.
Factors considered include the individual's stability on medication, the severity of their condition, and the operational needs of the unit.
Confidentiality and Stigma
Fear of stigma and potential career repercussions can deter service members from seeking mental health treatment.
Efforts are underway to reduce the stigma surrounding mental health and encourage individuals to seek help without fear of judgment.
Confidentiality is paramount, but limitations exist when safety or mission readiness is at risk.
Alternative Treatments
The military also emphasizes alternative treatments for depression, such as therapy, exercise, and mindfulness techniques.
These approaches can be used in conjunction with or as an alternative to medication.
The goal is to provide individualized treatment plans that address the specific needs of each service member. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is frequently used.
Impact on Career
Antidepressant use can impact a service member's career trajectory. Some career fields are closed to individuals requiring long-term medication.
Security clearances may also be affected, depending on the severity of the condition and the specific requirements of the job.
Transparency and honest communication with medical providers and supervisors are essential to navigate these challenges.
The Future of Mental Health Policy
The military's mental health policies are constantly evolving. Research into the effectiveness of different treatments and the impact of mental health on readiness continues to inform policy decisions.
Increased awareness and reduced stigma surrounding mental health are also driving positive change.
The Department of Defense is committed to providing comprehensive mental health care to all service members and ensuring they have the resources they need to succeed. Military OneSource is a key resource.
The debate surrounding antidepressant use in the military will likely continue as medical understanding advances and operational demands shift.
Service members struggling with depression should seek help immediately. Resources like the Veterans Crisis Line and military mental health clinics are available to provide support and guidance.
Stay informed about policy updates and advocate for your mental health needs.