Digital Twin Technology Challenges And Applications A Comprehensive Review

In an era defined by rapid technological advancement, the concept of a perfect replica, existing not in the physical world but in the digital realm, is rapidly transforming industries. Digital twin technology, once relegated to the realm of science fiction, is now a tangible reality, promising unprecedented levels of efficiency, optimization, and predictive capability.
However, the path to widespread adoption is paved with significant challenges, ranging from data integration and security concerns to the need for skilled professionals and robust infrastructure.
This article delves into the multifaceted world of digital twins, examining its diverse applications, the hurdles hindering its widespread implementation, and the potential future trajectory of this groundbreaking technology.
What is a Digital Twin?
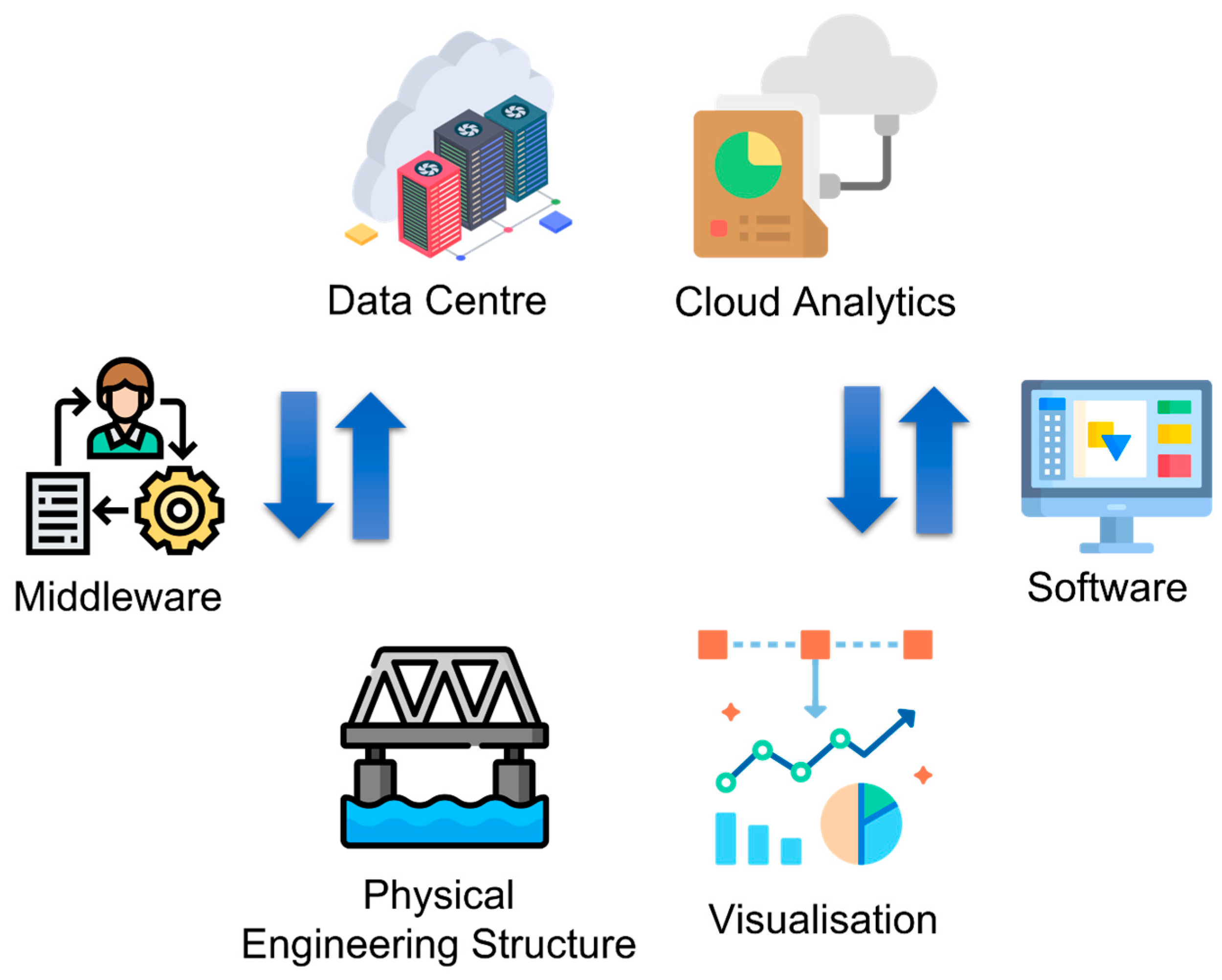
At its core, a digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical object or system. This representation is continuously updated with real-time data collected from sensors and other sources, allowing for continuous monitoring, analysis, and prediction of the physical entity's performance.
Unlike simple simulations, digital twins are dynamic and adaptive, evolving alongside their physical counterparts. This dynamic nature is what distinguishes them and unlocks their immense potential.
Applications Across Industries
The versatility of digital twin technology has led to its adoption across a wide spectrum of industries, each leveraging its capabilities in unique ways.
Manufacturing
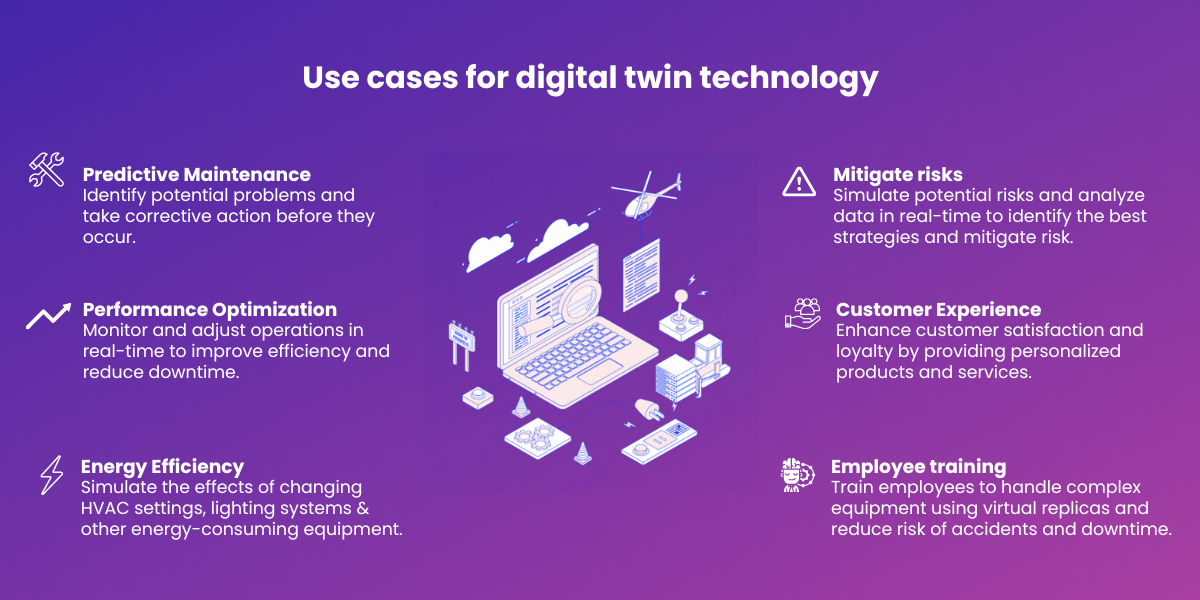
In manufacturing, digital twins are used to optimize production processes, predict equipment failures, and improve product quality. General Electric, for instance, utilizes digital twins to monitor and optimize the performance of its jet engines, reducing downtime and improving fuel efficiency.
By simulating various scenarios, manufacturers can identify potential bottlenecks, test new designs, and optimize resource allocation, leading to significant cost savings and increased productivity.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry is exploring the use of digital twins to personalize treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. A digital twin of a patient, created using medical imaging and sensor data, can be used to simulate the effects of different therapies and predict individual responses.
This approach allows doctors to tailor treatments to specific patient needs, minimizing risks and maximizing effectiveness. The Mayo Clinic is researching the use of digital twins to model and predict the progression of heart disease.
Infrastructure
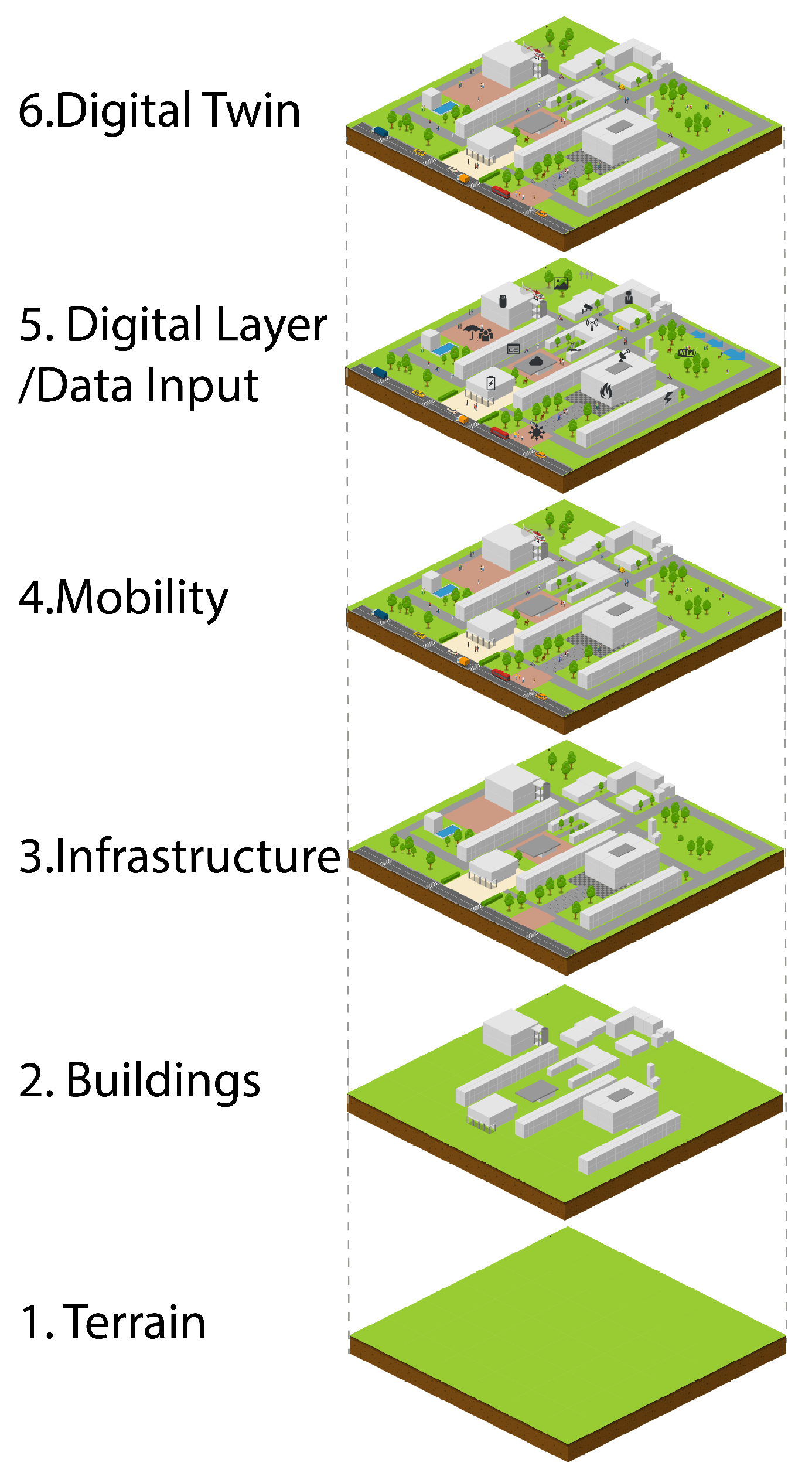
Digital twins are revolutionizing the way infrastructure is designed, built, and maintained. Cities are creating digital twins of their infrastructure networks, including roads, bridges, and utilities, to monitor their condition, predict maintenance needs, and optimize traffic flow.
The city of Singapore, for example, has developed a comprehensive digital twin to support urban planning and resource management.
This allows for proactive maintenance, minimizing disruptions and extending the lifespan of critical infrastructure.
Energy
The energy sector leverages digital twins to optimize the performance of power plants, manage renewable energy resources, and improve grid stability. Digital twins of wind turbines, for example, can be used to predict maintenance needs and optimize energy production based on weather conditions.
According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), digital twins can play a crucial role in accelerating the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy system.
Challenges to Adoption
Despite its immense potential, the widespread adoption of digital twin technology faces several significant challenges.
Data Integration and Interoperability
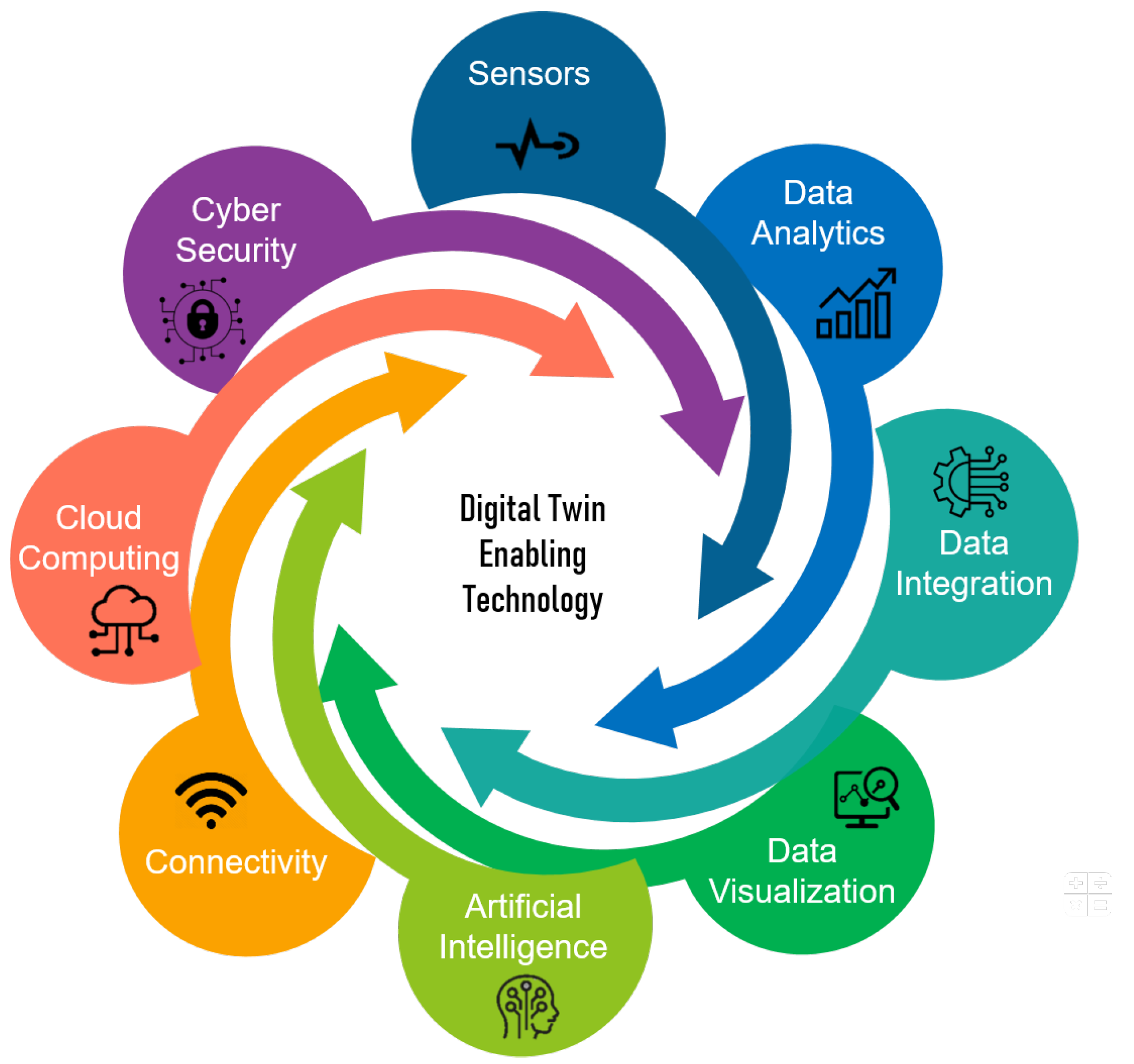
One of the biggest hurdles is the need to integrate data from diverse sources and systems. Digital twins rely on real-time data from sensors, databases, and other sources, which often use different formats and protocols.
Ensuring seamless data integration and interoperability is crucial for creating accurate and reliable digital twins. This often requires significant investment in data standardization and integration tools.
Data Security and Privacy
The collection and storage of vast amounts of data raise concerns about data security and privacy. Digital twins often contain sensitive information about physical assets and systems, making them attractive targets for cyberattacks.
Protecting this data requires robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems. Furthermore, compliance with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, is essential.
Skills Gap
The development and deployment of digital twins require a skilled workforce with expertise in data science, modeling, simulation, and software engineering. The current shortage of qualified professionals is a significant barrier to adoption.
Addressing this skills gap requires investment in education and training programs to equip individuals with the necessary skills to develop and manage digital twins.
Cost and Complexity
The initial investment in digital twin technology can be substantial, particularly for complex systems. The cost of sensors, software, and infrastructure can be prohibitive for some organizations.
Furthermore, the complexity of developing and maintaining digital twins requires specialized expertise and resources. As technology matures and costs decrease, adoption is expected to accelerate.
Scalability
Scaling digital twin deployments from individual assets to entire systems or networks presents a significant challenge. Managing and synchronizing data from a large number of interconnected digital twins requires robust infrastructure and sophisticated data management tools.
Organizations need to carefully consider the scalability of their digital twin solutions to ensure they can accommodate future growth and expansion.
The Future of Digital Twins
The future of digital twin technology is bright, with ongoing advancements promising to overcome current challenges and unlock even greater potential. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will further enhance the capabilities of digital twins, enabling them to learn from data, predict future outcomes, and optimize performance in real-time.
The increasing availability of cloud computing resources will make it easier and more cost-effective to deploy and manage digital twins, particularly for organizations with limited IT infrastructure. The standardization of data formats and protocols will improve interoperability and facilitate the creation of more complex and integrated digital twin ecosystems.
As the technology matures and adoption accelerates, digital twins are poised to become an indispensable tool for organizations across a wide range of industries. From optimizing manufacturing processes to personalizing healthcare treatments, the potential applications are virtually limitless.
Gartner predicts that by 2027, over 25% of large enterprises will be utilizing digital twins in their operational activities, showing a significant increase from the 2% reported in 2022.This showcases the exponential growth projected for this technology.
By embracing digital twin technology and addressing the associated challenges, organizations can unlock new levels of efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness in an increasingly digital world. The journey to the "perfect replica" is underway, promising a future where the physical and digital worlds are seamlessly intertwined.
.png)






![Digital Twin Technology Challenges And Applications A Comprehensive Review How Digital Twins and IoT Work Together [With Example]](https://a.storyblok.com/f/122804/3334x2083/64141b34f5/digital-twin-in-automotive-industry.webp)