Different Kinds Of Leadership Styles

The effectiveness of a leader isn't solely determined by their position, but significantly influenced by their approach. A one-size-fits-all mentality rarely succeeds, prompting leaders across industries to adopt and adapt various styles to navigate complex organizational landscapes. Understanding these diverse leadership styles is crucial for fostering productive teams and achieving organizational goals.
This article explores several prominent leadership styles, examining their defining characteristics, potential benefits, and drawbacks. It aims to provide insights for individuals seeking to understand their own leadership tendencies and for organizations striving to cultivate effective leadership at all levels. The choice of leadership style profoundly impacts employee morale, team dynamics, and ultimately, the success of the organization.
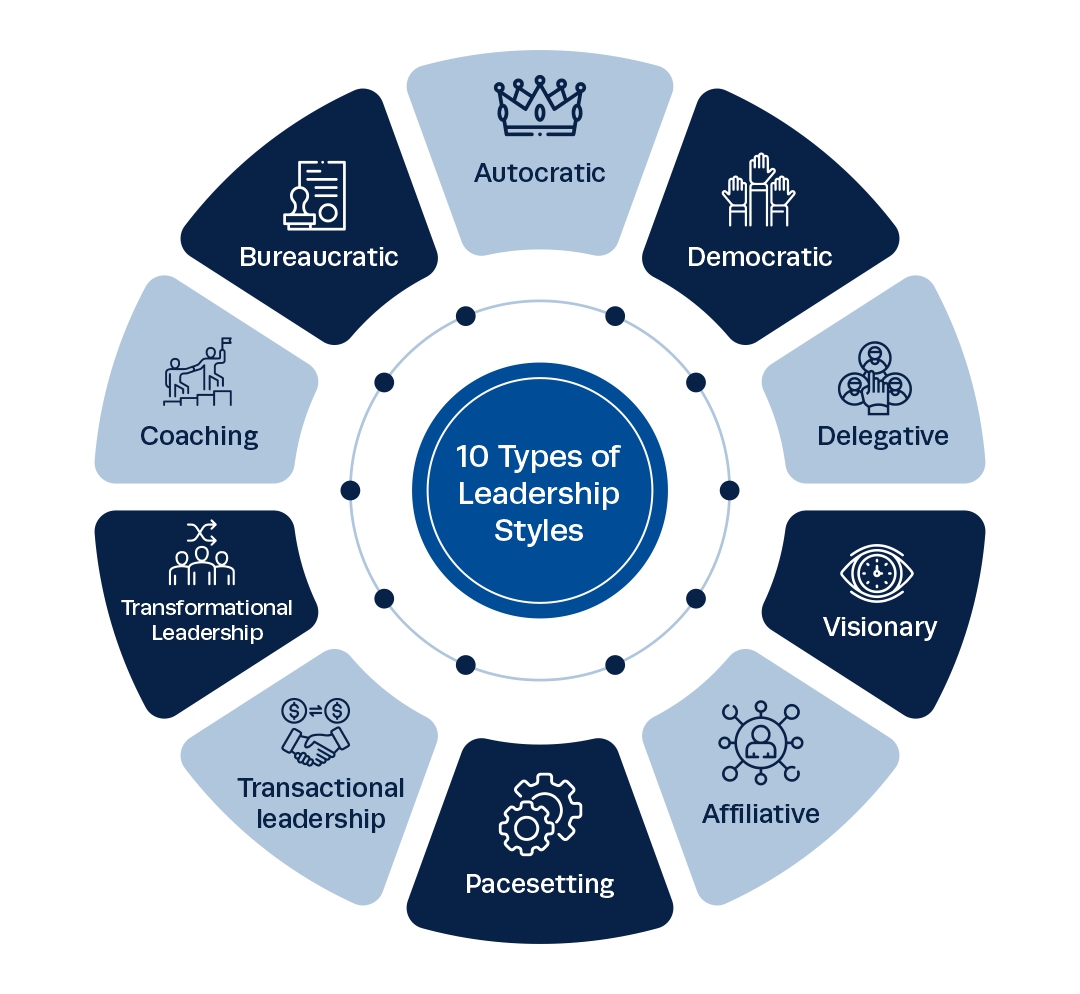
Common Leadership Styles
Transformational Leadership
Transformational leaders inspire and motivate their teams by articulating a clear vision and fostering a sense of purpose. They focus on individual development, encourage innovation, and challenge the status quo. This style, often associated with Jack Welch, former CEO of General Electric, can lead to increased employee engagement and organizational growth.
However, transformational leadership requires strong communication skills and a genuine commitment to employee well-being. If not executed authentically, it can be perceived as manipulative or insincere.
Transactional Leadership
In contrast to transformational leadership, transactional leadership focuses on managing performance through rewards and punishments. These leaders set clear expectations and monitor progress, intervening when deviations occur. Contingent reward and management by exception are core elements of this style.
Transactional leadership can be effective in stable environments with well-defined tasks, but it may stifle creativity and innovation. Critics argue that it only motivates employees to meet minimum requirements, not to exceed expectations.
Servant Leadership
Servant leadership prioritizes the needs of the team above the leader's own personal ambition. These leaders empower their followers, provide support, and foster a collaborative environment. Robert K. Greenleaf, who coined the term, emphasized the importance of service to others as the foundation of leadership.
This style can build strong relationships and foster a culture of trust and respect. However, it requires patience, empathy, and a willingness to relinquish control, which may not be suitable for all situations.
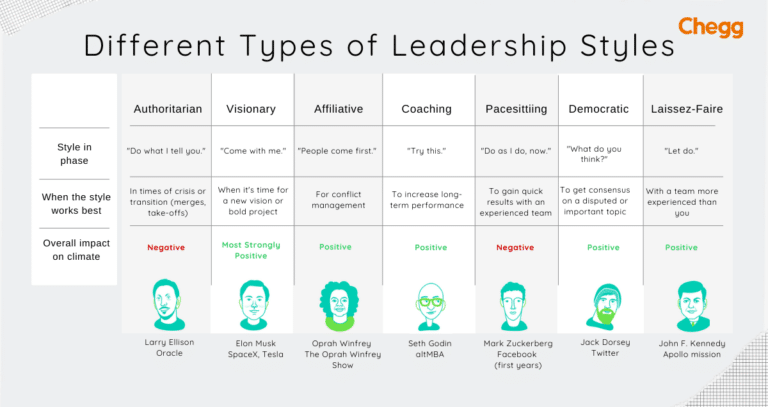
Autocratic Leadership
Autocratic leaders maintain strong control over decision-making and expect strict obedience from their followers. They typically make decisions unilaterally without seeking input from the team. This style is often seen in crisis situations where quick decisions are needed, or in highly structured environments like the military.
While autocratic leadership can be efficient in certain contexts, it can also stifle creativity, demotivate employees, and lead to a high turnover rate. The lack of employee input can result in resentment and a feeling of powerlessness.
Laissez-faire Leadership
Laissez-faire leaders provide minimal guidance and allow their teams a high degree of autonomy. They delegate responsibility and trust their followers to make decisions independently. This style can be effective with highly skilled and self-motivated teams.
However, laissez-faire leadership can lead to confusion, lack of direction, and poor performance if the team lacks the necessary skills or motivation. It requires careful selection of team members and ongoing monitoring to ensure accountability.
Democratic Leadership
Democratic leaders involve their team members in the decision-making process, valuing their input and perspectives. They foster collaboration and empower their followers to contribute to the organization's success. This style promotes a sense of ownership and encourages creativity and innovation.
While democratic leadership can lead to increased engagement and improved decision-making, it can also be time-consuming and inefficient in situations requiring quick action. The need to consider multiple perspectives can slow down the process.
The Importance of Context
The most effective leadership style is not static but rather adapts to the specific situation and the needs of the team. A leader may need to be autocratic in a crisis, democratic when brainstorming new ideas, and servant-oriented when supporting employee development. Adaptability is key.
Organizations should encourage leaders to develop a range of skills and be mindful of the impact their leadership style has on their team. Training programs and mentorship opportunities can help leaders hone their skills and learn to effectively navigate different situations.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of different leadership styles is essential for creating a positive and productive work environment. By embracing a flexible and adaptable approach, leaders can foster employee engagement, drive innovation, and ultimately achieve organizational success. The most effective leaders are those who can recognize the needs of their team and adjust their style accordingly to create an environment where everyone can thrive.