Dizziness And Ringing In Ears After Exercise

Reports are surging nationwide of individuals experiencing dizziness and ringing in the ears, known as tinnitus, immediately following exercise. Health officials are urging anyone experiencing these symptoms to seek medical evaluation to rule out serious underlying conditions.
The sudden onset of dizziness and tinnitus post-exercise is raising concerns among athletes and fitness enthusiasts. While these symptoms can stem from benign causes, they can also indicate more serious issues like cardiovascular problems or inner ear disorders requiring prompt attention.
Who is Affected?
The reports are diverse, affecting individuals across various age groups and fitness levels. Both seasoned athletes and those new to exercise routines have reported experiencing these symptoms.
There isn't a clearly defined demographic at higher risk, suggesting the underlying causes may vary significantly from person to person.
What are the Symptoms?
Individuals report a range of symptoms, primarily dizziness described as a spinning sensation or lightheadedness. This is often accompanied by tinnitus, characterized by ringing, buzzing, or hissing sounds in one or both ears.
Some also report nausea, headaches, and blurred vision in conjunction with the dizziness and tinnitus.
The intensity and duration of symptoms vary, with some experiencing them for only a few minutes, while others report lingering effects for hours.
Where are Reports Originating?
Reports are emerging across the United States, with clusters noted in metropolitan areas with high concentrations of fitness centers and gyms. Online forums and social media groups dedicated to fitness are filled with anecdotal accounts.
Specific geographic hotspots haven't been identified, suggesting this is a widespread phenomenon not limited to a particular region.
When do Symptoms Occur?
The onset of symptoms almost always occurs immediately after or within a few minutes of completing exercise. The type of exercise doesn't seem to be a determining factor; reports include experiences following cardiovascular workouts, weightlifting, and yoga.
Some individuals report symptoms occurring more frequently after high-intensity workouts, while others note no correlation between intensity and symptom onset.
How is This Being Investigated?
Medical professionals are advising a thorough evaluation, including a physical examination, neurological assessment, and audiological testing. Blood pressure monitoring and electrocardiograms (ECGs) are also recommended to rule out cardiovascular causes.
In some cases, imaging studies like MRI or CT scans may be necessary to further investigate potential underlying conditions. Researchers are beginning to explore possible links between exercise-induced dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and inner ear function.
Possible Causes and Considerations
Several factors could contribute to dizziness and tinnitus after exercise. Dehydration is a common culprit, as it can lead to reduced blood volume and decreased blood flow to the brain and inner ear.
Electrolyte imbalances, particularly low sodium or potassium levels, can also affect nerve function and contribute to these symptoms.
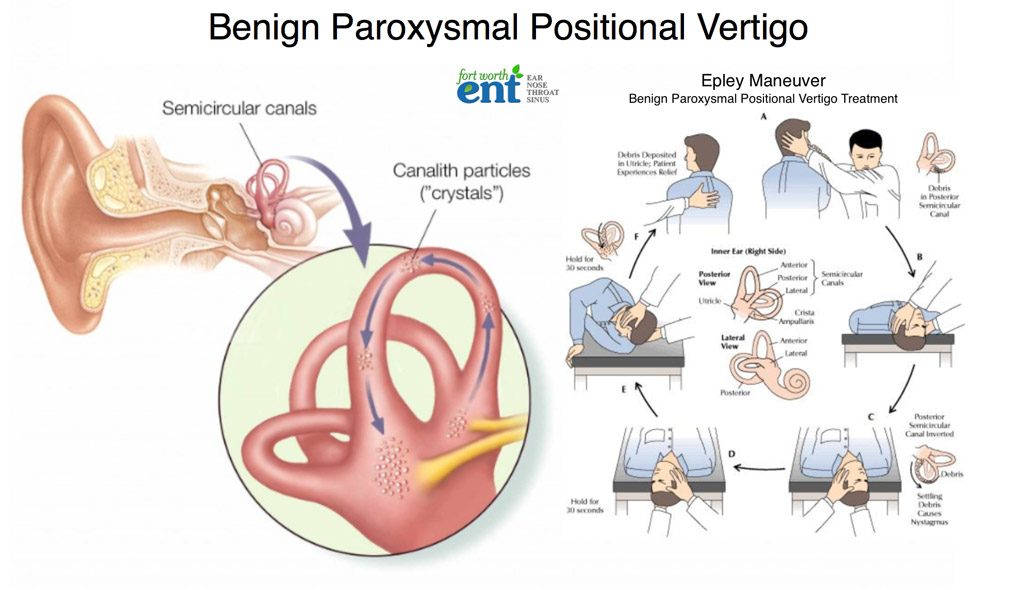
Inner ear disorders, such as Meniere's disease or benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), can be exacerbated by physical exertion. Cardiovascular issues, including arrhythmias or low blood pressure, need to be ruled out.
Rarely, tumors affecting the auditory nerve can present with similar symptoms.
Additionally, certain medications can increase the risk of dizziness and tinnitus, especially when combined with exercise.
Expert Opinion
“It’s crucial to differentiate between benign and potentially serious causes,” states Dr. Emily Carter, a cardiologist at the National Institute of Health. “While dehydration or overexertion are common explanations, persistent or severe symptoms warrant immediate medical attention to rule out underlying cardiovascular or neurological issues.”
Next Steps
Anyone experiencing dizziness and ringing in the ears after exercise should consult with their healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation. Documenting the frequency, duration, and intensity of symptoms can aid in diagnosis.
Maintaining adequate hydration and electrolyte balance during and after exercise is crucial preventative measure. Health officials are closely monitoring the situation and will release updated guidelines as more information becomes available.