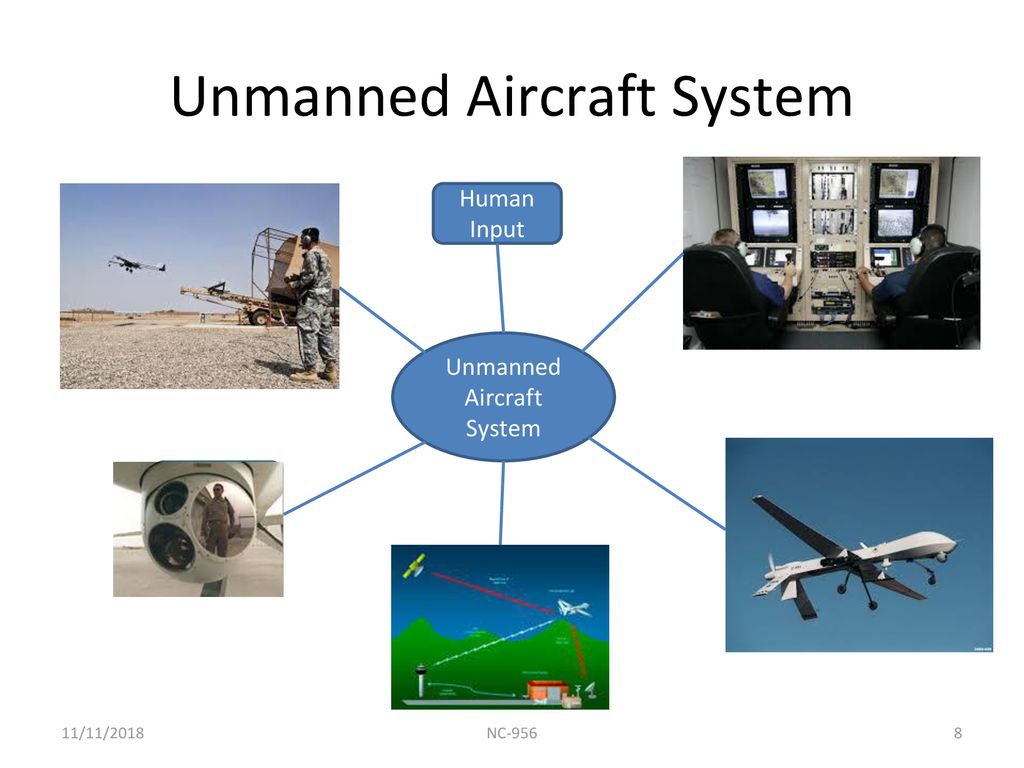
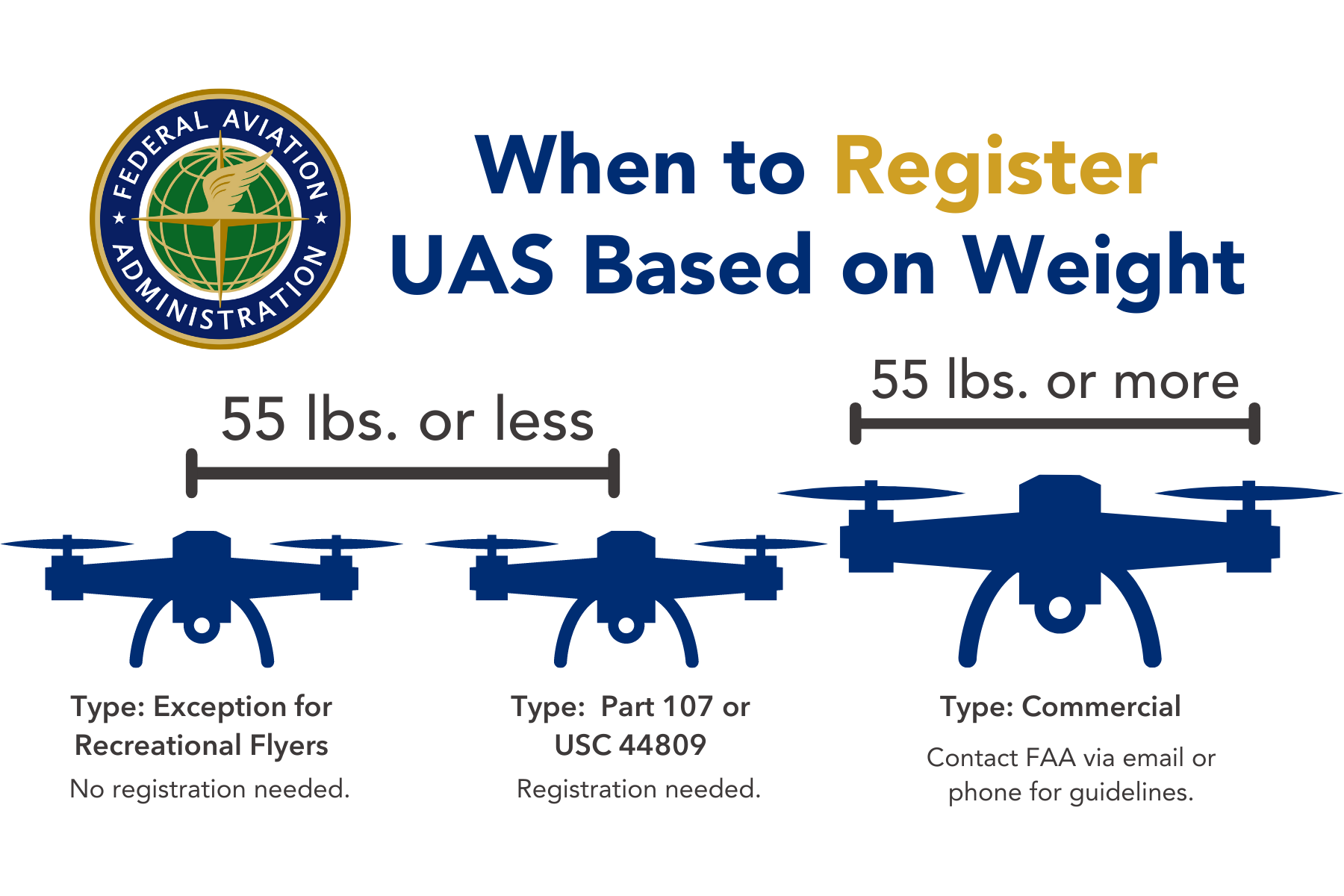
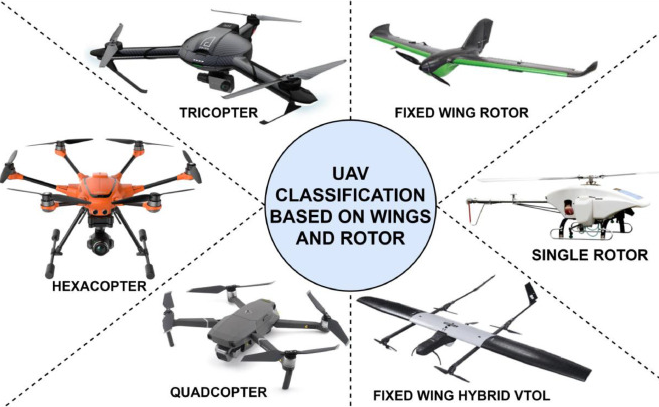
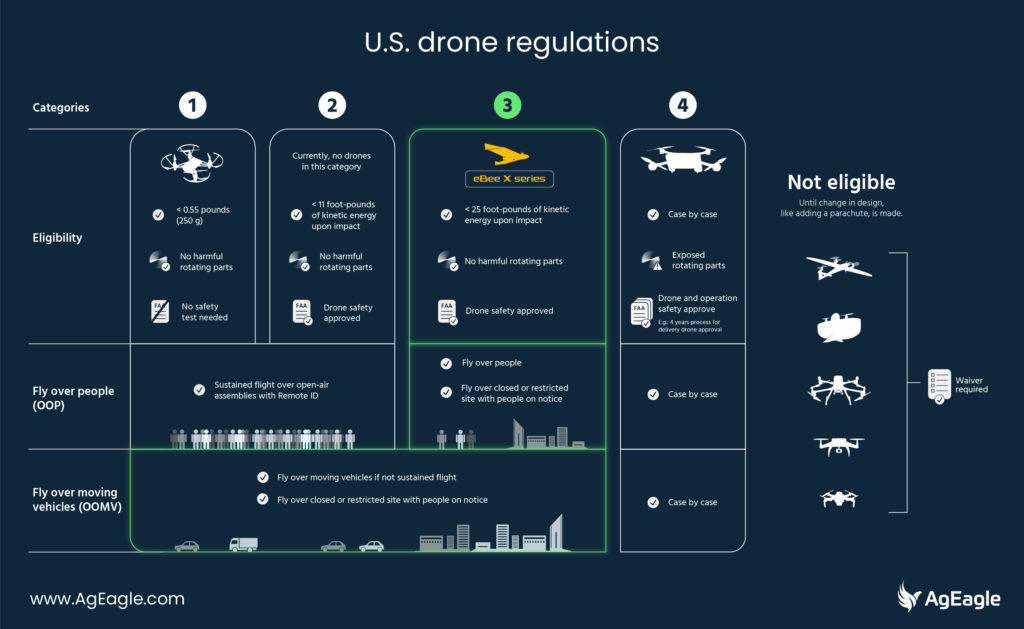
Category 4 Operations Are Limited To Unmanned Aircraft:
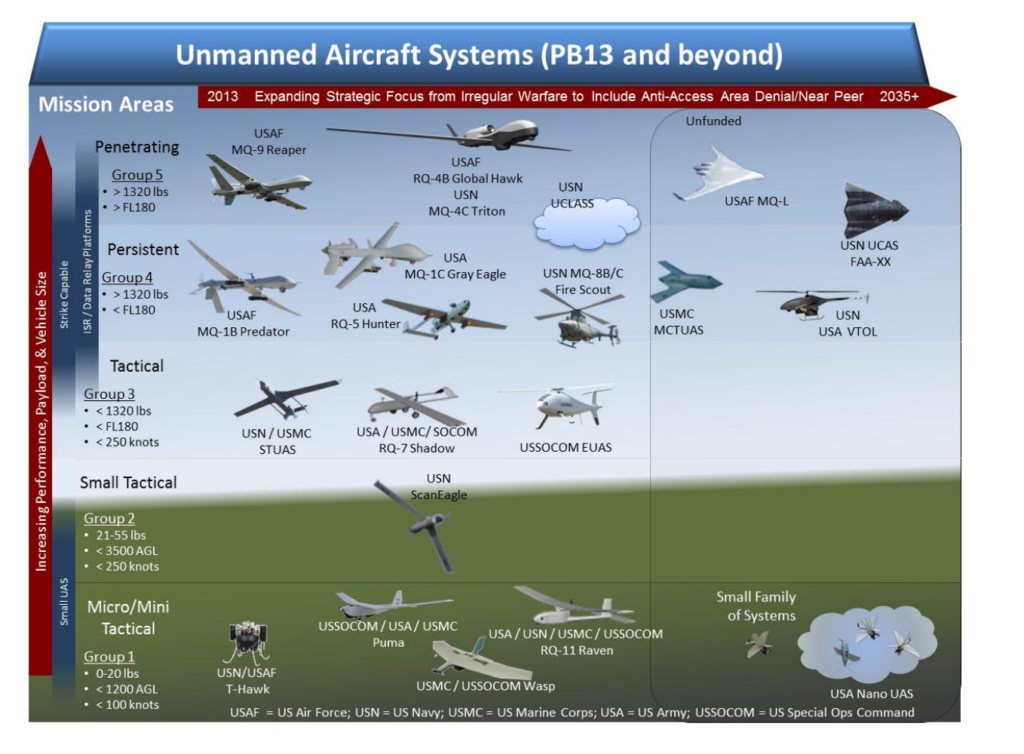
The future of disaster response and critical infrastructure inspection is rapidly changing. New regulations and technological advancements are pushing the boundaries of unmanned aircraft systems (UAS), particularly in what are classified as Category 4 operations – the most demanding and complex aerial tasks.
But now, Category 4 operations will be solely the domain of unmanned aircraft. This shift, driven by safety concerns and the increasing capabilities of drone technology, has sparked both excitement and apprehension across various industries, from emergency services to power grid maintenance.
Unpacking Category 4 Operations
Before diving into the implications, understanding what constitutes a Category 4 operation is crucial. These operations typically involve flying Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) in complex airspace or densely populated areas.
They may also include carrying heavy payloads, operating at night, or conducting missions in challenging weather conditions. Historically, such operations would have relied heavily on manned aircraft.
A comprehensive report by the FAA (Federal Aviation Administration) details the risk assessment framework used to categorize these operations, emphasizing the stringent safety requirements associated with Category 4.
The Rationale Behind the Shift
The decision to limit Category 4 operations to unmanned aircraft stems from several factors. Safety is paramount.
Unmanned systems inherently reduce the risk of pilot injury or loss of life in hazardous environments. The increasing sophistication of drone technology is another key driver.
Modern drones are equipped with advanced sensors, navigation systems, and fail-safe mechanisms that enhance operational efficiency and safety.
According to a statement from the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB), the potential for human error in manned aircraft operations is a significant contributor to accidents.
Unmanned systems, with their reliance on automation and remote control, can mitigate some of these risks.
Industry Reactions: A Mixed Bag
The announcement has elicited a range of responses from different sectors. Emergency services are generally positive.
Drones can provide real-time situational awareness during disasters, assess damage, and deliver critical supplies without risking human lives. "This is a game-changer for search and rescue," said a spokesperson for the International Search and Rescue Dog Association (IRSARDA) in an official statement.
"The ability to deploy drones in dangerous environments, where manned aircraft would be too risky, will significantly improve our response times and effectiveness."
However, concerns remain in other industries, particularly those that have traditionally relied on manned aircraft for infrastructure inspection. Power grid operators, for example, have expressed worries about the reliability and performance of drones in extreme weather conditions.
"While we recognize the potential benefits of drone technology, we need to ensure that it can meet the stringent requirements of our operations," stated a representative from the Edison Electric Institute (EEI).
"The current generation of drones may not be capable of handling the heavy lifting and long-range missions required for inspecting high-voltage transmission lines."
Technological Challenges and Opportunities
Several technological hurdles need to be overcome to fully realize the potential of unmanned Category 4 operations. Battery life remains a major constraint.
Extending the flight time of drones is crucial for conducting long-range missions. Developing more robust and reliable sensors is also essential.
Drones need to be able to operate effectively in all weather conditions, including rain, snow, and high winds. Another challenge is improving autonomous navigation capabilities.
Drones need to be able to navigate complex airspace and avoid obstacles without human intervention. These challenges also present significant opportunities for innovation.
Companies are investing heavily in developing new battery technologies, advanced sensors, and autonomous navigation systems. The market for drone technology is expected to grow exponentially in the coming years.
Regulatory Considerations and Ethical Implications
The regulatory landscape surrounding unmanned aircraft operations is constantly evolving. The FAA is working to develop new regulations that will accommodate the increasing use of drones in complex operations.
These regulations will need to address issues such as airspace management, operator certification, and data privacy. Ethical considerations are also important.
As drones become more capable, it is crucial to ensure that they are used responsibly and ethically. Issues such as surveillance, data security, and the potential for misuse need to be carefully addressed.
The ACLU (American Civil Liberties Union) has raised concerns about the potential for drones to be used for mass surveillance.
"We need to ensure that appropriate safeguards are in place to protect privacy and civil liberties," said a spokesperson for the organization.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Aerial Operations
The decision to limit Category 4 operations to unmanned aircraft marks a significant turning point in the evolution of aerial operations. It is a clear indication that the future of many industries will be shaped by drone technology.
As drone technology continues to advance and regulations become more refined, unmanned systems will play an increasingly important role in disaster response, infrastructure inspection, and a wide range of other applications. However, it is important to address the technological challenges, regulatory considerations, and ethical implications to ensure that these technologies are used safely, responsibly, and for the benefit of society.
The transition will require collaboration between government, industry, and academia to develop the necessary technologies, regulations, and training programs. The potential benefits are enormous, but realizing them will require careful planning and execution.