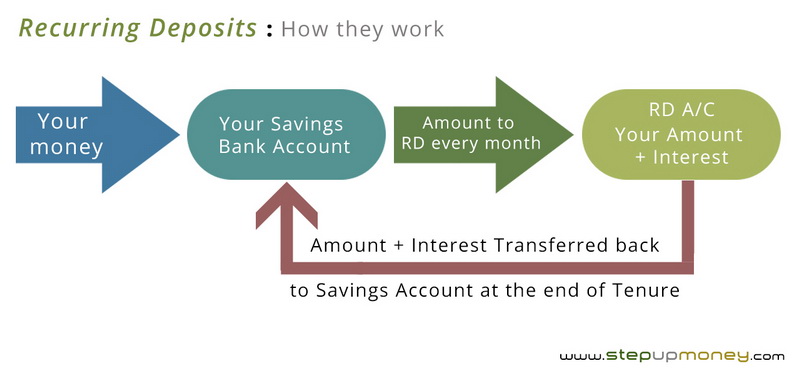
Disadvantages Of Recurring Deposit Account

Recurring Deposit (RD) accounts, often touted as a safe and disciplined savings tool, aren't without their drawbacks. While they offer a structured approach to accumulating funds, understanding their limitations is crucial for making informed financial decisions. These disadvantages can range from lower interest rates compared to other investment options to restrictive withdrawal policies and potential tax implications.
This article delves into the often-overlooked disadvantages of RD accounts, providing a balanced perspective to help readers assess whether this savings instrument aligns with their financial goals. Examining factors such as interest rate competitiveness, liquidity constraints, taxability, and opportunity costs, we aim to equip individuals with the knowledge necessary to make well-informed choices about their savings strategy. Ultimately, the suitability of an RD account depends on individual circumstances and financial priorities.
Lower Interest Rates Compared to Alternatives
One of the primary disadvantages of RD accounts is the relatively lower interest rates they offer compared to other investment options. While RD rates are generally higher than regular savings accounts, they often fall short of the returns offered by instruments like mutual funds or even some fixed deposits, particularly those with longer tenures. This disparity in returns can significantly impact the overall growth of your savings, especially over the long term.
The difference in interest rates can be attributed to the lower risk profile associated with RD accounts. As a debt instrument, they are considered safer than equity investments, but this safety comes at the cost of potentially higher returns. Therefore, individuals seeking higher growth potential may find RD accounts less appealing.
Liquidity Constraints and Premature Withdrawal Penalties
RD accounts typically impose restrictions on withdrawals before maturity. While partial withdrawals might be allowed in some cases, they usually come with penalties, reducing the overall return on investment. This lack of liquidity can be a significant drawback for individuals who anticipate needing access to their funds before the maturity date.
In contrast, other savings options, such as liquid mutual funds or even some types of fixed deposits, offer greater flexibility and easier access to funds. Before investing in an RD, consider if the possibility of unexpected expenses arising will be a concern.
Tax Implications and Tax Deduction at Source (TDS)
The interest earned on RD accounts is fully taxable according to your individual income tax slab. This can reduce the effective return on investment, particularly for individuals in higher tax brackets. Additionally, banks are required to deduct tax at source (TDS) if the interest earned exceeds a certain threshold in a financial year.
This taxability further diminishes the attractiveness of RD accounts compared to tax-advantaged investment options like the Public Provident Fund (PPF) or Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS). A PPF or ELSS account might be more appropriate depending on the amount and the personal tax situation.
Opportunity Cost: Missing Out on Potentially Higher Returns
By investing in an RD account, you are foregoing the opportunity to invest in potentially higher-yielding assets. The opportunity cost of choosing an RD should be weighed. This opportunity cost can be significant, especially over longer investment horizons, where the power of compounding can amplify the difference in returns.
For example, investing in the stock market (through a diversified portfolio) or certain types of real estate may offer higher returns, although with correspondingly higher risk. It's crucial to carefully evaluate your risk tolerance and investment goals before committing to an RD account.
Fixed Installment Amounts and Lack of Flexibility
RD accounts require fixed installment amounts to be deposited regularly, regardless of your financial situation. This lack of flexibility can be challenging for individuals with fluctuating income or those who may experience unexpected financial setbacks. Missing installment payments can result in penalties or even closure of the account.
Other savings options, such as systematic investment plans (SIPs) in mutual funds, offer greater flexibility, allowing you to pause or adjust your investment amount based on your circumstances. Weigh the benefits of structure against the freedom of a SIP.
Inflation Risk and Eroding Purchasing Power
While RD accounts offer a fixed rate of return, this return may not always keep pace with inflation. Over time, the purchasing power of your savings can be eroded if the inflation rate exceeds the interest rate earned on the RD account. This is a particularly important consideration in periods of high inflation.
Investing in assets that are likely to outpace inflation, such as equities or real estate, may be a more effective way to preserve and grow your wealth in the long run. Compare the current rate of inflation to the rate being offered.
Conclusion: A Balanced Perspective is Key
RD accounts can be a useful savings tool for some, particularly those seeking a disciplined and low-risk approach to accumulating funds. However, it's essential to be aware of their limitations, including lower interest rates, liquidity constraints, tax implications, and the potential for missed opportunities. A balanced perspective and a thorough understanding of your financial goals are crucial for determining whether an RD account is the right choice for you.
Before investing in an RD, carefully compare its features and benefits to those of other available savings and investment options. Consider your risk tolerance, investment horizon, and financial needs to make an informed decision that aligns with your overall financial strategy. Consulting with a financial advisor can also provide valuable insights and personalized guidance.