Does Thca Convert To Delta 9

The legal landscape surrounding cannabis continues to evolve, creating confusion for consumers and businesses alike. At the heart of this uncertainty lies the question of THCA, the non-intoxicating precursor to Delta-9 THC, the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. The potential for THCA to convert into Delta-9 raises significant legal and regulatory concerns, demanding a deeper understanding of the science and its implications.
This article delves into the complex relationship between THCA and Delta-9 THC. We will examine the scientific process of conversion, the factors influencing it, and the resulting legal and regulatory ramifications for the cannabis industry. This in-depth exploration aims to provide clarity on a crucial aspect of cannabis chemistry and its impact on the evolving legal framework.
The Science of Decarboxylation: THCA to Delta-9 THC
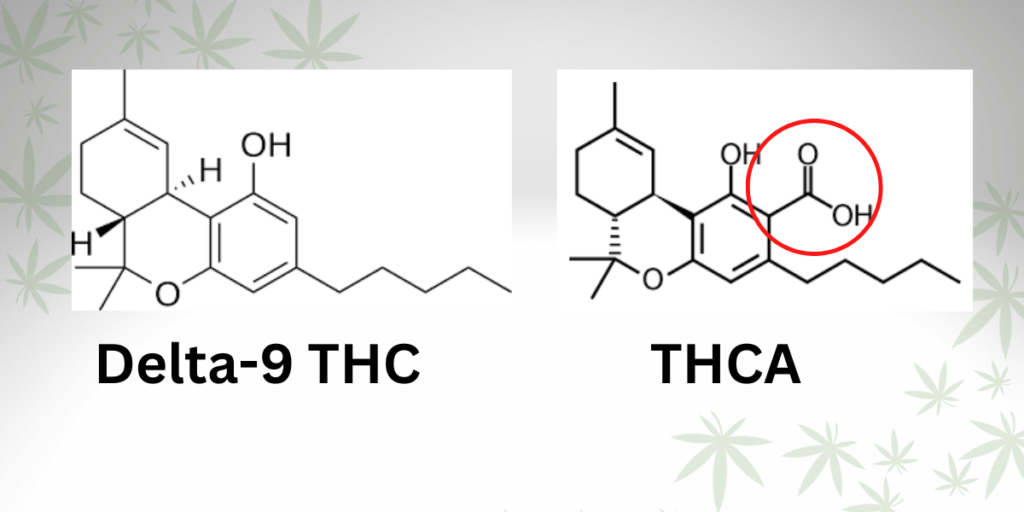
THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) is the naturally occurring, non-psychoactive form of THC found in raw cannabis plants. In its acidic form, THCA does not bind effectively to the body's cannabinoid receptors, hence its lack of intoxicating effects. To unlock the psychoactive potential of cannabis, THCA must undergo a process called decarboxylation.
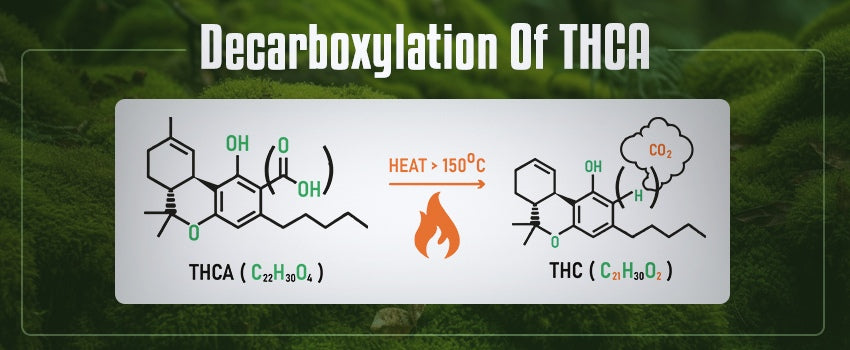
Decarboxylation is the chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group (COOH) from the THCA molecule. This process typically occurs when heat is applied, converting THCA into Delta-9 THC. The amount of Delta-9 produced depends on the temperature, duration, and method of heating.
Exposure to light and air can also cause a slow decarboxylation over time, but heat is the most efficient and common method. This is why cannabis is typically smoked, vaporized, or baked into edibles, all of which involve heating the plant material.
Factors Influencing Conversion Rates
The conversion of THCA to Delta-9 THC is not a simple, all-or-nothing process. Several factors can influence the efficiency and completeness of this conversion. Understanding these variables is crucial for both consumers and producers.
Temperature is a primary driver. Different temperatures result in varying levels of decarboxylation, with higher temperatures leading to faster conversion, but also potentially degrading the desired cannabinoids and terpenes. Optimal temperatures exist for maximizing Delta-9 THC production while preserving other valuable compounds.
Duration of exposure to heat is another significant factor. Longer heating times can ensure more complete decarboxylation. However, excessive heat exposure can lead to the degradation of Delta-9 THC into other compounds like CBN (cannabinol), which has different effects.
The specific strain of cannabis also plays a role. Different strains contain varying levels of THCA. Therefore, the potential yield of Delta-9 THC upon decarboxylation will differ accordingly. The environment in which the plant was grown can also impact cannabinoid production.
Legal and Regulatory Implications
The ability of THCA to convert to Delta-9 THC has profound legal and regulatory implications. The legality of cannabis products hinges on the concentration of Delta-9 THC. This creates a gray area regarding THCA-rich products.
The 2018 Farm Bill legalized hemp, defined as cannabis containing no more than 0.3% Delta-9 THC on a dry weight basis. This definition has been interpreted differently by various states and federal agencies. It has resulted in a complex patchwork of regulations concerning THCA products.
Some argue that THCA, in its raw form, is not a controlled substance since it's non-psychoactive. However, others contend that because it can be converted to Delta-9 THC, it should be regulated similarly. This debate continues to play out in courtrooms and legislative bodies across the country.
The ambiguity surrounding THCA's legal status has led to a surge in the sale of "THCA flower" and other products. These products are often marketed as legal hemp, despite containing high levels of THCA that can be easily converted to Delta-9 THC.
State laws vary widely, with some states explicitly banning THCA products while others remain silent. The lack of federal clarity further complicates the situation. This creates compliance challenges for businesses operating across state lines.
Perspectives from the Cannabis Industry
The cannabis industry is grappling with the evolving legal landscape surrounding THCA. Producers, retailers, and consumers hold varying perspectives on the issue. These diverse viewpoints reflect the complexity of the situation.
Some in the industry advocate for clear and consistent regulations based on scientific evidence. They argue that regulations should focus on the total potential THC content of a product after decarboxylation. This approach aims to provide a more accurate measure of a product's potential psychoactive effects.
Others believe that THCA, in its raw form, should remain legal. They argue that consumers should have the freedom to choose whether or not to decarboxylate their products. They also say regulations should consider that consumers can control how they consume it.
Concerns exist about the potential for unregulated THCA products to flood the market. Also, consumers could unknowingly purchase products with higher-than-expected THC levels. This fuels the argument for greater regulation and consumer education.
The Future of THCA Regulation
The future of THCA regulation remains uncertain. However, several factors are likely to shape the legal landscape in the coming years. These factors include ongoing litigation, evolving scientific understanding, and potential federal action.
Courts will likely continue to play a crucial role in interpreting existing laws and defining the legal status of THCA. Rulings in these cases could set precedents that significantly impact the industry. Also, rulings can provide some guidelines for lawmakers to follow.
Further research into the decarboxylation process and the effects of THCA is needed. More scientific data can inform more accurate and effective regulations.
Federal action, whether in the form of revised legislation or regulatory guidance, could provide much-needed clarity and consistency. Such action could preempt conflicting state laws and create a more uniform national framework.
Ultimately, the path forward requires a collaborative approach involving lawmakers, regulators, the cannabis industry, and the scientific community. Clear, science-based regulations are essential for protecting consumers and fostering a sustainable and responsible cannabis market. The goal should be to balance the potential risks and benefits of THCA, ensuring public safety while allowing for legitimate business activity.