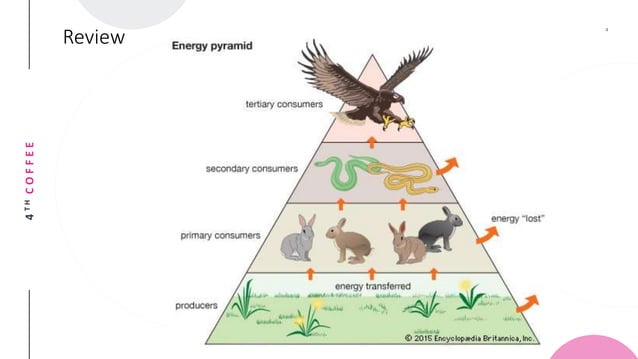
Determine The Stability Of Each Ecosystem.

Global ecosystems are facing unprecedented instability, threatening biodiversity and human well-being. Rapid assessments are now critical to pinpoint vulnerable areas and deploy immediate conservation efforts.
This article details the critical need for urgent ecosystem stability assessments, focusing on the methodologies being employed and the alarming trends identified across various biomes. Actionable data is crucial for informed interventions to mitigate further ecological damage.
Ecosystem Instability: A Global Crisis
Researchers are deploying a multi-pronged approach to determine the stability of ecosystems worldwide. This involves analyzing biodiversity metrics, climate data, and human impact assessments.
The urgency stems from increasing habitat loss, climate change impacts, and pollution levels. These factors are destabilizing ecosystems at an alarming rate, demanding immediate attention.
Assessing Vulnerability: Methods and Data
Biodiversity indices, such as species richness and evenness, are key indicators. Declining numbers and skewed distributions often signal instability.
Climate data, including temperature fluctuations and precipitation patterns, are vital. Extreme weather events are increasingly stressing ecosystems beyond their capacity to recover.
Human impact assessments consider factors like deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural practices. These activities directly contribute to habitat fragmentation and resource depletion.
Case Study: The Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon Rainforest, a vital carbon sink, is showing signs of severe instability. Deforestation rates are climbing, driven by agricultural expansion and illegal logging.
Rising temperatures and altered rainfall patterns are exacerbating the situation. This is leading to increased drought frequency and intensity.
The potential for the Amazon to transition from a rainforest to a savanna-like ecosystem is a major concern. This shift would have catastrophic consequences for global climate and biodiversity.
Case Study: Coral Reefs Worldwide
Coral reefs are bleaching at unprecedented rates due to rising ocean temperatures. Ocean acidification, caused by increased atmospheric carbon dioxide, further weakens coral structures.
These factors are killing coral colonies, disrupting reef ecosystems, and threatening the livelihoods of millions who depend on them.
Some reefs are showing signs of resilience, but these are increasingly rare. Immediate action to reduce carbon emissions is crucial for their long-term survival.
Case Study: Arctic Tundra
The Arctic tundra is experiencing rapid warming, leading to permafrost thaw. This releases vast amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, further accelerating climate change.
Changes in vegetation cover and animal migration patterns are also observed. The delicate balance of the Arctic ecosystem is being fundamentally altered.
Indigenous communities are experiencing significant impacts on their traditional way of life. They are also at the forefront of monitoring and adapting to these changes.
Intervention Strategies and Ongoing Efforts
Conservation efforts focus on habitat restoration, protected area management, and sustainable resource use. These initiatives aim to enhance ecosystem resilience and promote biodiversity.
Climate change mitigation strategies, such as reducing carbon emissions and promoting renewable energy, are essential. These efforts address the root causes of ecosystem instability.
International collaboration is crucial for effective ecosystem management. Global agreements and partnerships are needed to address transboundary environmental challenges.
"The speed and scale of ecosystem degradation demand immediate and coordinated action," stated Dr. Evelyn Reed, lead ecologist at the Global Ecosystem Monitoring Initiative. "We must prioritize interventions based on the most vulnerable ecosystems and implement solutions that address both local and global drivers of instability."
Next Steps and Future Outlook
Ongoing research aims to refine ecosystem stability assessments and develop more effective intervention strategies. This includes incorporating advanced technologies like remote sensing and artificial intelligence.
Public awareness campaigns are essential to educate individuals about the importance of ecosystem conservation. Empowering communities to take action is crucial for achieving long-term sustainability.
The future of global ecosystems depends on our collective commitment to protecting and restoring these vital natural systems. Failure to act now will have irreversible consequences for future generations.

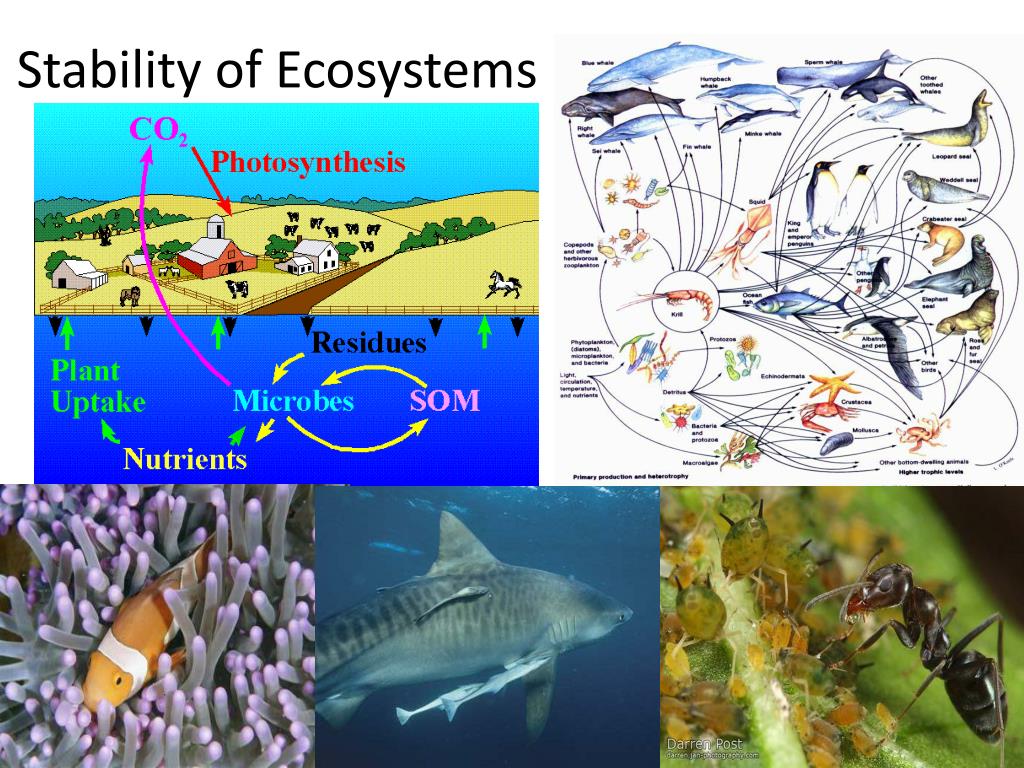

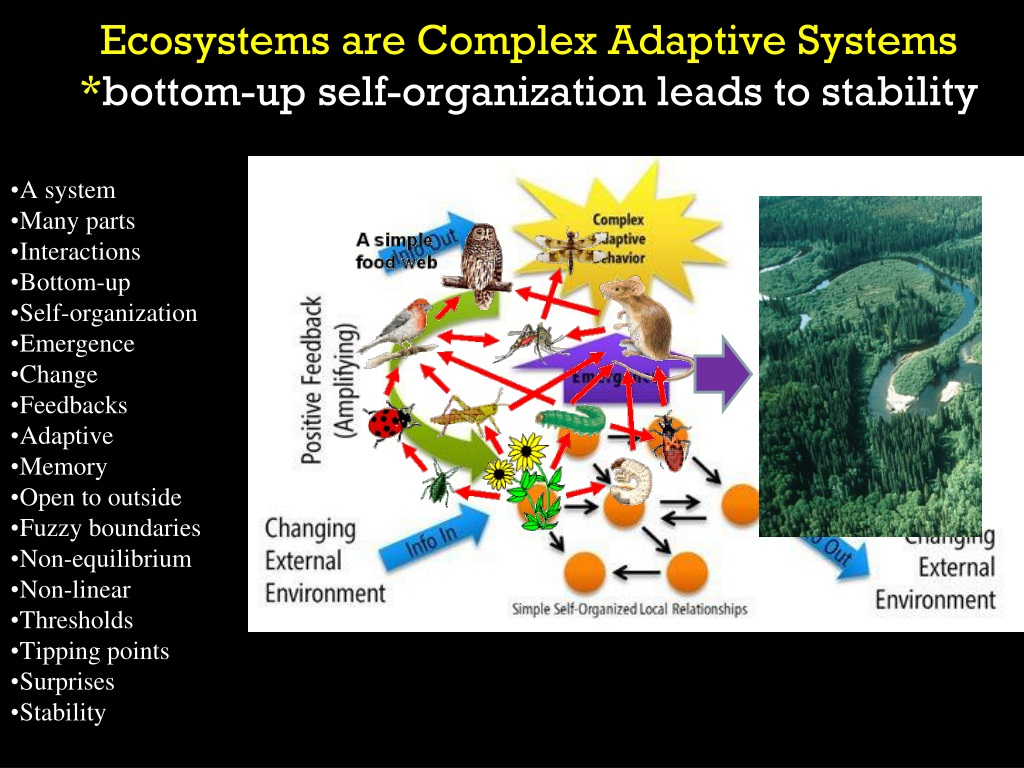
+How+does+great+biodiversity+maintain+ecosystem+stability.jpg)

![Determine The Stability Of Each Ecosystem. [FREE] Determine the stability of each ecosystem - brainly.com](https://media.brainly.com/image/rs:fill/w:750/q:75/plain/https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/d43/711482c9a002d32457ae30b96316e43b.png)

+What+happens+to+an+ecosystem+when+biodiversity+decreases.jpg)