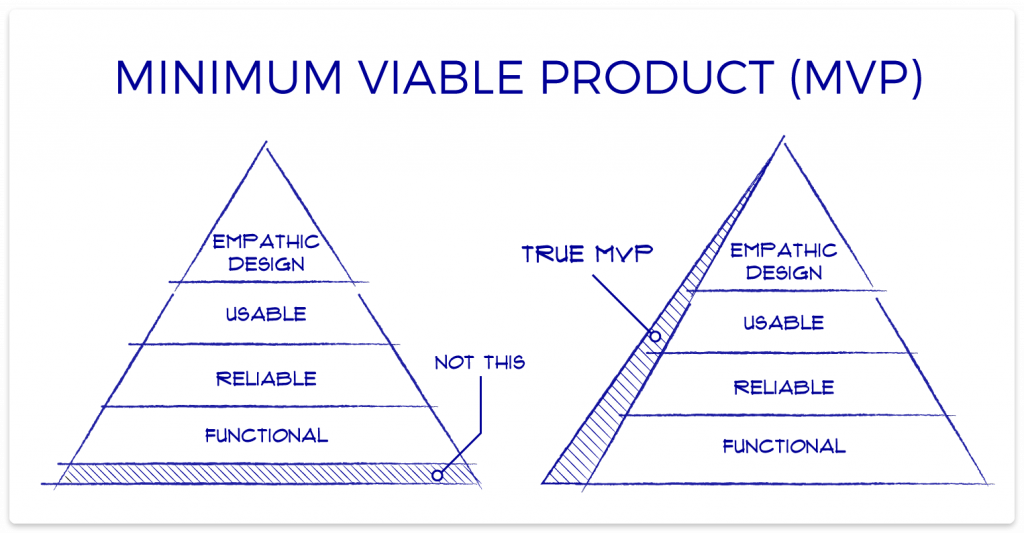
Definition Of Viability In Business

In the complex world of business, "viability" is a term thrown around frequently, but its true meaning often gets lost in the shuffle. Understanding what truly makes a business viable is crucial for entrepreneurs, investors, and even consumers. But what is it?
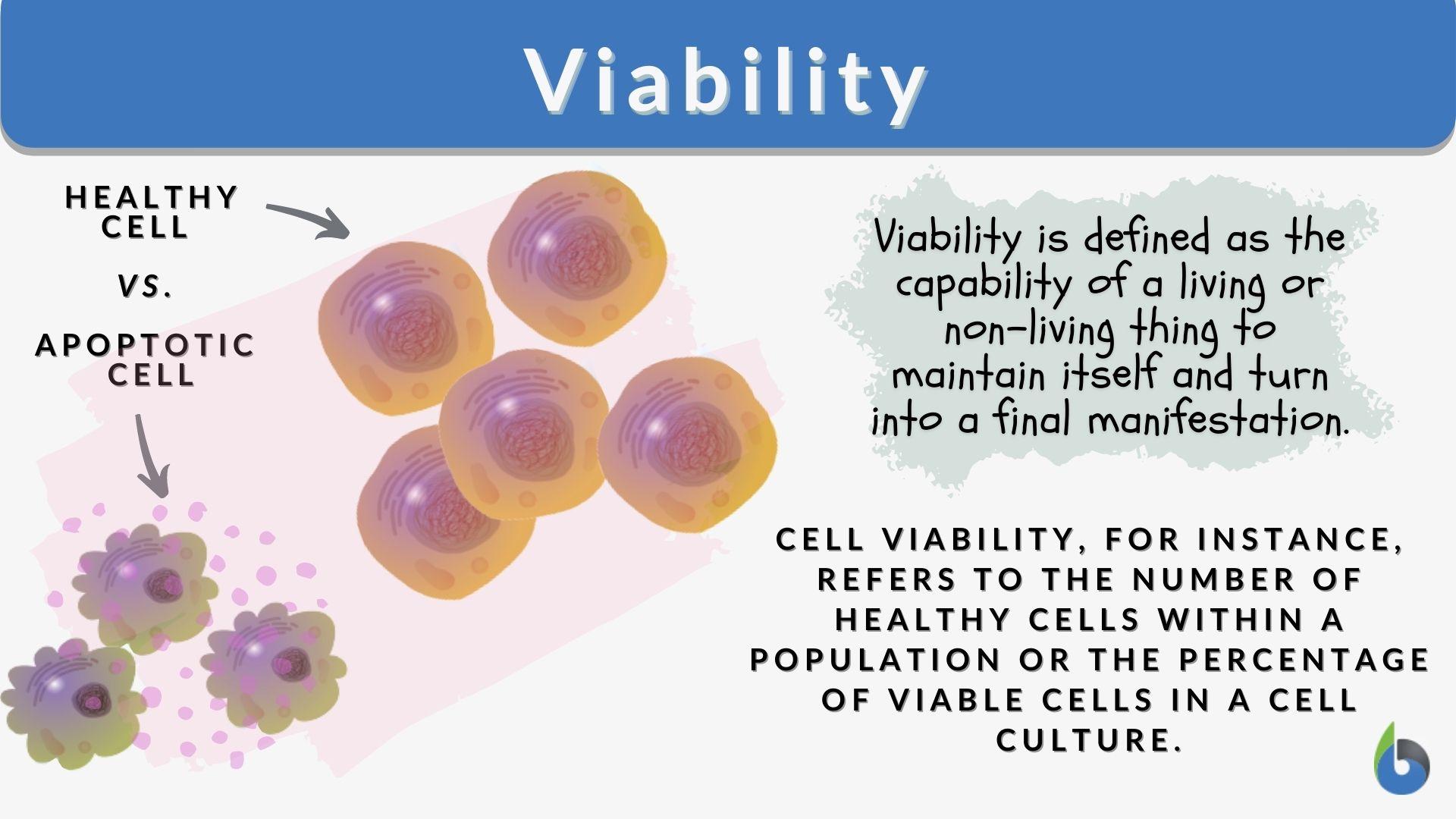
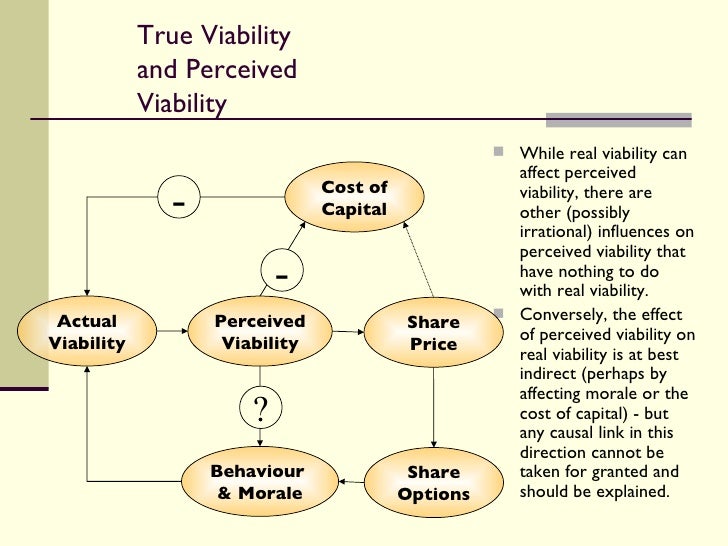
At its core, viability in business refers to the ability of an enterprise to sustain itself and thrive over the long term. This encompasses financial stability, operational efficiency, market relevance, and adaptability to change. It is a complex interplay of factors that determine whether a business can not only survive but also prosper.
Defining Viability: A Multifaceted Approach
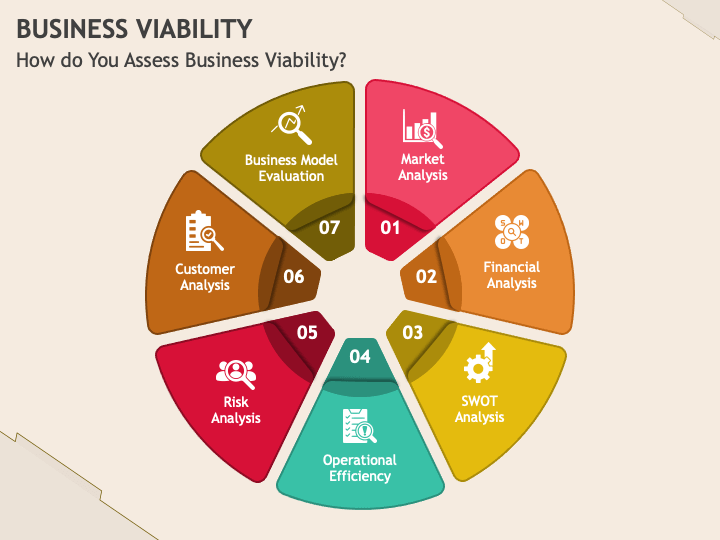
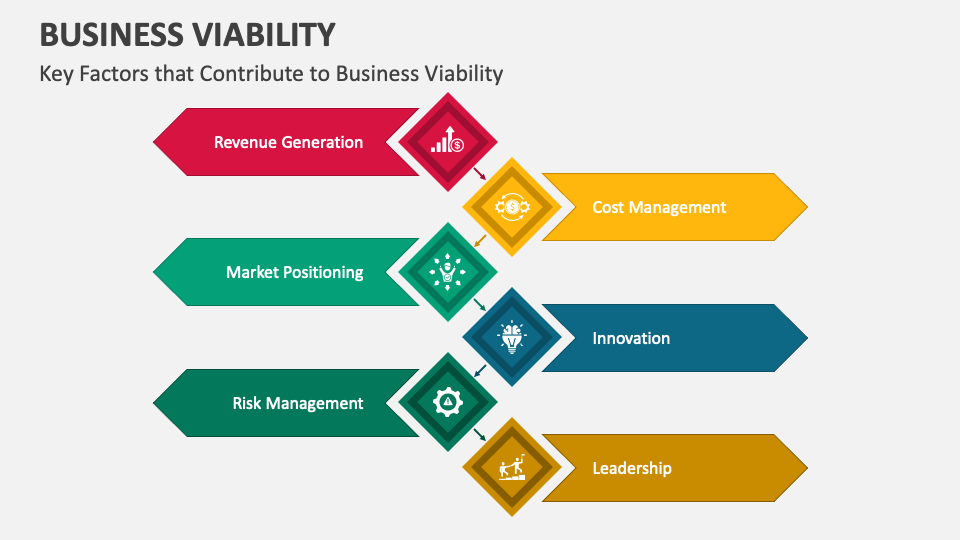
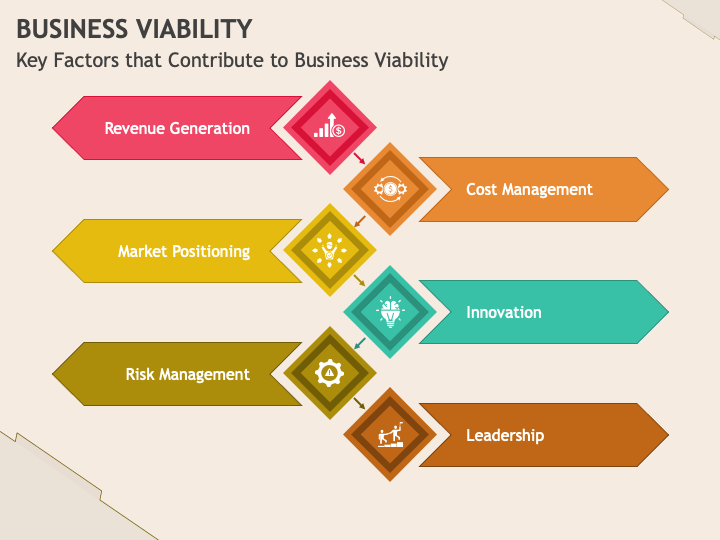
Viability isn't just about making a profit in the short term. It requires a holistic assessment considering several key components. These include financial sustainability, market demand, operational efficiency, and adaptability.
Financial Sustainability
A financially viable business generates sufficient revenue to cover its expenses, including salaries, rent, and the cost of goods sold. It also requires a healthy cash flow to manage short-term obligations and invest in future growth.
Profitability is a crucial metric, but it's not the only one. Factors like debt levels, access to capital, and effective financial management are equally important.
Market Demand
A viable business addresses a real need or desire in the market. This requires a thorough understanding of the target audience, the competitive landscape, and emerging trends.
Market research, customer feedback, and competitor analysis are crucial for assessing and maintaining market relevance.
Operational Efficiency
Efficiency in operations is critical for viability. Streamlined processes, effective resource allocation, and cost management are crucial.
Technology, automation, and a skilled workforce contribute significantly to operational efficiency. Businesses like Amazon have based their strategies upon these.
Adaptability
The business world is constantly evolving, so businesses must adapt to survive. This includes embracing new technologies, responding to changing customer preferences, and adjusting to economic shifts.
A company’s ability to innovate and anticipate future challenges is a key indicator of its long-term viability.
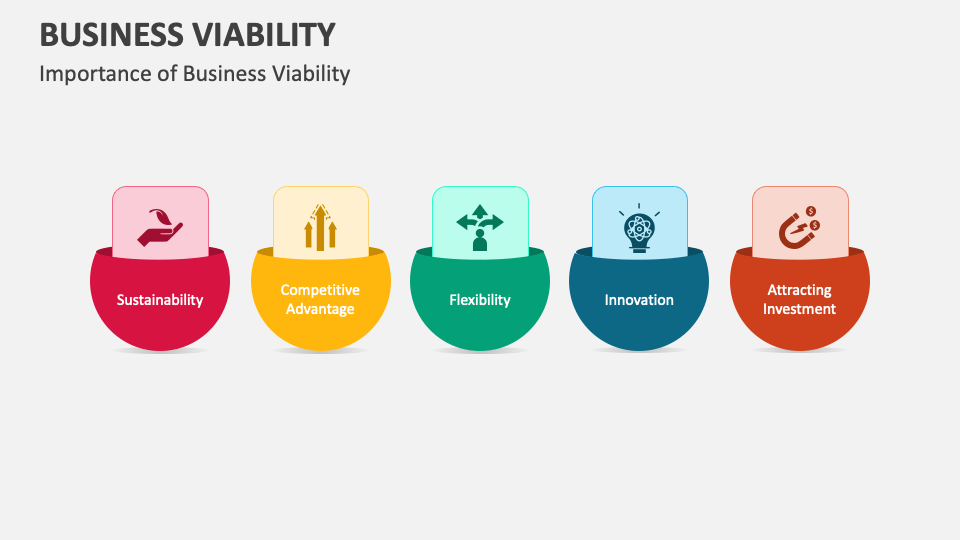
Why Viability Matters
Understanding the concept of viability is crucial for a multitude of stakeholders. For entrepreneurs, it's the foundation upon which they build their dreams. For investors, it’s a critical factor in determining where to allocate capital. For consumers, it signifies trust in a reliable product or service.
A viable business contributes positively to the economy, creating jobs and stimulating innovation. Conversely, businesses lacking viability can experience failure and negatively impact the market.
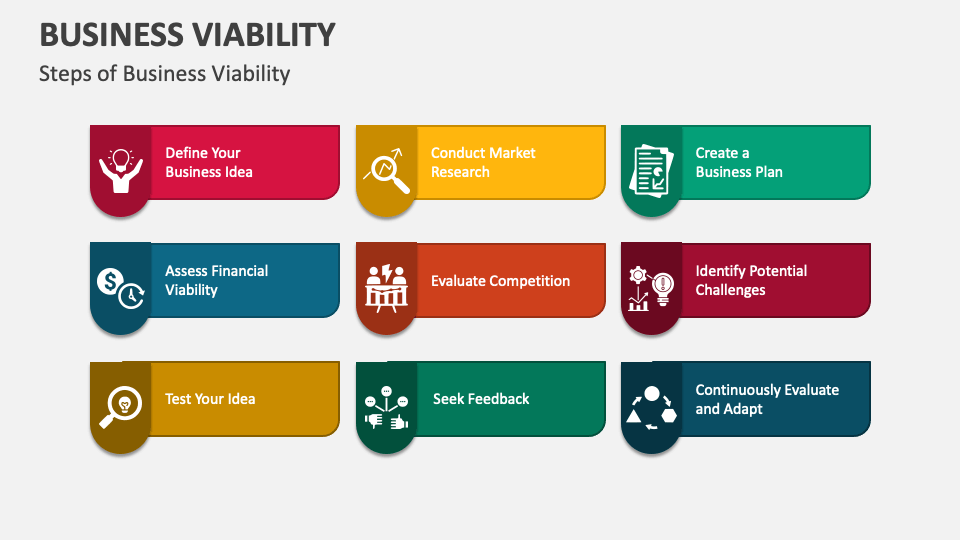
Assessing Viability: Key Indicators
Several key performance indicators (KPIs) can help assess a business's viability. These include profit margins, return on investment (ROI), customer retention rates, and market share.
Analyzing these metrics provides valuable insights into a company’s financial health, operational efficiency, and market competitiveness.
For example, a consistently high customer retention rate suggests a strong value proposition and customer satisfaction, contributing to long-term viability.
The Human Element
Beyond the numbers and data, the human element plays a vital role in business viability. A strong leadership team, a skilled and motivated workforce, and a positive company culture can significantly impact an enterprise's ability to succeed.
Employee engagement, innovation, and adaptability are all influenced by the human element. Steve Jobs once said "Great things in business are never done by one person. They’re done by a team of people."
The Path Forward
In conclusion, viability is not a static state but a dynamic process that requires continuous monitoring, adaptation, and improvement. By understanding and addressing the key factors that contribute to viability, businesses can increase their chances of long-term success and create lasting value for their stakeholders.
As the business landscape becomes increasingly complex and competitive, a keen focus on viability is more critical than ever before.