Communication Barriers In Business

Businesses are bleeding profits due to pervasive communication breakdowns. Misunderstandings, delays, and fractured collaborations are costing companies millions annually, demanding immediate action.
This article exposes the critical communication barriers crippling businesses, highlighting the "who, what, where, when, why, and how" of this escalating crisis. The focus is on data-backed insights and actionable strategies for a rapid turnaround.
The High Cost of Miscommunication
Project Management Institute (PMI) research reveals that ineffective communication contributes to a staggering $75 million wasted per $1 billion spent on projects. These financial losses stem from duplicated efforts, missed deadlines, and rework.
A ClearCompany study indicates that 86% of employees and executives cite lack of communication as a primary cause of workplace failures. This deficiency breeds frustration, decreased morale, and ultimately, higher employee turnover.
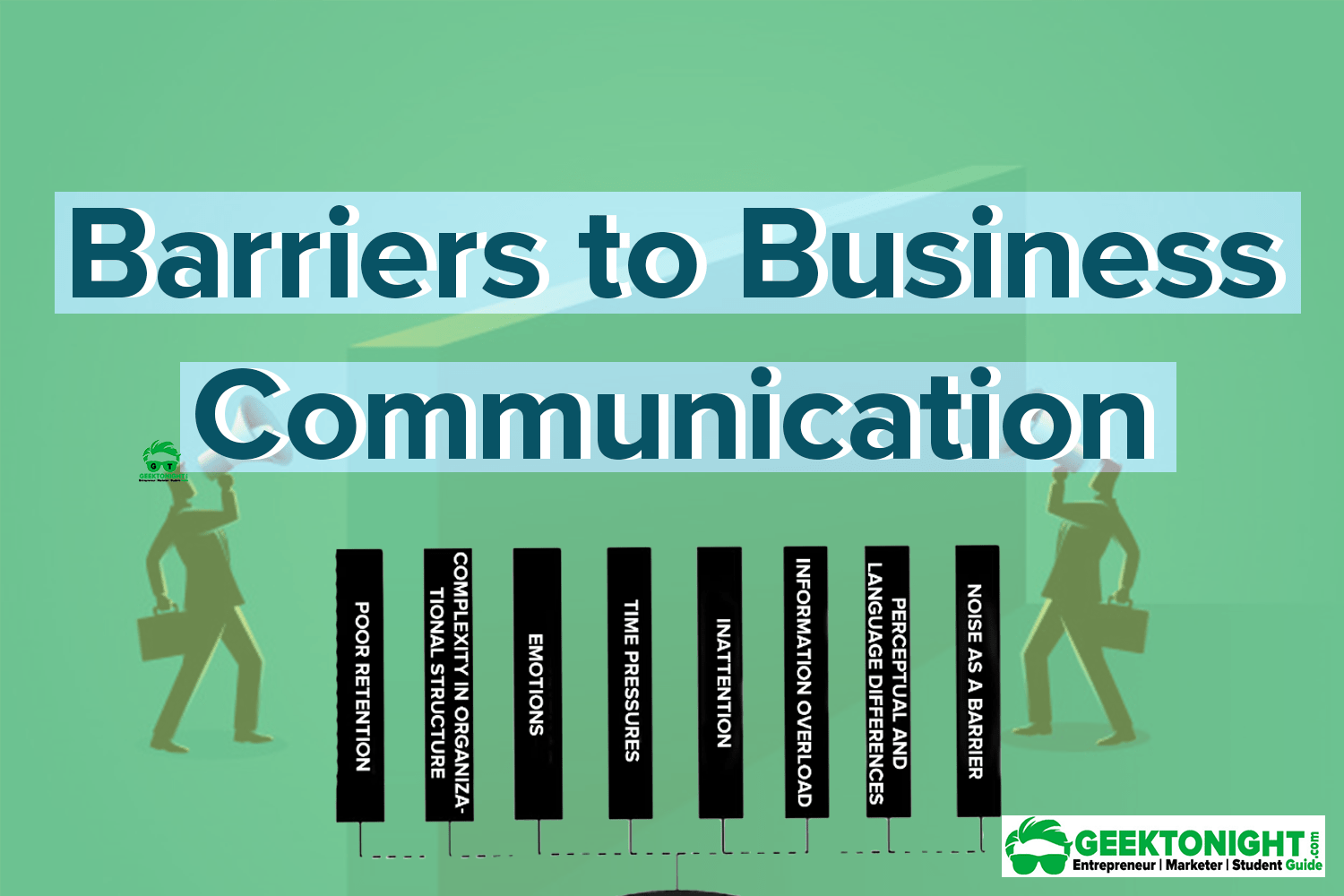
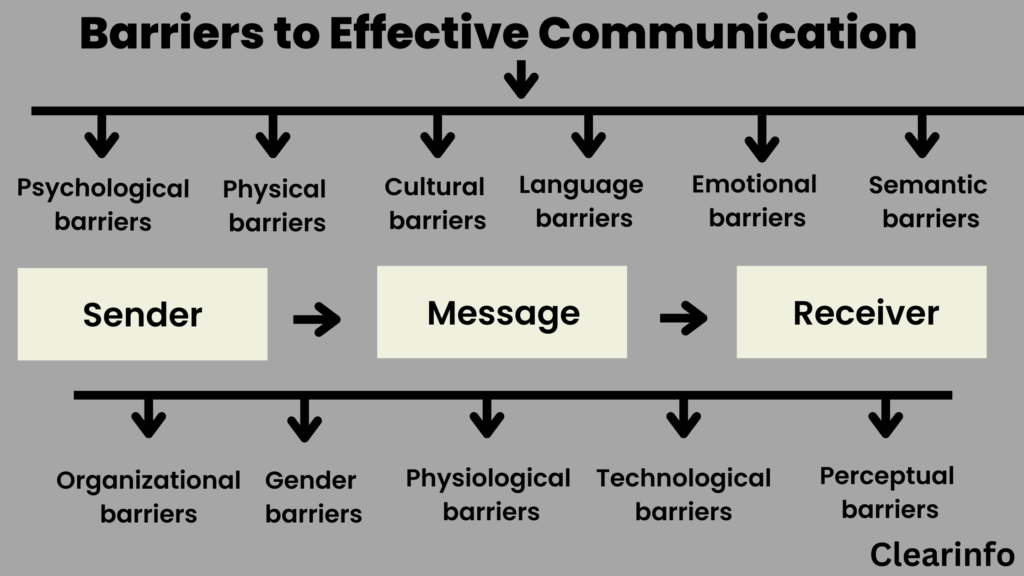
Identifying the Culprits: Common Communication Barriers
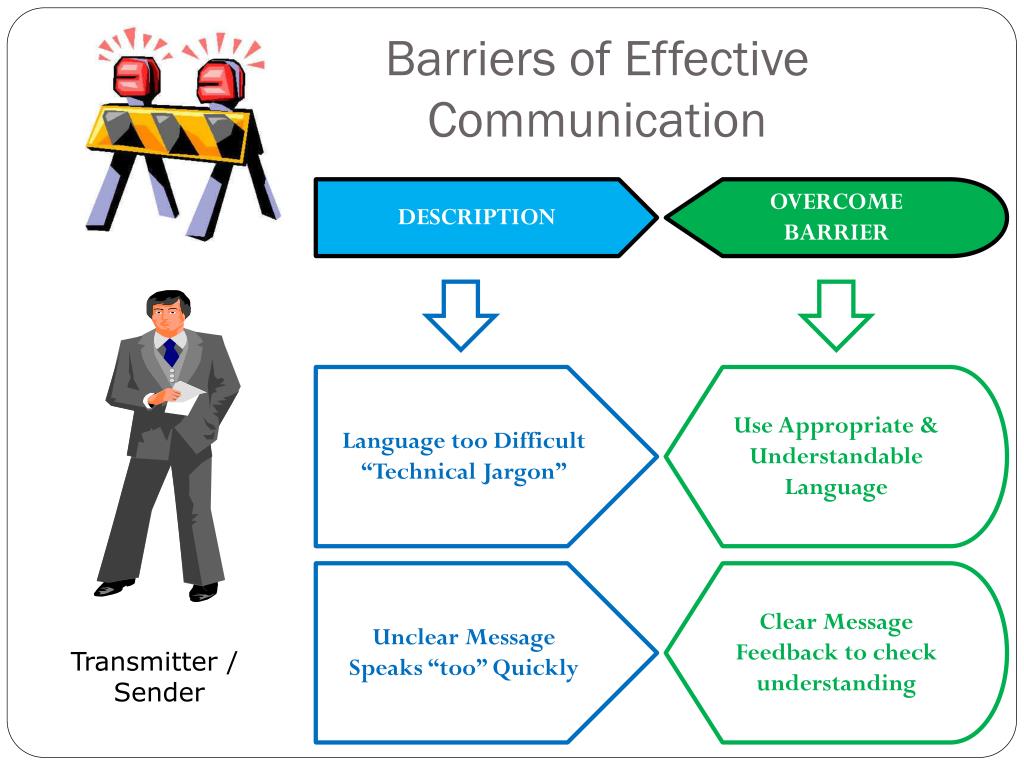
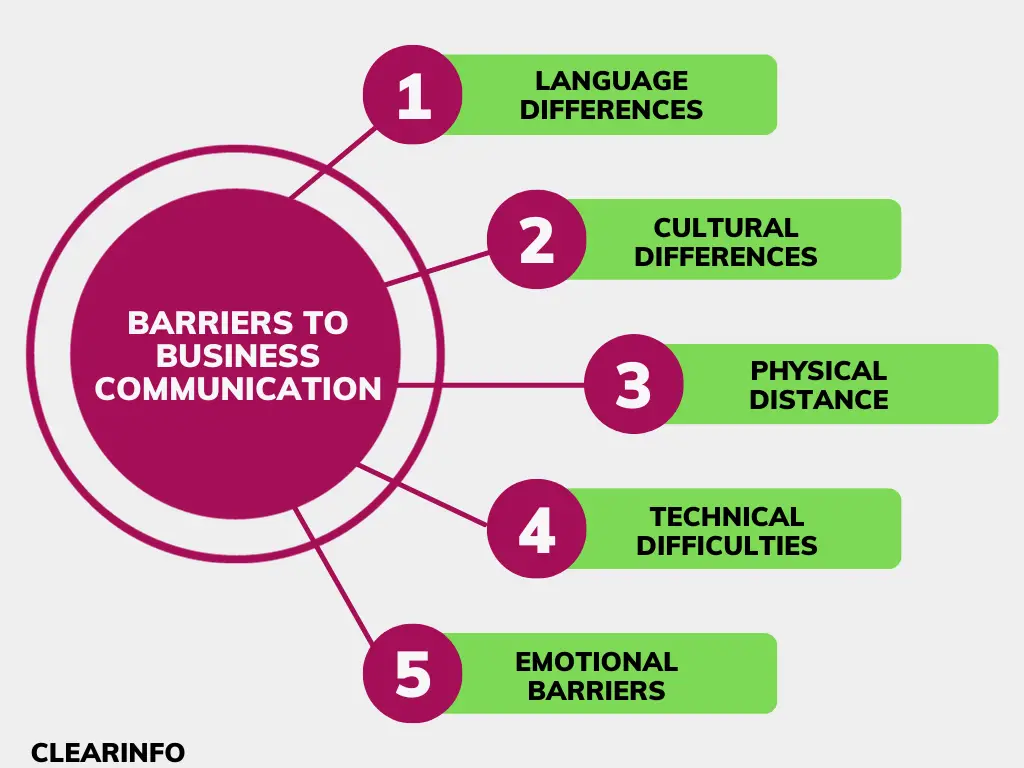
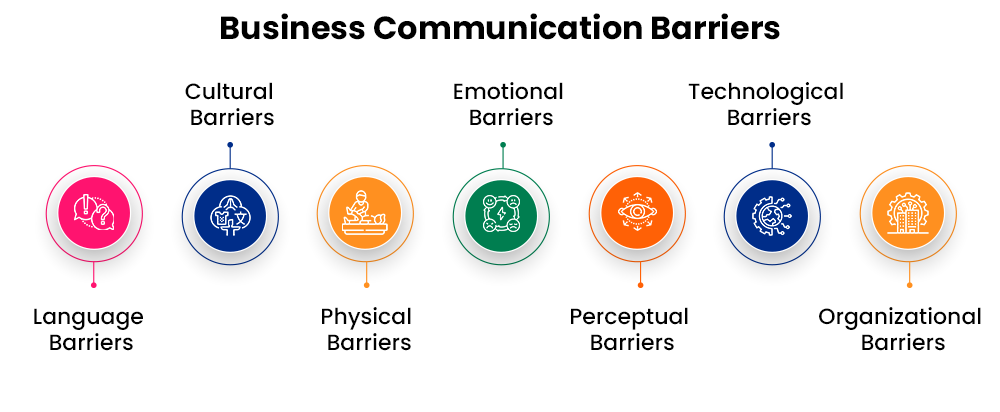
Language and Jargon
Multinational corporations grapple with linguistic differences, often necessitating costly translation services and dedicated interpreters. Even within a single language, industry-specific jargon can create a divide between departments and external stakeholders.
Cultural Differences
Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory underscores the impact of cultural norms on communication styles. Varying levels of directness, formality, and nonverbal cues can lead to misinterpretations and strained relationships.
Technological Overload and Misuse
While technology offers numerous communication channels, its overuse can be counterproductive. Email overload, constant notifications, and poorly managed virtual meetings contribute to information fatigue and decreased attention spans.
Lack of Active Listening
A critical yet often overlooked barrier is the failure to actively listen. Employees may be preoccupied with formulating responses instead of fully absorbing the speaker's message, leading to misinterpretations and flawed decision-making.
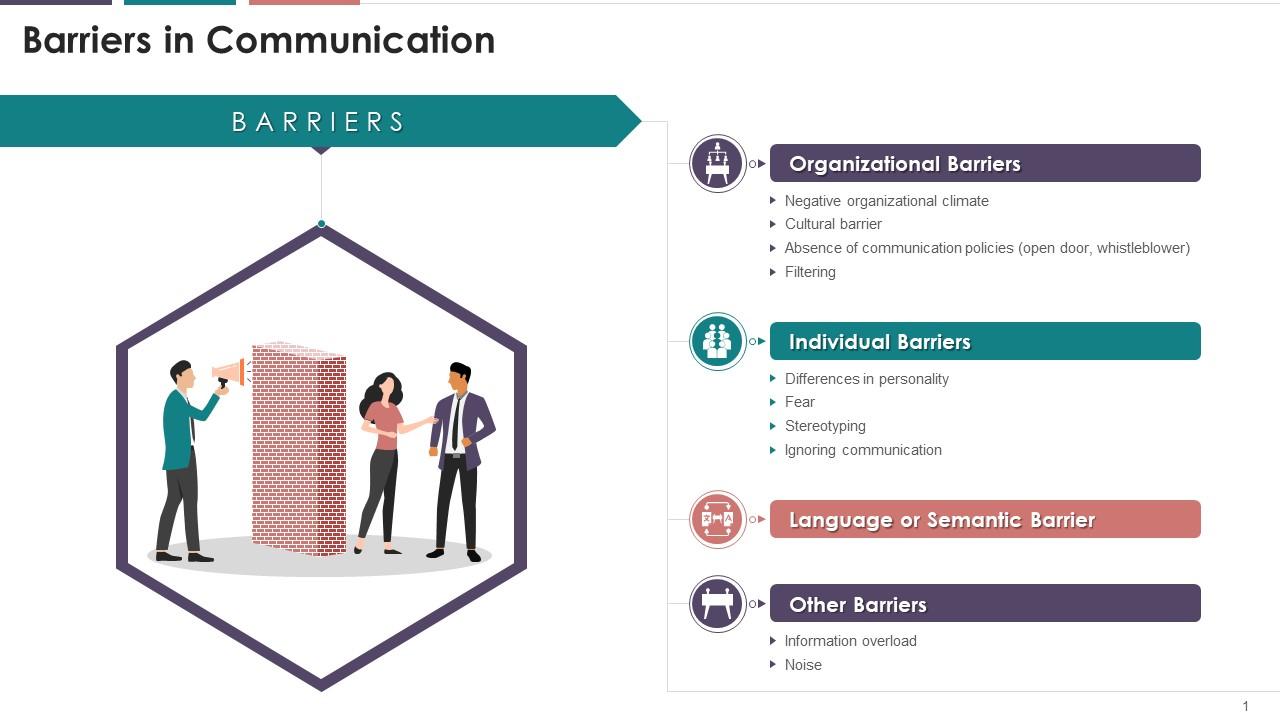
Hierarchical Structures
Rigid hierarchies can stifle open communication, particularly when junior employees feel intimidated to voice concerns or challenge senior management. This top-down approach can limit the flow of information and hinder innovation.
Impact Across Departments: Case Studies
In marketing, unclear communication between creative teams and account managers can result in off-brand campaigns and missed target audiences. This disconnect translates directly into reduced sales and brand damage.
Human resources suffers from miscommunication regarding employee benefits, policies, and performance expectations, fostering dissatisfaction and legal vulnerabilities.
Sales departments, plagued by poor communication between field representatives and headquarters, often face inconsistencies in messaging and pricing, impacting customer acquisition and retention.
"Communication is a skill that you can learn. It's like riding a bicycle or typing. If you're willing to work at it, you can rapidly improve the quality of every part of your life." - Brian Tracy
The Way Forward: Strategies for Improvement
Companies must prioritize communication training programs for all employees, focusing on active listening, intercultural communication, and effective written/verbal skills.
Implementing clear communication protocols and guidelines is crucial, establishing preferred channels for different types of information and setting expectations for response times.
Leveraging technology strategically, rather than allowing it to overwhelm, involves utilizing project management software, collaborative platforms, and video conferencing tools to enhance transparency and streamline communication.
Encouraging open-door policies and feedback mechanisms creates a culture of psychological safety, fostering a willingness among employees to share ideas, concerns, and suggestions without fear of reprisal.
Immediate Action Required
The cost of inaction is simply too high. Businesses must urgently assess their current communication practices, identify key barriers, and implement targeted strategies for improvement.
Ongoing monitoring and evaluation of communication effectiveness are essential to ensure continuous progress and adapt to evolving business needs. Failure to address these critical issues will inevitably lead to further financial losses and competitive disadvantage.