Difference Between Low Self Esteem And Insecurity

Millions struggle daily, mistaking low self-esteem for insecurity, leading to ineffective coping mechanisms and delayed recovery. Understanding the distinction is crucial for targeted interventions and improved mental well-being.
Unpacking the Core Differences
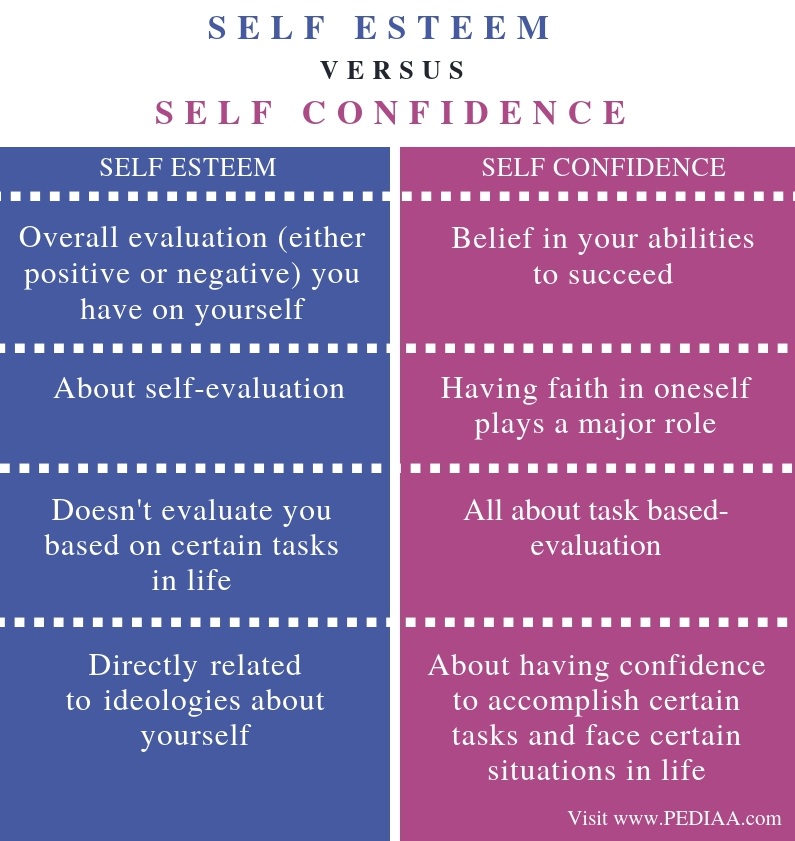
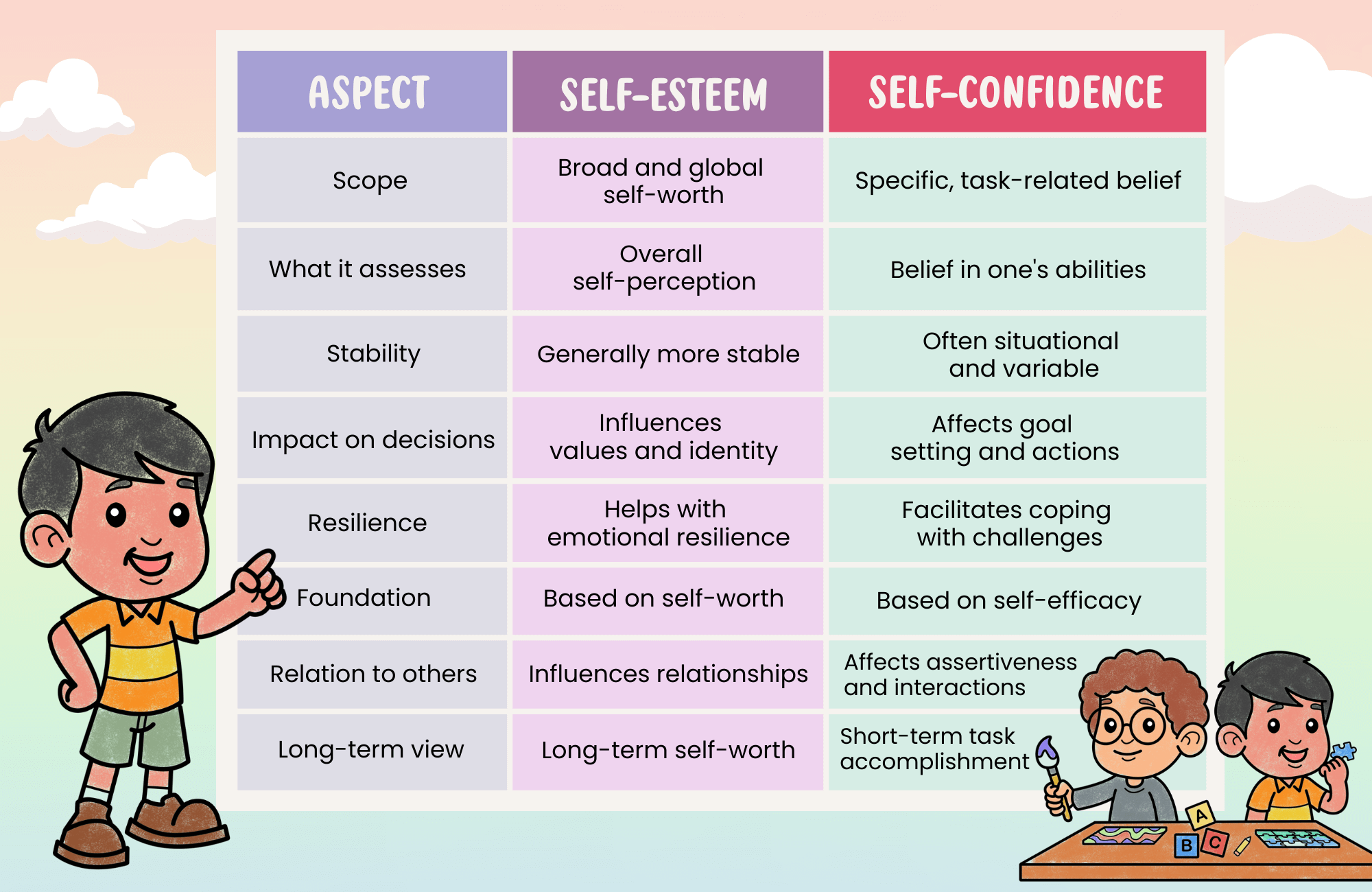
Insecurity stems from a fear of specific outcomes or situations. It's often triggered by external factors like social interactions or professional performance.
Low self-esteem, however, is a pervasive negative self-perception. This negative perception influences all aspects of an individual's life.
Insecurity: A Situational Response
Insecurity manifests as anxiety related to perceived threats or uncertainties. These threats can be real or imagined.
A 2023 study by the American Psychological Association (APA) revealed that 68% of adults report feeling insecure in social situations at least occasionally. Insecurity could come from fear of judgement to comparison.
Triggers include public speaking, dating, or job interviews.
Low Self-Esteem: A Global Self-Assessment
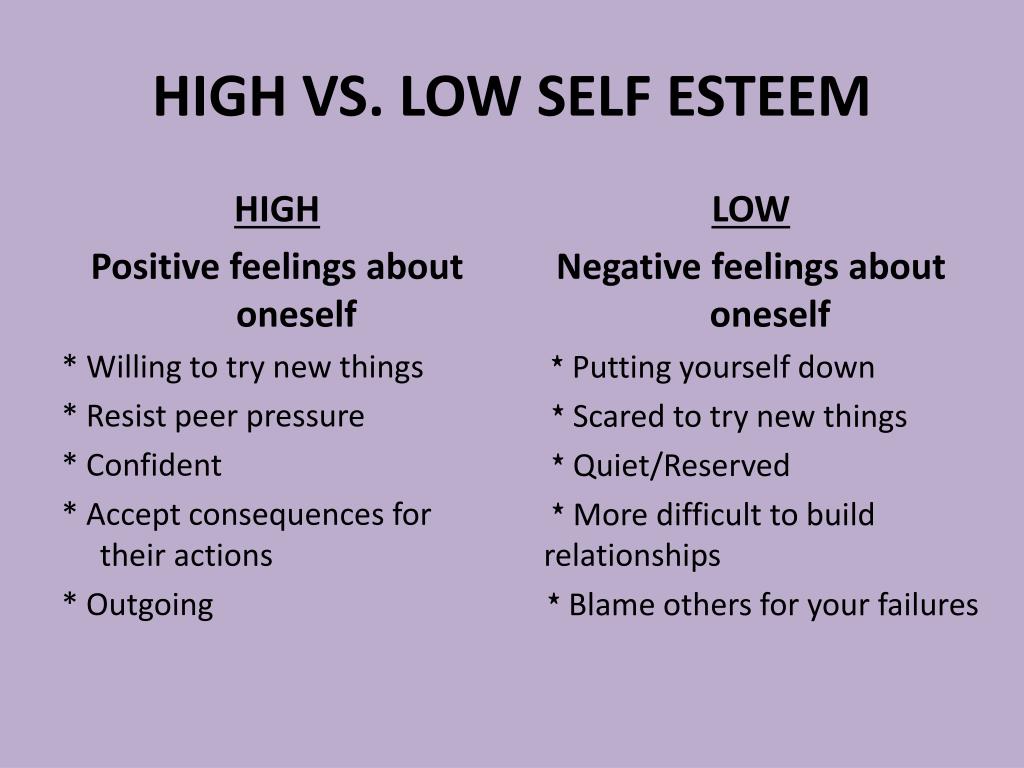
Low self-esteem reflects a belief that one is fundamentally inadequate or unworthy.
It’s a deeply ingrained feeling. It is less about specific events and more about an overall sense of self-worth.
Individuals with low self-esteem often criticize themselves harshly. They also have difficulty accepting compliments.
Key Distinctions in Behavior
Insecure individuals might engage in behaviors to seek reassurance. These behavior help them mitigate immediate anxiety.
According to a 2022 survey by Mental Health America (MHA), people with low self-esteem exhibit greater rates of social withdrawal and depression.
In contrast, those with low self-esteem may avoid challenges altogether. It is driven by a fear of failure or reinforcing their negative self-image.
Impact on Relationships
Insecurity can lead to clinginess or jealousy in relationships. This is due to the fear of abandonment.
Low self-esteem often results in difficulty forming and maintaining healthy relationships. It is because of a belief they are undeserving of love and respect.
"Understanding these differences is the first step to effective treatment," states Dr. Emily Carter, a leading psychologist at the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH).
Treatment Approaches
Therapy focuses on addressing the root causes. It teaches coping mechanisms to manage these negative feelings.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is often effective for addressing both insecurity and low self-esteem.
CBT helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns.
Seeking Professional Help
If feelings of insecurity or low self-esteem are persistent and interfering with daily life, seeking professional help is crucial.
Resources like the SAMHSA National Helpline provide confidential support and referrals.
Early intervention can prevent these issues from escalating into more serious mental health conditions.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Researchers are actively exploring the neurological underpinnings of self-esteem. The research may pave the way for innovative treatments.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is currently funding several studies to investigate the long-term effects of low self-esteem. The study is exploring the effects on physical and mental health.
Continued research and public awareness campaigns are vital to destigmatize mental health challenges. Further work will support those struggling with insecurity and low self-esteem.