Candida And Bv At The Same Time

The simultaneous occurrence of Candida and Bacterial Vaginosis (BV), often referred to as a co-infection, presents a particularly challenging and uncomfortable experience for women. This complex scenario, while not uncommon, can lead to prolonged symptoms, increased difficulty in diagnosis, and a potentially frustrating treatment journey. Understanding the intricate interplay between these two distinct vaginal infections is crucial for effective management and prevention.
This article delves into the complexities of co-infection with Candida and BV. We will explore the diagnostic challenges, treatment strategies, and preventative measures to equip women with the knowledge they need to navigate this often-overlooked aspect of vaginal health. We aim to provide clarity on a condition that can significantly impact a woman's quality of life, drawing on current research and expert opinions.
Understanding Candida and BV
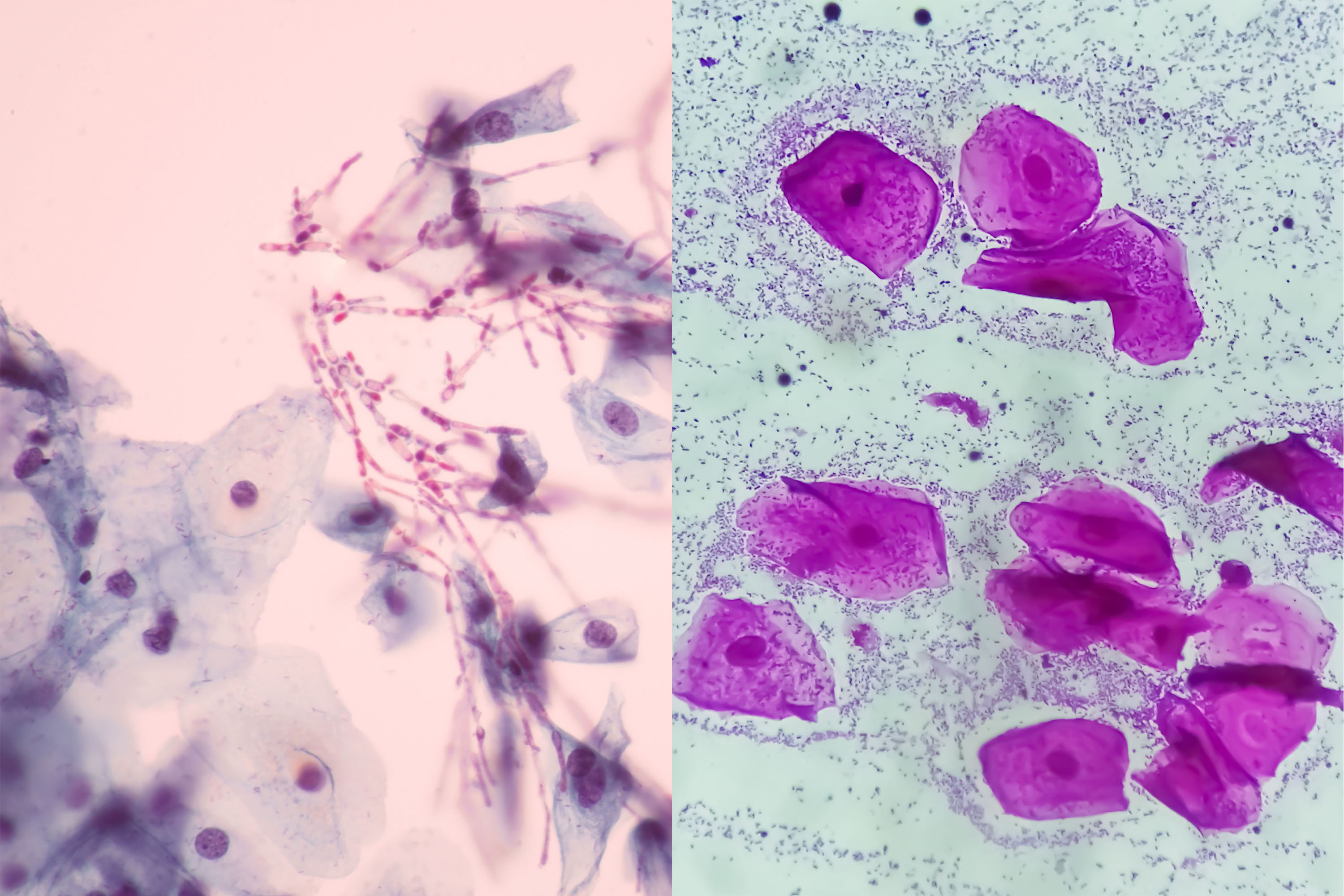
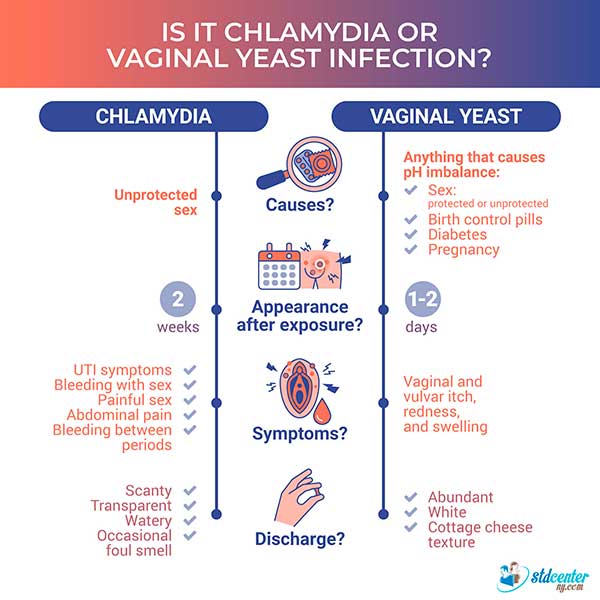
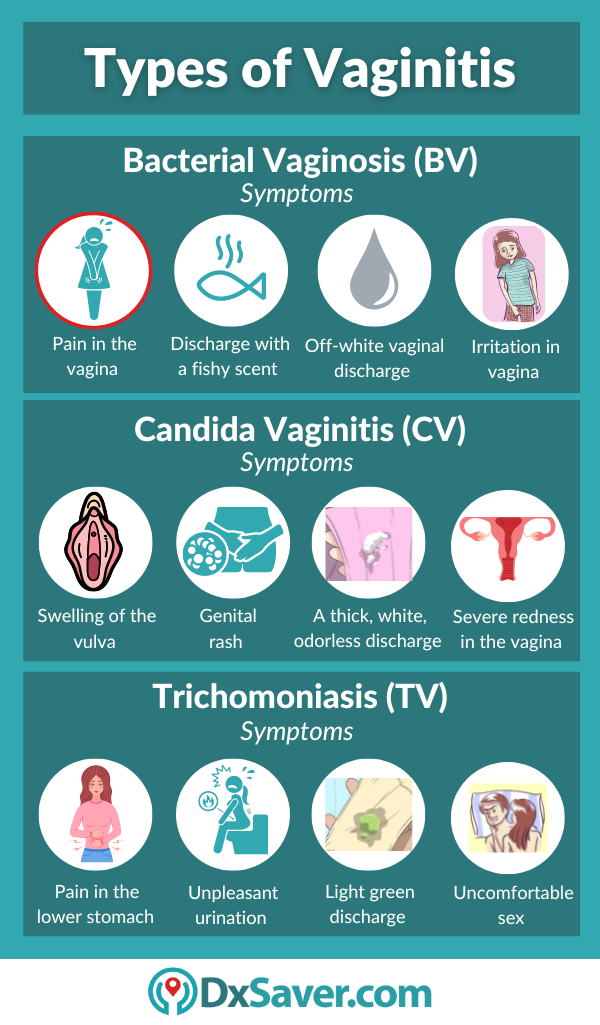
Candida, commonly known as a yeast infection, is caused by an overgrowth of the Candida fungus, most often Candida albicans. This imbalance disrupts the normal vaginal flora, leading to symptoms like intense itching, burning, and a thick, white, cottage cheese-like discharge. Hormonal changes, weakened immune systems, and antibiotic use are common triggers for Candida overgrowth.
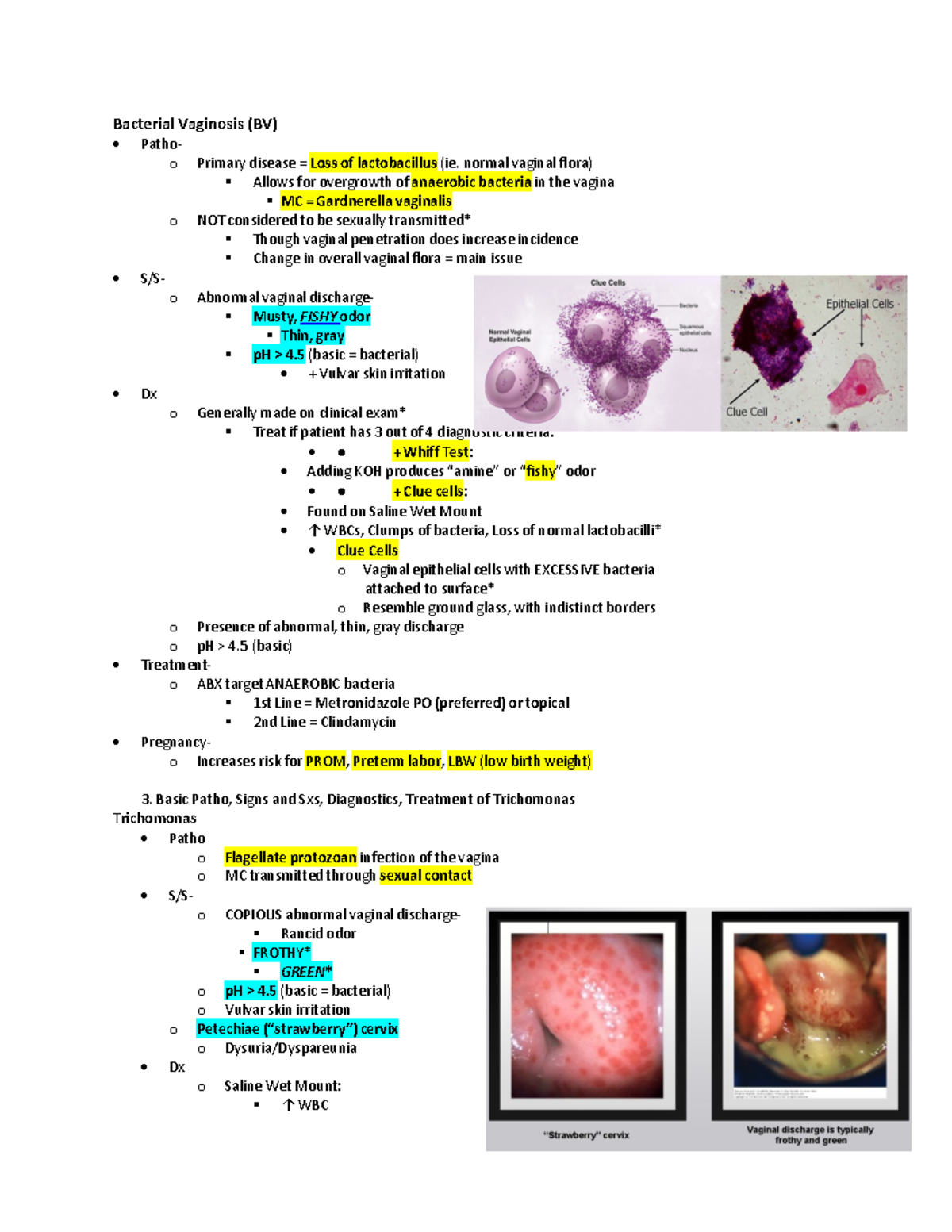
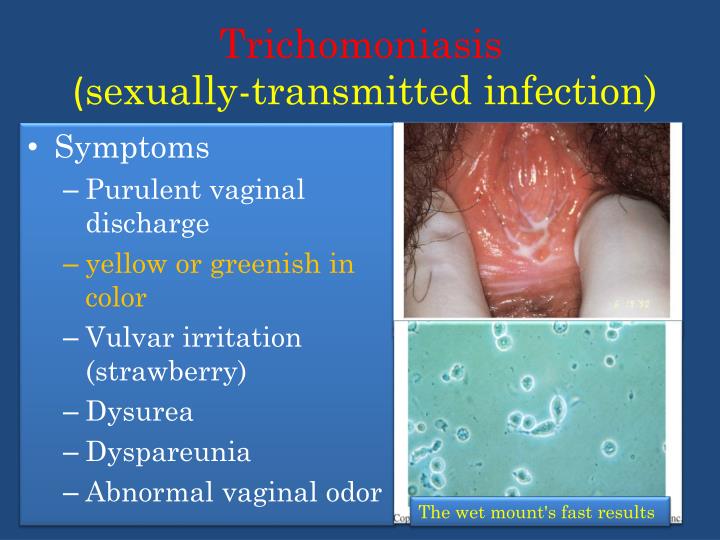
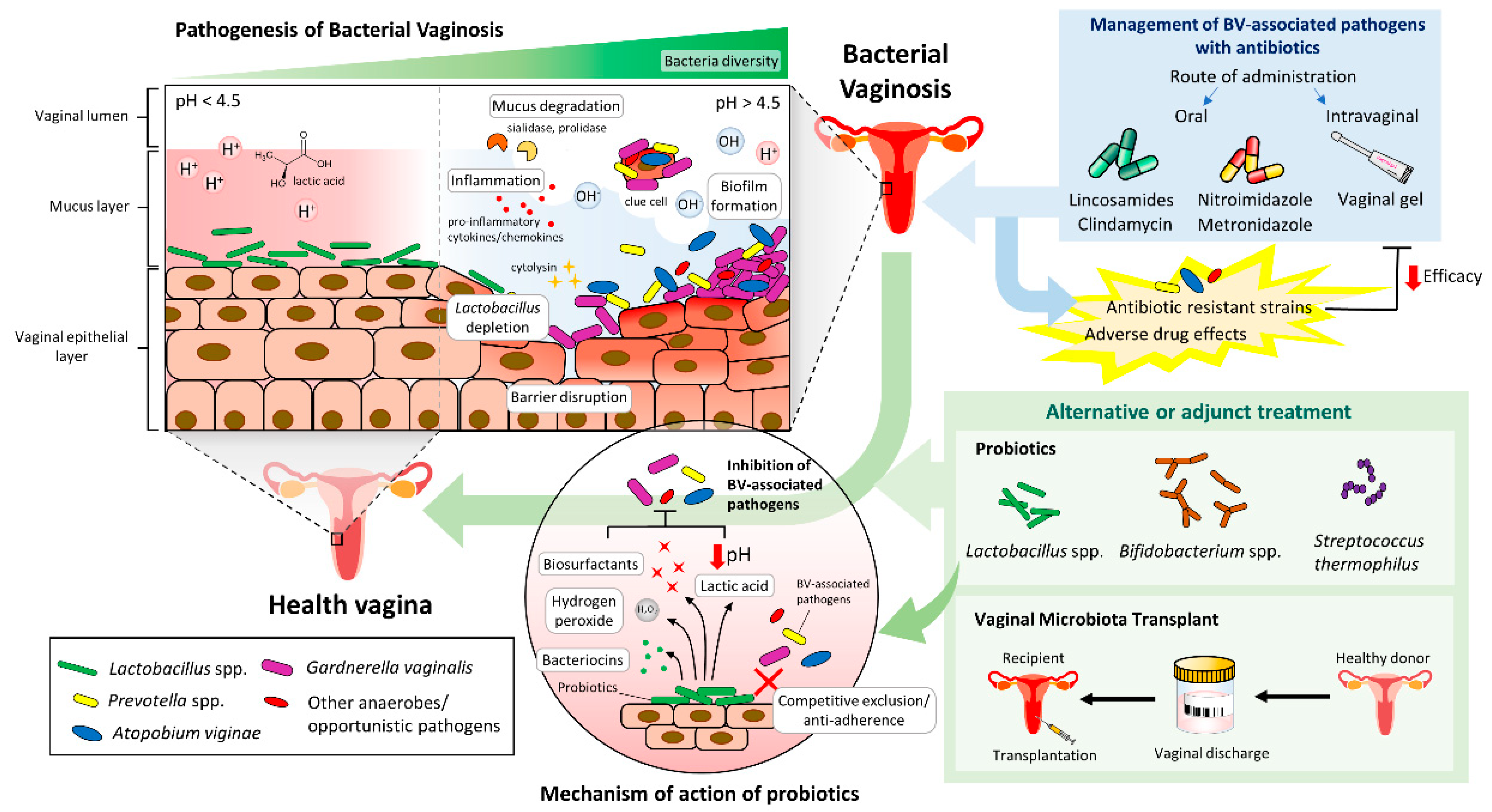
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV), on the other hand, results from an imbalance of bacteria in the vagina. The normal, healthy bacteria (primarily Lactobacillus) are replaced by an overgrowth of other bacteria, such as Gardnerella vaginalis. BV is characterized by a fishy odor, thin, grayish-white discharge, and sometimes, itching or burning, although many women experience no symptoms at all.
The Challenge of Co-infection
Diagnosing a co-infection of Candida and BV can be more challenging than diagnosing either infection alone. The overlapping symptoms can obscure the true nature of the problem. Some symptoms, like itching and burning, are common to both infections, making differentiation difficult without proper testing.
Moreover, the presence of one infection can sometimes mask or exacerbate the symptoms of the other. A woman might primarily experience symptoms of Candida while unknowingly harboring BV, or vice versa. This can lead to misdiagnosis and ineffective treatment strategies.
Diagnostic Hurdles
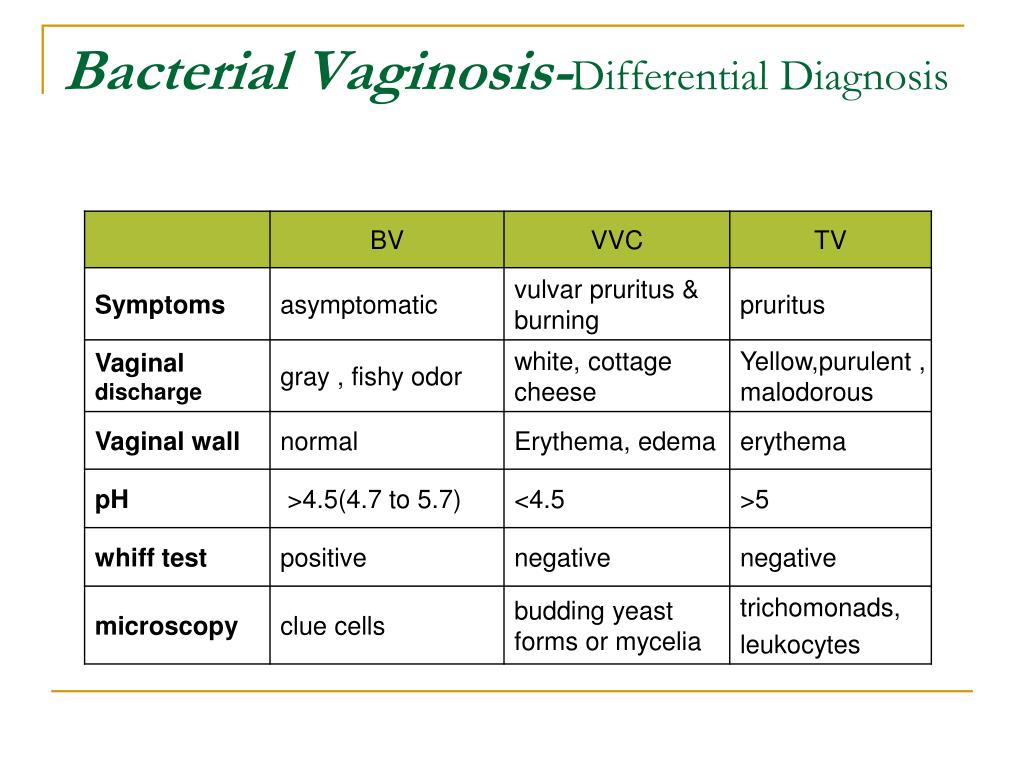
Accurate diagnosis relies heavily on a combination of symptom evaluation and laboratory testing. A pelvic exam allows a healthcare provider to visually assess the vaginal discharge and surrounding tissues. Vaginal fluid samples are then collected and examined under a microscope to identify the presence of yeast cells and abnormal bacteria, as well as to determine the pH level.
The pH level is a critical indicator. Candida typically does not significantly alter vaginal pH, whereas BV often elevates it above 4.5. However, in cases of co-infection, the presence of BV can mask the typical characteristics of a Candida infection, making accurate assessment more complicated.
The Impact of pH
A normal vaginal pH is acidic, typically ranging from 3.8 to 4.5. This acidity helps maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms, preventing the overgrowth of harmful bacteria and yeast. BV disrupts this balance, leading to a less acidic, more alkaline environment.
When both Candida and BV are present, the altered pH can create a favorable environment for both pathogens to thrive. This can lead to more persistent and difficult-to-treat infections. Therefore, understanding the pH level is crucial for tailoring an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Strategies for Co-infection
Treating a co-infection of Candida and BV typically requires a multi-pronged approach. Addressing both infections simultaneously is crucial to prevent recurrence and alleviate symptoms effectively. Often, this involves using both antifungal and antibacterial medications.
For Candida, antifungal medications, available as creams, suppositories, or oral tablets, are commonly prescribed. For BV, antibiotics, such as metronidazole or clindamycin, are the standard treatment, available in gel or oral form. However, selecting the appropriate treatment regimen requires careful consideration of individual factors and potential drug interactions.
Sequential vs. Concurrent Treatment
Healthcare providers may choose to treat the infections sequentially or concurrently, depending on the severity and presentation of the symptoms. Sequential treatment involves addressing one infection first, followed by the other, whereas concurrent treatment addresses both infections simultaneously.
Concurrent treatment may be preferred for severe co-infections, as it aims to provide faster relief and prevent the untreated infection from exacerbating the other. However, it is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of each approach with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate strategy.
Probiotics and Their Role
Probiotics, particularly those containing Lactobacillus strains, are often recommended as an adjunct to traditional treatment. They can help restore the balance of healthy bacteria in the vagina and prevent recurrence of BV. Some studies suggest that probiotics may also help prevent Candida overgrowth.
However, it's important to note that probiotics are not a substitute for medical treatment and should be used in conjunction with prescribed medications. It is also advisable to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate type and dosage of probiotics.
Prevention and Management
Preventing Candida and BV involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits and practicing good hygiene. Avoiding douching, using unscented feminine hygiene products, and wearing breathable cotton underwear can help maintain a healthy vaginal environment. Maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, and getting enough sleep can also contribute to overall health and reduce the risk of infection.
For women who experience recurrent infections, identifying and addressing potential triggers is essential. This may involve working with a healthcare provider to evaluate hormonal imbalances, immune system deficiencies, or other underlying medical conditions.
The Importance of Communication
Open and honest communication with a healthcare provider is paramount for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Women should feel comfortable discussing their symptoms and concerns, as well as asking questions about their treatment plan. This collaborative approach can lead to better outcomes and improved overall health.
Furthermore, it is important to complete the full course of prescribed medication, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished. This helps ensure that the infection is fully eradicated and reduces the risk of recurrence.
Looking Ahead
Research into the complex interplay between Candida and BV is ongoing. Scientists are working to better understand the underlying mechanisms that contribute to co-infection and to develop more effective treatment and prevention strategies. This includes exploring novel approaches, such as targeted therapies and microbiome-based interventions.
Improved diagnostic tools and a greater awareness of the challenges posed by co-infection will lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses. Ultimately, this will empower women to take control of their vaginal health and improve their overall quality of life.