Choose The Correct Order Of Steps In The Production Process
Imagine a symphony orchestra tuning up. Each instrument, from the delicate flute to the booming timpani, is essential, but the real magic happens when they play together, in the right order, guided by the conductor's baton. Similarly, in the world of manufacturing and production, the correct sequence of steps is the key to turning raw materials into valuable goods, ensuring efficiency, quality, and ultimately, customer satisfaction.
Understanding and implementing the optimal sequence of steps in a production process is crucial for any business aiming to succeed. A poorly planned process can lead to delays, increased costs, and compromised product quality, while a well-orchestrated system ensures smooth operations, maximizes resource utilization, and enhances overall competitiveness.
The Foundation: Understanding the Production Process
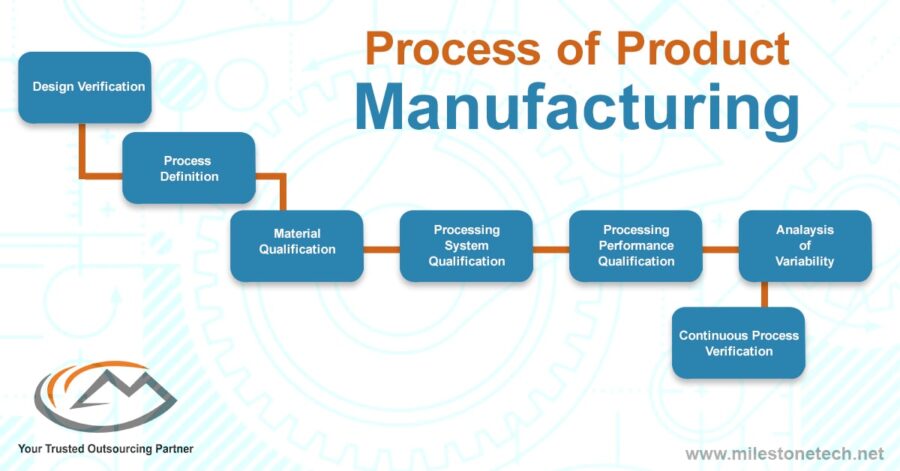
At its core, the production process is the transformation of inputs (raw materials, labor, and resources) into outputs (finished goods or services). This transformation involves a series of interconnected steps, each playing a vital role in the final outcome.
From the earliest days of manufacturing, businesses have sought to optimize these steps. The Industrial Revolution saw the rise of assembly lines, famously popularized by Henry Ford, demonstrating the power of sequencing and division of labor.
Today, with advancements in technology and automation, understanding the intricacies of process optimization is even more critical.
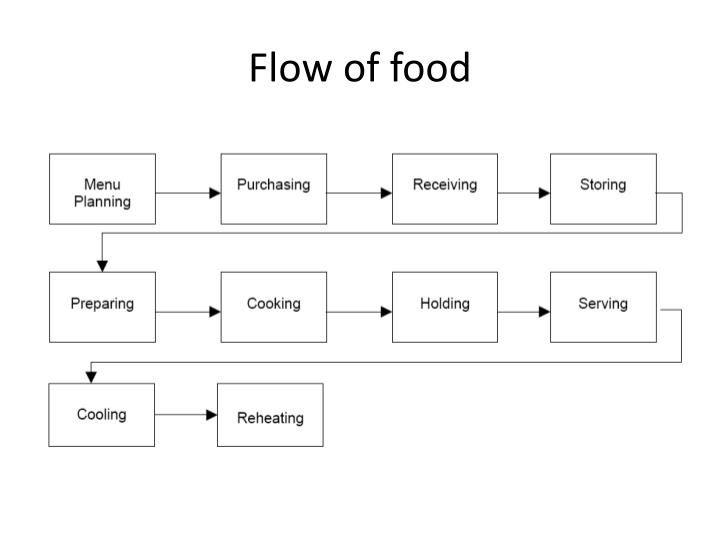
The Essential Steps: A General Overview
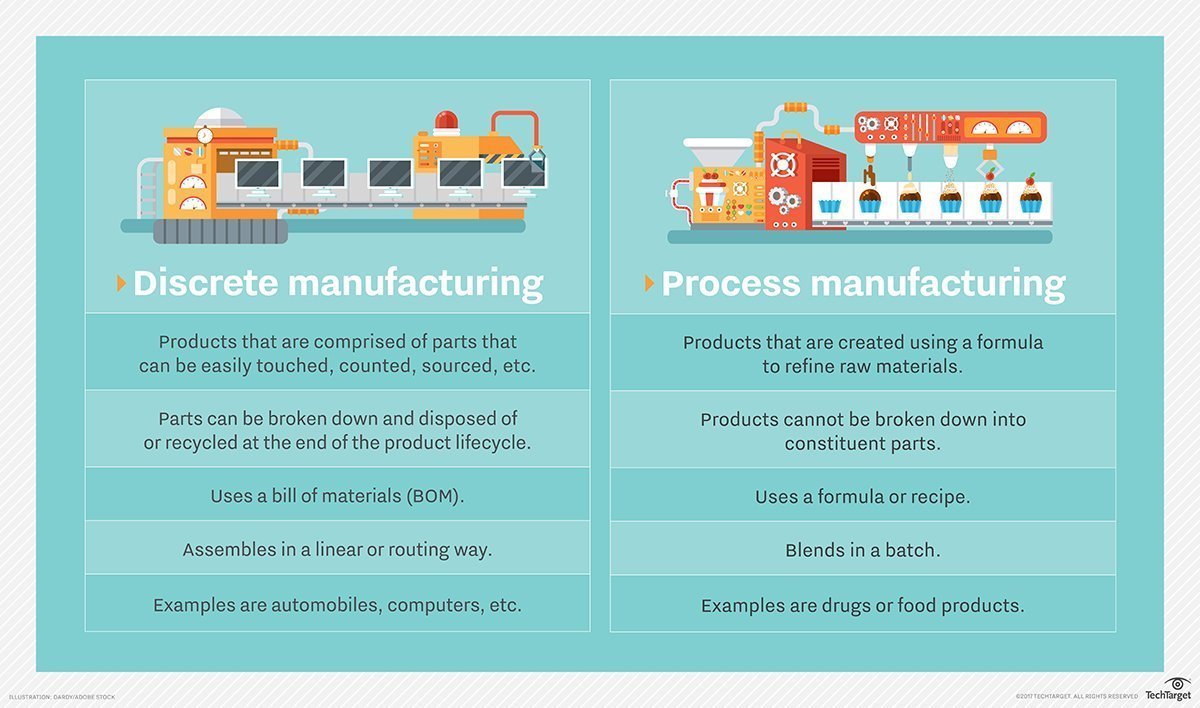
While the specific steps in a production process vary depending on the industry, product, or service, some fundamental stages are common across most operations.
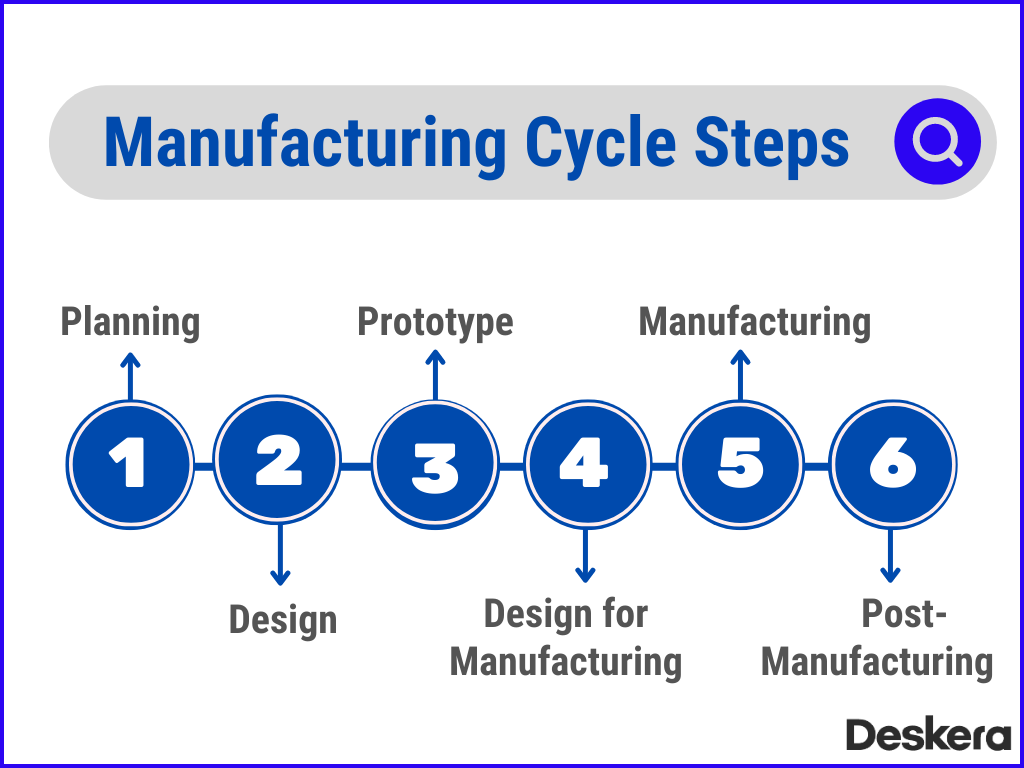
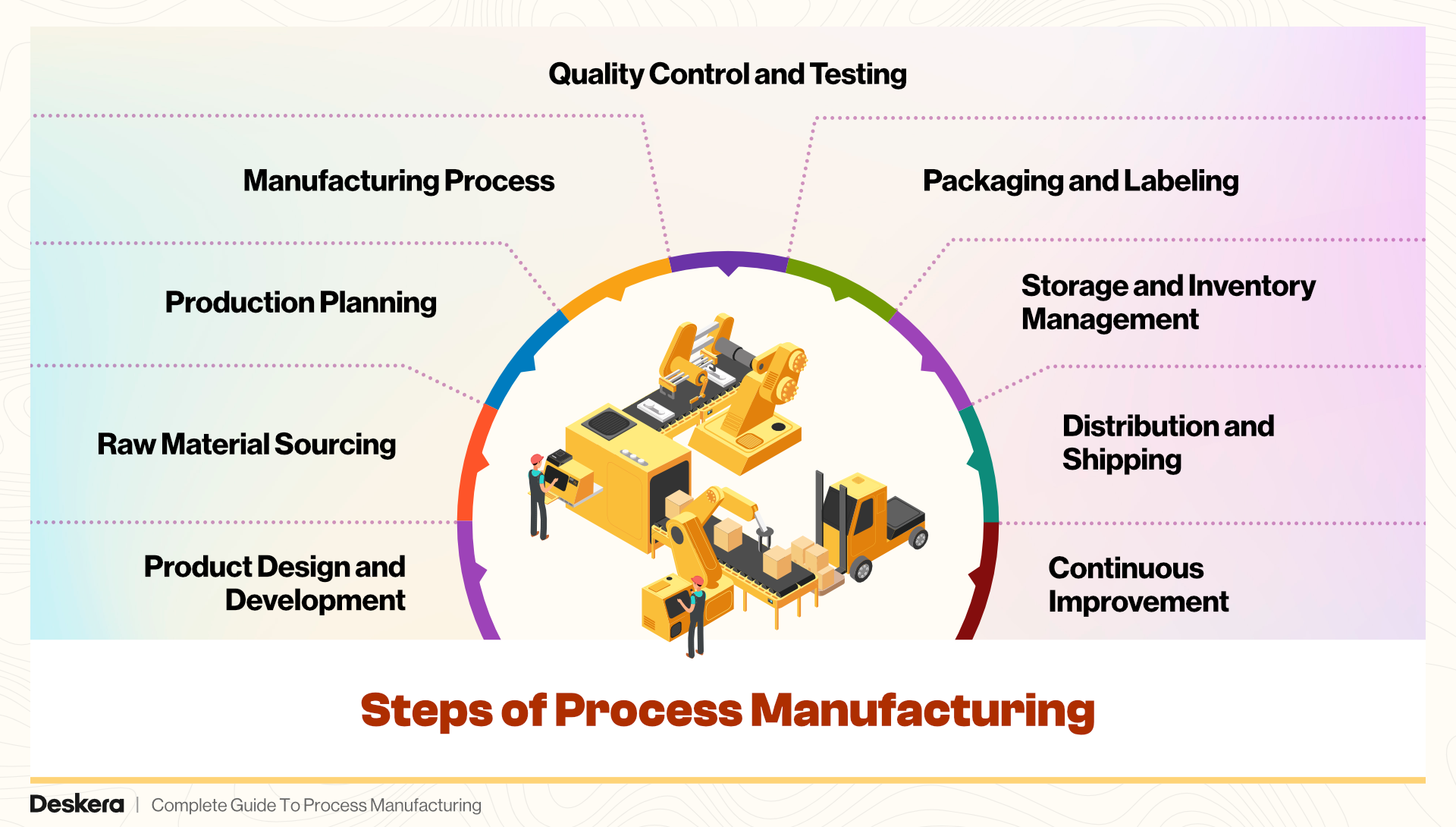
1. Sourcing and Procurement
This initial stage involves identifying and acquiring the necessary raw materials, components, and resources. Efficient sourcing ensures a consistent supply chain and helps minimize costs. Supplier relationships are key here.
2. Pre-Production Planning
This involves meticulous planning before actual production begins. It includes tasks like designing the product, creating blueprints, and establishing quality control measures.
A well-defined plan minimizes errors and ensures everyone is on the same page.
3. Production or Manufacturing
This is where the actual transformation of raw materials into finished goods takes place. It may involve various processes like cutting, shaping, assembling, and finishing.
The specific methods and equipment used will depend on the product and industry.
4. Quality Control and Testing
Quality control is essential to ensure that the final product meets the required standards. This involves inspecting and testing the product at various stages of production.
Catching defects early prevents further resources from being wasted on faulty goods.
5. Packaging and Labeling
Once the product passes quality control, it is packaged and labeled for distribution. Proper packaging protects the product and provides essential information to consumers.
Attention to detail in this stage enhances brand perception.
6. Storage and Warehousing
The finished goods are then stored in a warehouse until they are ready for distribution. Proper storage ensures that the products are not damaged or spoiled.
Inventory management systems are critical at this point.
7. Distribution and Logistics
This stage involves transporting the finished goods to retailers or directly to consumers. Efficient logistics ensures timely delivery and minimizes transportation costs.
The rise of e-commerce has highlighted the importance of this step.
The Importance of the Correct Order
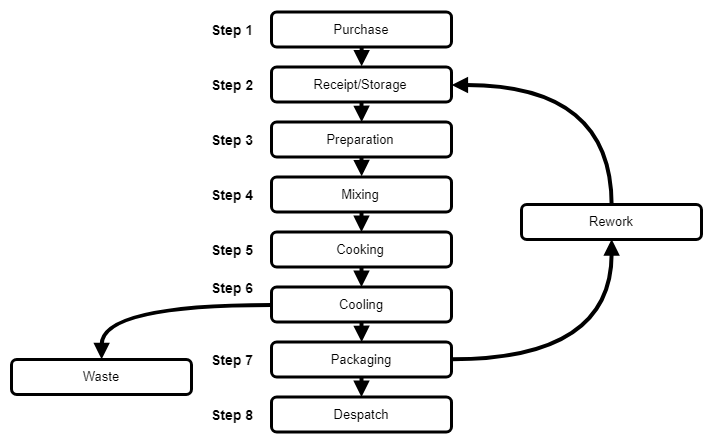
The order in which these steps are performed is paramount. Performing a task out of sequence can lead to significant problems.
For example, attempting to package a product before quality control could result in defective goods being shipped to customers, damaging the company's reputation.
Similarly, beginning production without proper planning can lead to errors and rework, wasting time and resources. Data from the American Society for Quality consistently emphasizes the positive correlation between process adherence and product quality.
Optimizing the Production Process: Key Strategies
Several strategies can be employed to optimize the production process and ensure the correct order of steps.
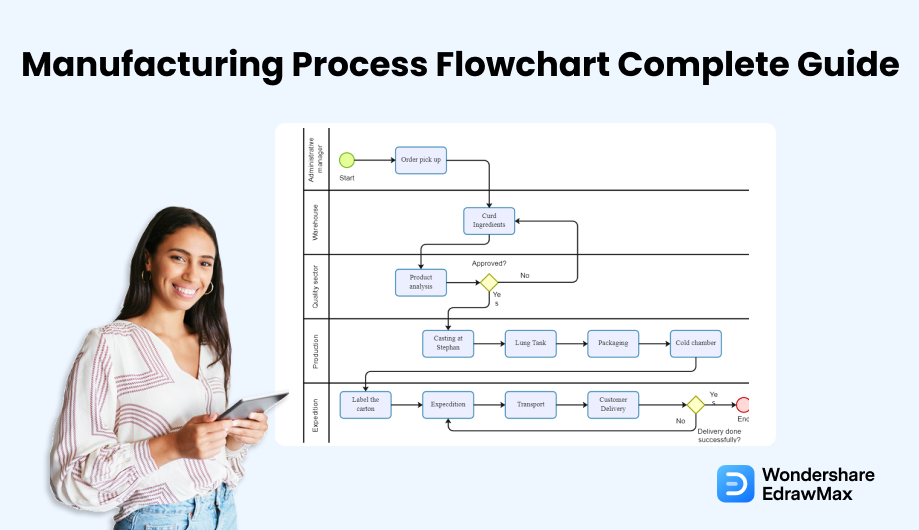
Process Mapping
Visualizing the entire production process through flowcharts and diagrams can help identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. Process mapping provides a clear understanding of the sequence of steps and their interdependencies.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Creating detailed SOPs ensures that all employees follow the same procedures and guidelines. SOPs minimize variations and ensure consistency in the production process.
Lean Manufacturing Principles
Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste and maximizing efficiency in the production process. Principles like Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory and Kaizen (continuous improvement) can significantly improve the flow of production.
Automation
Automating certain tasks can increase efficiency and reduce the risk of human error. Robotics and automated systems can perform repetitive tasks with greater precision and speed.
Data Analysis and Monitoring
Collecting and analyzing data on key performance indicators (KPIs) can help identify areas for improvement. Monitoring metrics like production time, defect rates, and resource utilization provides valuable insights.
Real-World Examples
Consider a bakery producing bread. The correct order would be: sourcing ingredients, mixing the dough, allowing it to rise, baking, cooling, slicing, packaging, and then distribution.
Imagine trying to bake the dough before it rises – the result would be a flat, dense loaf! A car manufacturer would follow a sequence from stamping body panels, welding them together, painting, installing the engine and components, interior fitting, quality checks, and then final delivery.
Deviation from this order could create costly rework or an unusable vehicle.
The Future of Production Processes
The future of production processes is increasingly shaped by technological advancements. The rise of Industry 4.0, characterized by the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing, is transforming how products are designed, manufactured, and delivered.
These technologies enable greater automation, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance, further optimizing the production process and ensuring the correct order of steps.
A Continuous Journey
Mastering the art of production is not a one-time achievement but a continuous journey. Companies must constantly adapt and evolve their processes to meet changing market demands and technological advancements.
By focusing on understanding the fundamentals, implementing optimization strategies, and embracing innovation, businesses can unlock the full potential of their production processes and achieve sustainable success.
Just as a conductor guides an orchestra to create beautiful music, a well-managed production process orchestrates resources to deliver exceptional value to customers. It requires careful planning, precise execution, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
![Choose The Correct Order Of Steps In The Production Process [DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Production Process - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/jkkZGHfEYBY/maxresdefault.jpg)
![Choose The Correct Order Of Steps In The Production Process [DIAGRAM] Process Flow Diagram Manufacturing - WIRINGSCHEMA.COM](http://www.presentationeze.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/Manufacturing-Process-Flow-Chart.jpg)



![Choose The Correct Order Of Steps In The Production Process [DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Production Process - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](http://www.indiastudychannel.com/attachments/Resources/157127-6648-Biscuit-manufacturing-process.jpg)