Difference Between Verizon 5g And 5g Ultra Wideband

The promise of 5G has been transformative: blazing-fast download speeds, near-instantaneous responsiveness, and a revolution in connectivity. But the reality is that not all 5G is created equal. Consumers are increasingly finding that the 5G experience varies significantly, particularly when it comes to carriers like Verizon, where the distinction between standard 5G and 5G Ultra Wideband is crucial.
This difference isn't merely a marketing ploy; it represents fundamentally different technologies with vastly different capabilities and user experiences. Understanding the nuances between Verizon's 5G flavors is essential for consumers making purchasing decisions, developers building applications, and businesses planning their technological futures. This article delves into the technical underpinnings, performance variations, availability, and real-world implications of Verizon's 5G and 5G Ultra Wideband networks.
The Nut Graf: Understanding the Core Difference
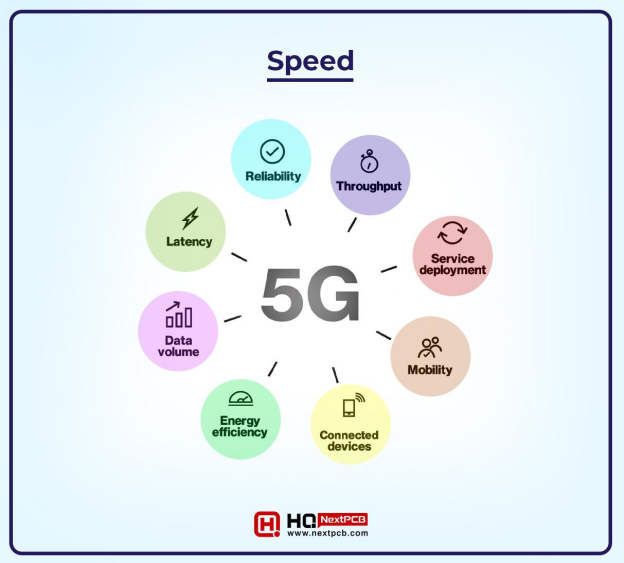
At its core, the distinction between Verizon 5G and 5G Ultra Wideband (UW) boils down to the radio frequencies used. Standard 5G primarily utilizes low-band and mid-band spectrum, offering broader coverage but comparatively slower speeds. Conversely, 5G Ultra Wideband relies on millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum, which delivers extremely high speeds but with limited range and penetration.
This means that while you might see a "5G" icon on your phone, the actual performance can vary wildly depending on whether you're connected to the standard 5G network or the coveted 5G Ultra Wideband network.
Deep Dive: Frequency Bands and Their Impact
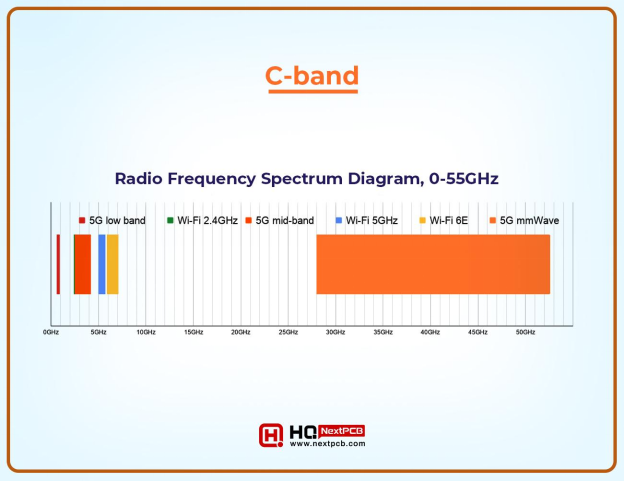
Low-band spectrum (below 1 GHz) is the workhorse for broad coverage. Verizon's low-band 5G provides relatively good reach, penetrating buildings and traveling long distances. However, speeds are often only marginally better than 4G LTE, providing a more consistent, but not groundbreaking, experience.
Mid-band spectrum (1 GHz to 6 GHz) strikes a balance between coverage and speed. This is often considered the "sweet spot" for 5G, offering a significant improvement over 4G LTE while maintaining reasonable coverage. Verizon has been aggressively deploying mid-band 5G, including through its acquisition of C-band spectrum, to enhance its network capabilities.
Millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum (above 24 GHz) is where 5G Ultra Wideband lives. This spectrum offers incredibly high bandwidth, enabling theoretical speeds of several gigabits per second. The catch is that mmWave signals are easily blocked by obstacles like walls, trees, and even weather, resulting in a much smaller coverage area.
Performance Benchmarks: Speed and Latency
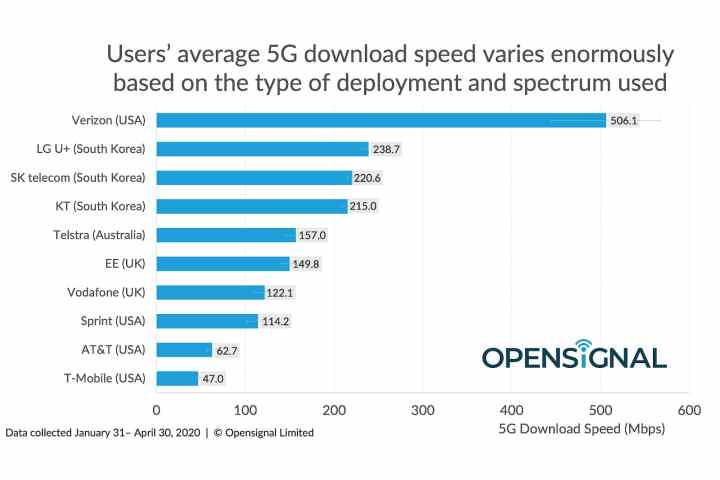
Independent testing consistently demonstrates the significant performance gap between Verizon's 5G and 5G Ultra Wideband. Standard 5G speeds often range from 50 Mbps to 200 Mbps, depending on network congestion and location. Latency, the delay in data transfer, is also improved over 4G LTE but not drastically so.
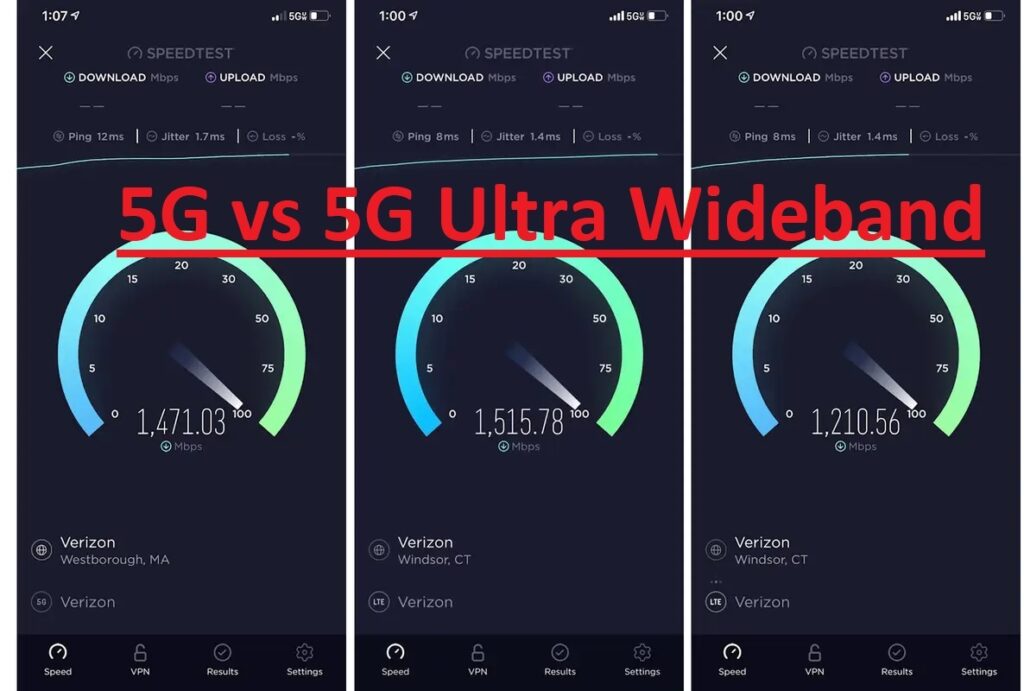
In contrast, 5G Ultra Wideband can deliver speeds exceeding 1 Gbps, and even reaching several Gbps in ideal conditions. Latency is significantly reduced, often dropping to single-digit milliseconds, enabling near-real-time responsiveness for applications like gaming and augmented reality.
These numbers are not just theoretical; they translate into tangible improvements in user experience. Downloading large files, streaming 4K video, and participating in interactive applications become seamless and instantaneous with 5G Ultra Wideband.
Coverage and Availability: A Tale of Two Networks
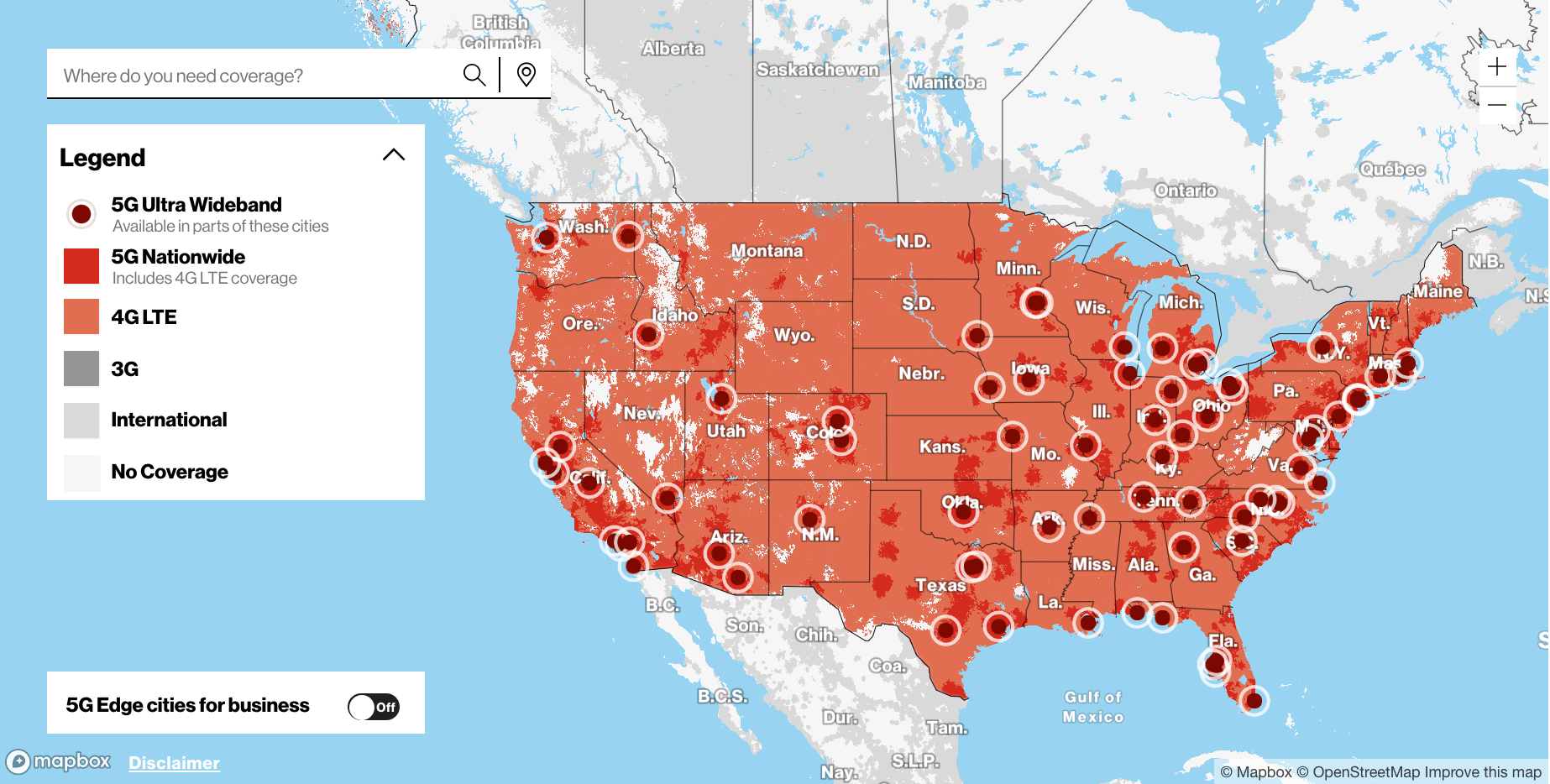
The limited range of mmWave technology means that 5G Ultra Wideband coverage is highly localized. Verizon has primarily deployed it in dense urban areas, stadiums, airports, and other high-traffic locations. This means that even within a city, 5G Ultra Wideband availability can be spotty.
Standard 5G, leveraging low-band and mid-band spectrum, offers a much broader footprint. You're more likely to find standard 5G coverage in suburban and rural areas, though speeds may be slower compared to 5G Ultra Wideband in urban centers.
Verizon's website and coverage maps provide information on 5G availability, but it's crucial to check specific locations and understand the type of 5G network available to avoid disappointment. Customer feedback and third-party testing are also valuable resources for gauging real-world coverage.
Real-World Implications: Use Cases and Applications
The difference in performance between Verizon 5G and 5G Ultra Wideband has significant implications for various use cases. Standard 5G is suitable for general browsing, social media, and streaming standard-definition video.
5G Ultra Wideband unlocks more demanding applications. These include augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR), high-resolution video conferencing, cloud gaming, and industrial automation. The low latency and high bandwidth enable these applications to function smoothly and reliably.
Businesses can leverage 5G Ultra Wideband for applications like remote surgery, autonomous vehicles, and smart manufacturing. The high speeds and low latency enable real-time data processing and control, transforming industries and creating new opportunities.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Verizon's 5G Network
Verizon is actively working to expand its 5G coverage and improve network performance. This includes deploying more mid-band spectrum and densifying its 5G Ultra Wideband network with more small cells. Network densification is adding more, smaller base stations to increase coverage and capacity.
As Verizon continues to invest in its 5G infrastructure, the gap between standard 5G and 5G Ultra Wideband may narrow over time. Technologies like carrier aggregation, which combines multiple frequency bands to increase bandwidth, will also play a crucial role in improving performance. The evolution of the 5G standard itself, with new features and capabilities being introduced in each iteration, will also drive improvements across the board.
Ultimately, understanding the difference between Verizon 5G and 5G Ultra Wideband is essential for making informed decisions about devices, plans, and applications. By staying informed about the latest developments in 5G technology, consumers and businesses can harness the full potential of this transformative technology.