Direct Lit Led-lcd Vs Full-array Led-lcd
The television market, already a complex landscape of competing technologies like OLED and QLED, presents consumers with numerous choices even within the LED-LCD category. Two common backlight technologies, Direct Lit and Full-Array Local Dimming (FALD), often leave buyers wondering about the actual differences and which option best suits their viewing needs.
This article aims to provide a clear and objective comparison of these two LED-LCD backlight technologies. We will explore the technical distinctions, performance characteristics, and practical implications of Direct Lit and Full-Array LED-LCD televisions.
Understanding the Backlight
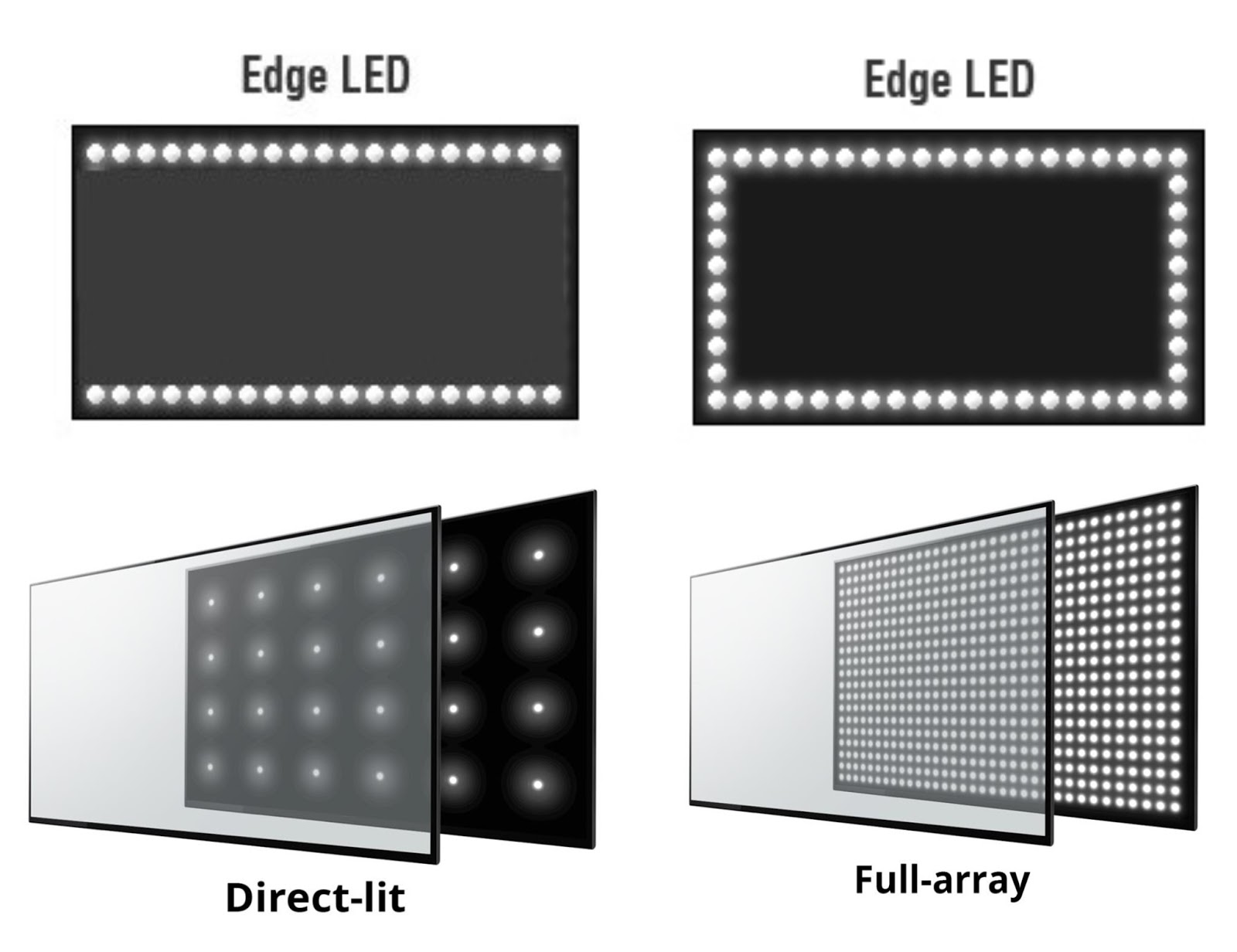
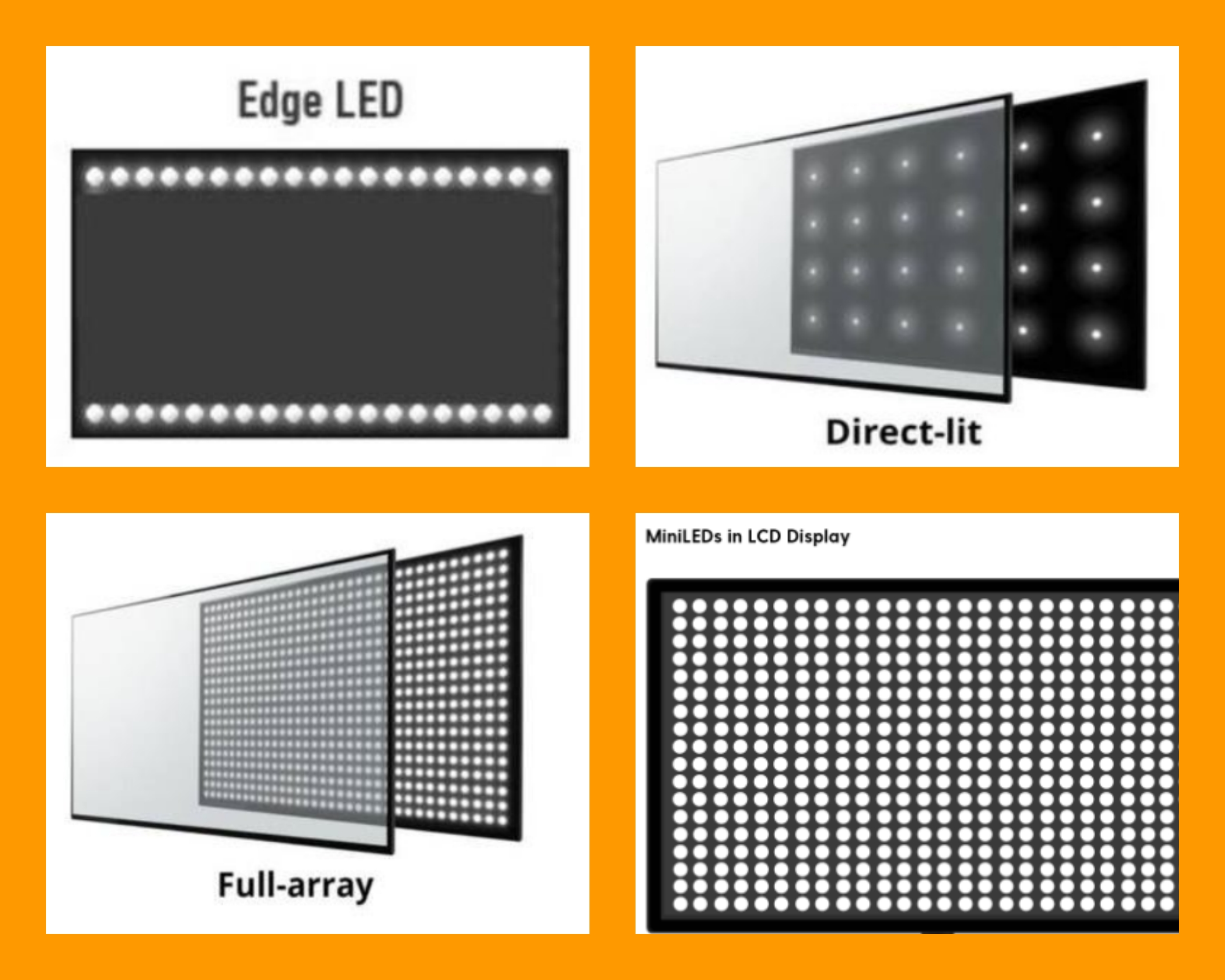
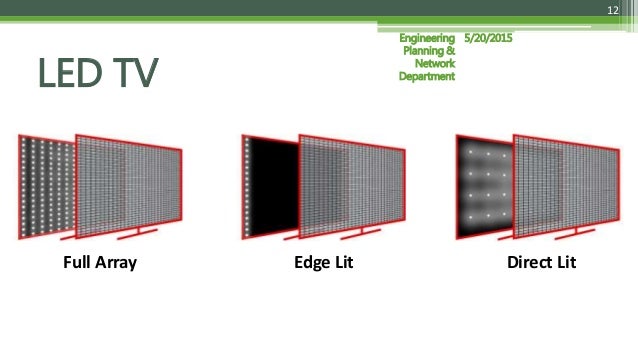
Both Direct Lit and Full-Array technologies fall under the broader category of LED-LCD TVs. The core difference lies in how the LED backlights are arranged behind the LCD panel.
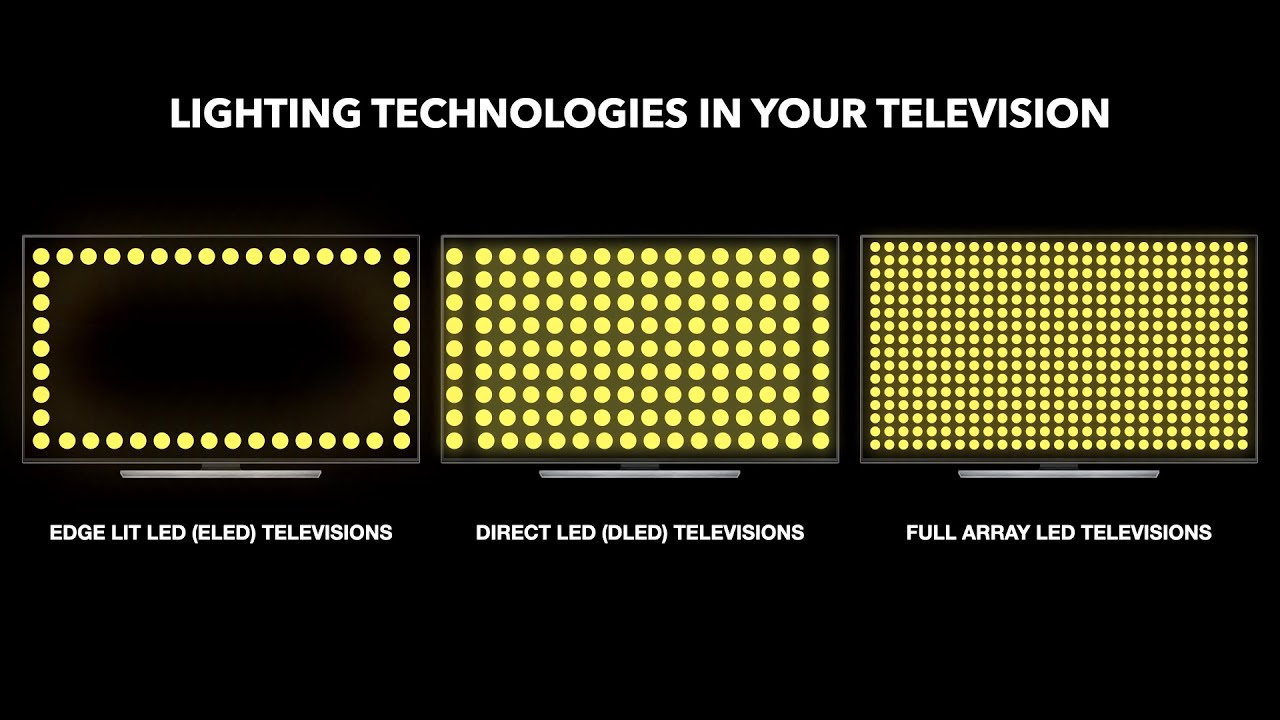
With Direct Lit, LEDs are positioned directly behind the screen, typically spread evenly across the entire surface. This contrasts with older edge-lit systems where LEDs were placed only along the edges of the display.
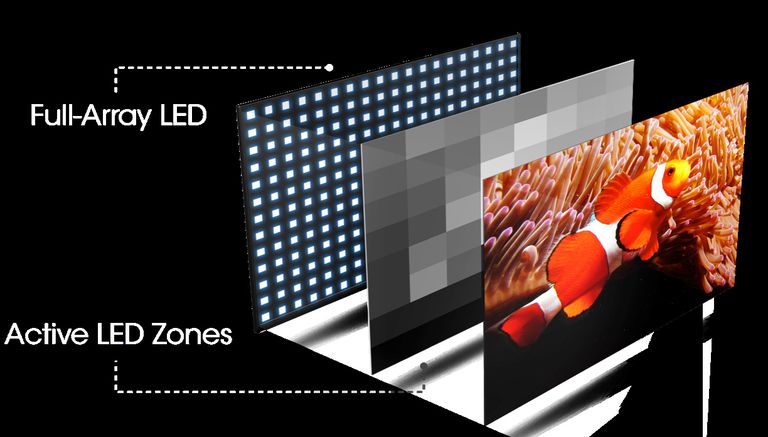
Full-Array Local Dimming (FALD), on the other hand, takes the Direct Lit approach further. In FALD, the LEDs are not just behind the screen but are also grouped into zones that can be individually controlled.
Key Differences in Performance
The arrangement of LEDs significantly impacts picture quality, particularly in terms of contrast ratio and black levels. Contrast ratio refers to the difference between the brightest white and the darkest black a TV can produce.
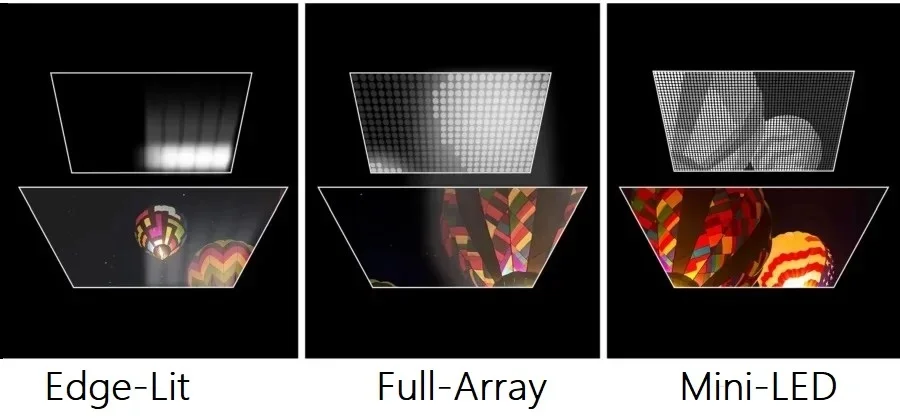
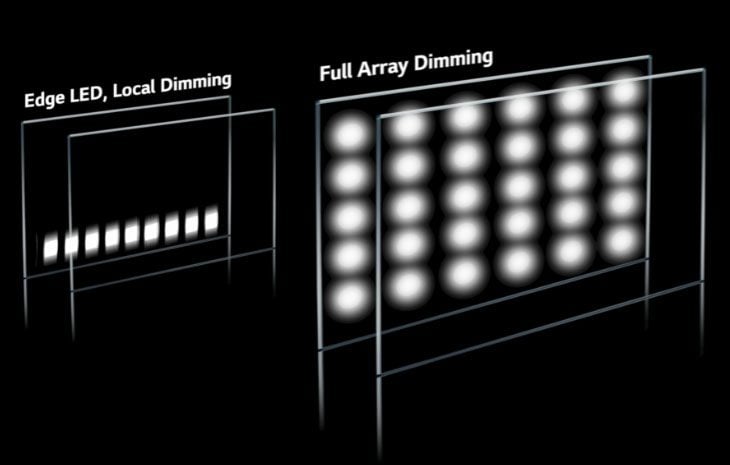
Direct Lit offers an improvement over edge-lit displays, providing more uniform brightness across the screen. However, it lacks the precision of FALD in controlling light output in specific areas of the image.
FALD technology excels in this area. By dimming or turning off LEDs in dark areas of the picture while simultaneously boosting brightness in bright areas, FALD significantly enhances contrast and black levels, resulting in a more dynamic and realistic image.
Local Dimming Explained
The effectiveness of FALD depends heavily on the number of dimming zones. More zones generally lead to more precise light control and fewer instances of "blooming," where light from bright areas bleeds into adjacent dark areas.
The processing power of the TV also plays a crucial role in accurately managing the dimming zones. Sophisticated algorithms are needed to analyze the image and adjust the backlight accordingly.
Cost and Availability
Direct Lit televisions are generally more affordable than Full-Array models. This makes them an attractive option for budget-conscious consumers seeking a step up from edge-lit displays without breaking the bank.
FALD TVs, due to their more complex design and advanced technology, command a higher price. These TVs are typically found in mid-range to high-end models, targeting users who prioritize picture quality and are willing to pay a premium for it.
Availability of both technologies varies depending on the manufacturer and screen size. Both technologies are widely available across different sizes.
Impact on the Viewing Experience
The choice between Direct Lit and FALD ultimately boils down to the viewer's preferences and budget. For casual viewers who primarily watch daytime content in well-lit environments, the benefits of FALD might be less noticeable.
However, for viewers who enjoy watching movies and playing video games in dark rooms, FALD can offer a significantly more immersive and engaging experience. The improved contrast and deeper black levels enhance detail and create a more realistic picture.
"The key consideration is the viewing environment. A dark room benefits more significantly from FALD's superior contrast," says David Katzmaier, a senior editor at CNET, specializing in TV reviews.
Conclusion
Both Direct Lit and Full-Array LED-LCD technologies offer distinct advantages. Direct Lit provides a solid baseline picture quality at an affordable price, while FALD elevates the viewing experience with superior contrast and black levels.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on individual needs, viewing habits, and budget considerations. Thorough research and in-person viewing are recommended to make an informed decision.