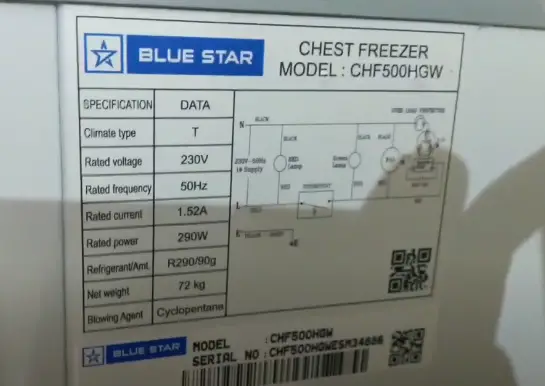
Does A Deep Freezer Use Much Electricity

Deep freezers are a convenient way to store food for extended periods, but rising energy costs are forcing homeowners to question their impact on electricity bills.
This article cuts through the confusion, providing a clear and concise breakdown of deep freezer energy consumption, factors influencing costs, and practical steps to minimize your energy footprint.
Energy Consumption: The Basics
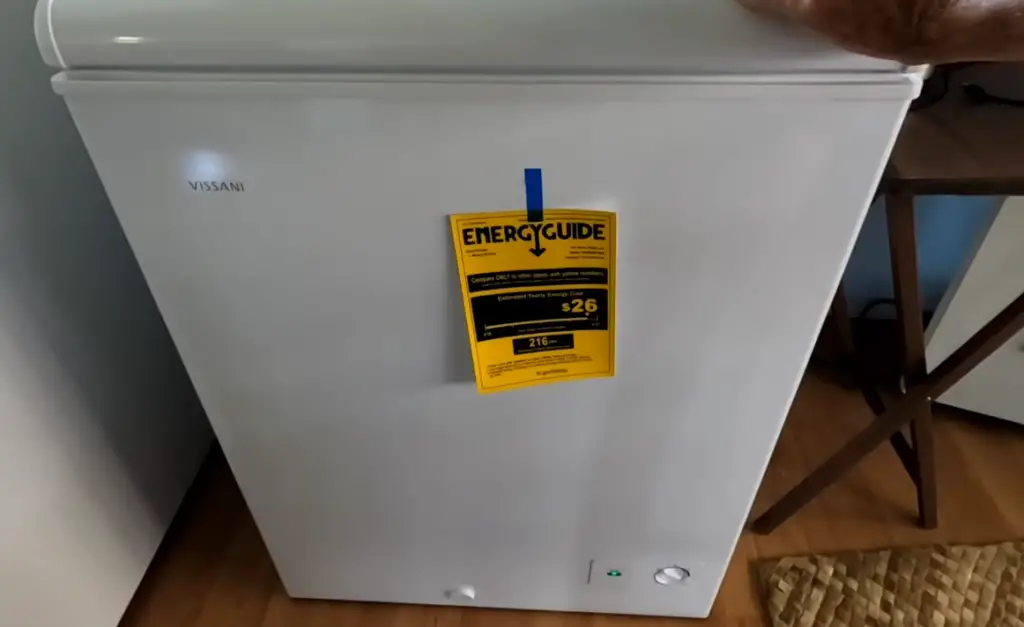
The amount of electricity a deep freezer uses varies significantly. Generally, expect a range of 100 to 400 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per year.
This translates to roughly $16 to $64 annually, based on the national average electricity rate of about 16 cents per kWh. However, actual costs depend heavily on several factors.
Key Factors Influencing Energy Usage
Several elements affect how much energy your deep freezer consumes. The most crucial is the size and type of the freezer.
Chest freezers are generally more energy-efficient than upright freezers because cold air doesn't escape as easily when the door is opened. Larger models, naturally, use more energy.
The age and condition of the freezer is crucial. Older models are significantly less efficient than newer, Energy Star-certified appliances.
Poor insulation or a malfunctioning door seal allows cold air to leak, forcing the freezer to work harder and consume more electricity.
The ambient temperature of the room where the freezer is located plays a role. A warmer environment increases the freezer's workload.
Finally, how full the freezer is also matters. A full freezer is more energy-efficient than an empty one because the frozen contents help maintain a consistent temperature.
Data and Estimates
Energy Star provides resources for comparing the energy efficiency of different freezer models. According to Energy Star data, a certified chest freezer (10-16 cubic feet) might use as little as 200 kWh per year.
However, an older, non-certified upright freezer of similar size could easily consume twice that amount. Independent testing consistently reveals older models are significantly less energy efficient.
Practical Tips to Reduce Energy Consumption
There are several immediate steps you can take to minimize your deep freezer's energy consumption. Start by ensuring the door seal is airtight.
Check for any gaps or cracks and replace the seal if necessary. Defrost your freezer regularly, as frost buildup significantly reduces efficiency.
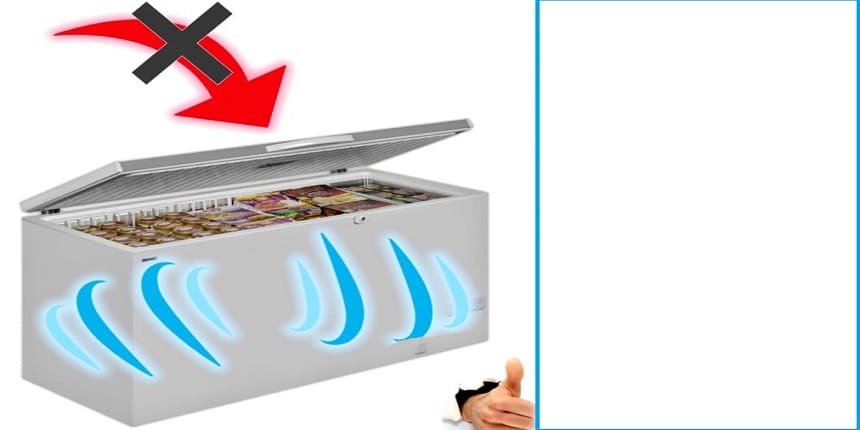
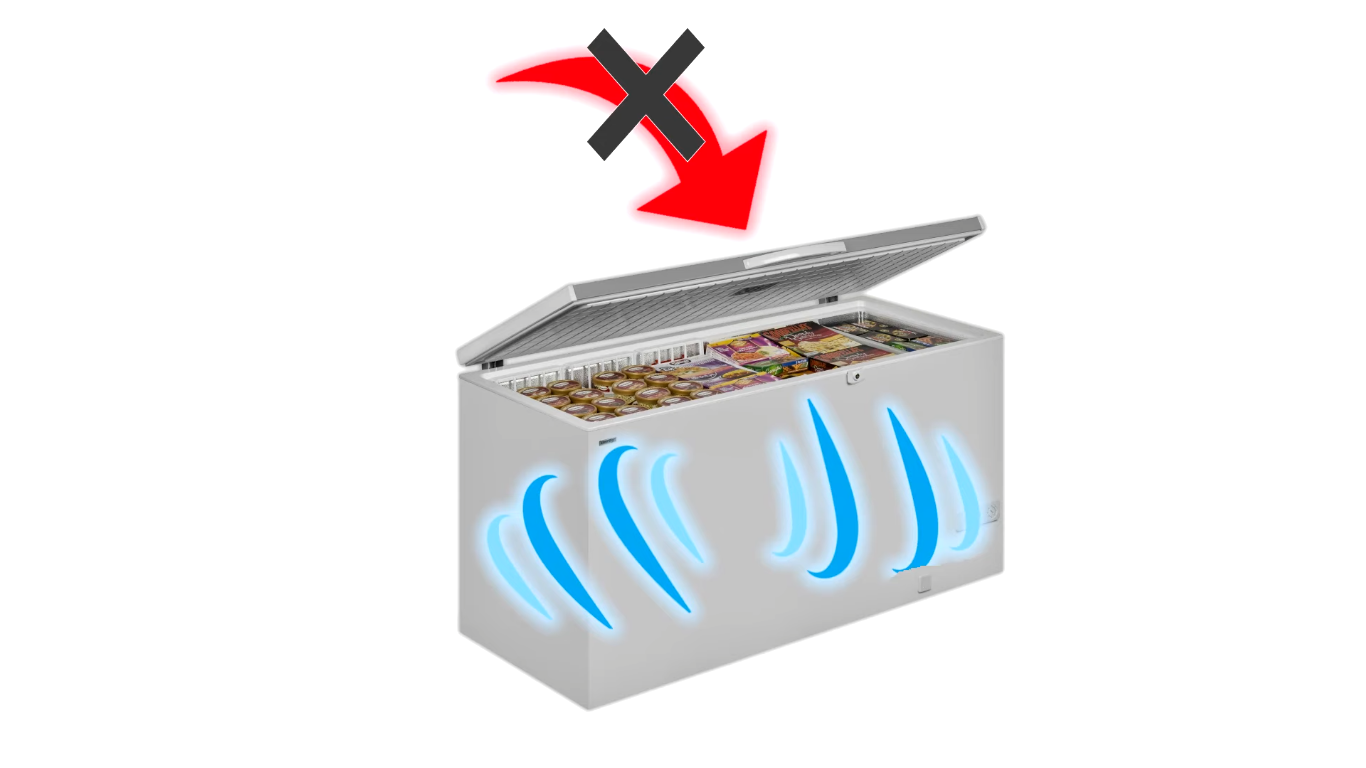
Ensure adequate ventilation around the freezer to allow heat to dissipate. Keep the freezer away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
Consider replacing an older, inefficient freezer with a new Energy Star-certified model. The long-term energy savings can quickly offset the initial cost.
Optimize how you fill your freezer. Fill empty spaces with water-filled containers to maintain a consistent temperature and reduce energy waste.
Regular maintenance is key. Clean the condenser coils regularly to ensure efficient heat transfer.
Ongoing Developments and Future Considerations
Energy efficiency standards for appliances are continuously evolving. Consumers should stay informed about new technologies and regulations.
Keep an eye on utility company programs offering rebates for energy-efficient appliance upgrades. Many utilities provide incentives to encourage consumers to purchase Energy Star-certified freezers.
Monitor your energy bill closely to identify any unexpected increases in consumption. If you suspect your deep freezer is using excessive energy, consult with an appliance repair technician.
The bottom line: Understanding your deep freezer's energy consumption and taking proactive steps to improve efficiency can significantly reduce your electricity bills.






![Does A Deep Freezer Use Much Electricity How Many Amps Does A Freezer Use [Surge, Running, Low Amp]](https://ecocostsavings.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/freezer-wattage.jpg)