Earned Value Management Is A Widely Accepted

In today's fast-paced and highly competitive business environment, project success hinges on meticulous planning, diligent execution, and, most importantly, rigorous performance measurement. One methodology, Earned Value Management (EVM), has emerged as a cornerstone of project management, providing a comprehensive framework for tracking progress, controlling costs, and forecasting outcomes.
Its widespread adoption across various industries underscores its proven effectiveness in mitigating project risks and maximizing return on investment. However, despite its merits, EVM implementation is not without its challenges, requiring careful consideration of organizational culture, data accuracy, and stakeholder buy-in.
This article will delve into the pervasive use of Earned Value Management, exploring its key principles, benefits, challenges, and future trends, while highlighting its continued relevance in shaping successful project outcomes.
The Core Principles of Earned Value Management
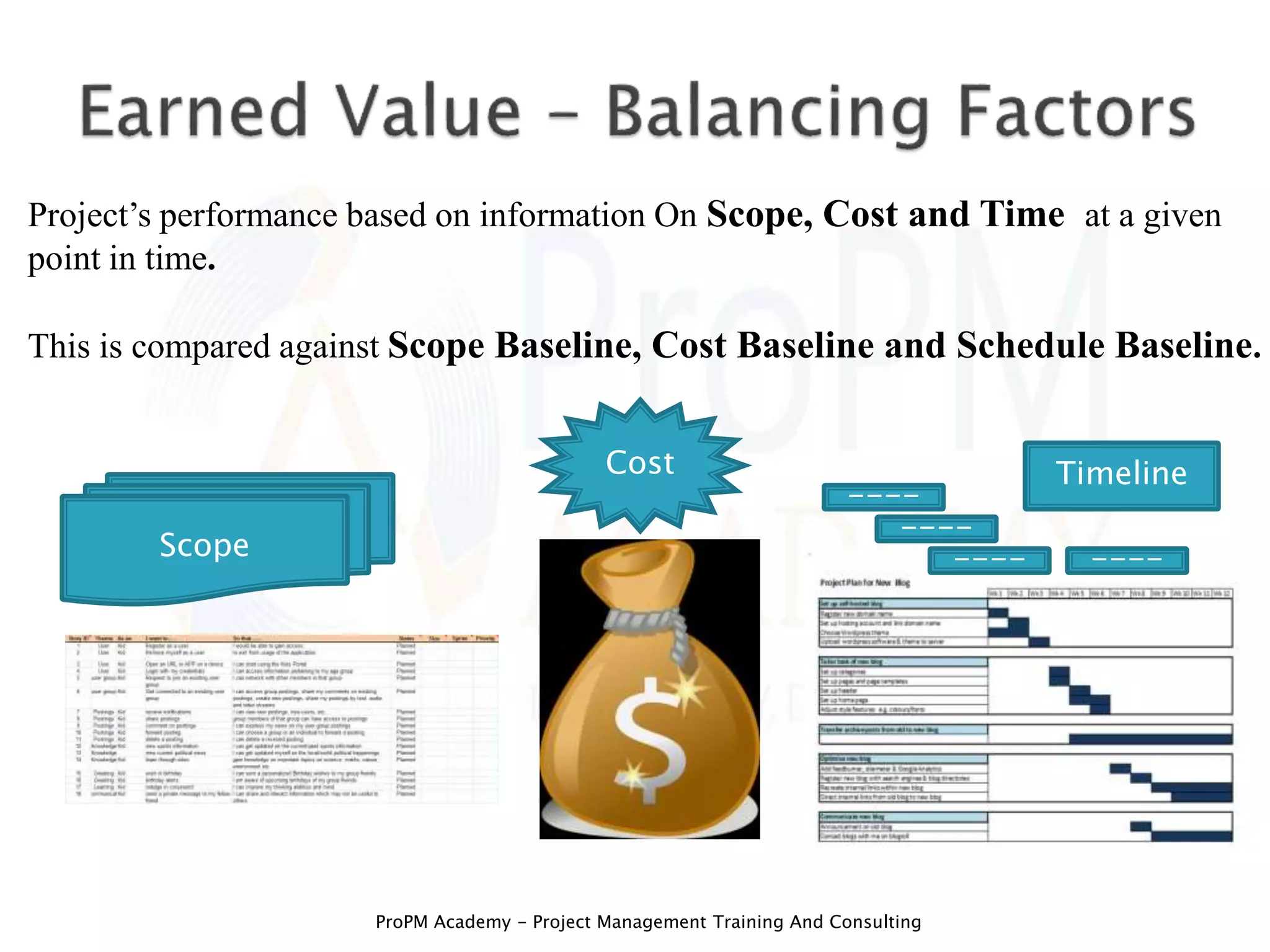
At its heart, Earned Value Management is a systematic approach to project performance measurement that integrates scope, schedule, and cost data. It provides a clear picture of project performance by comparing planned versus actual work completed, allowing project managers to proactively identify and address potential issues.
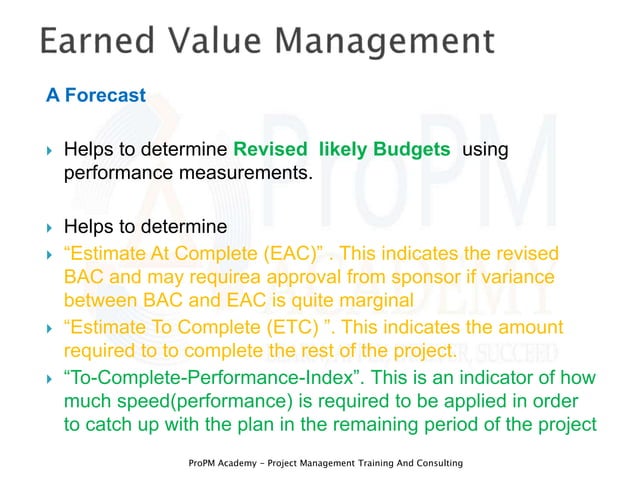
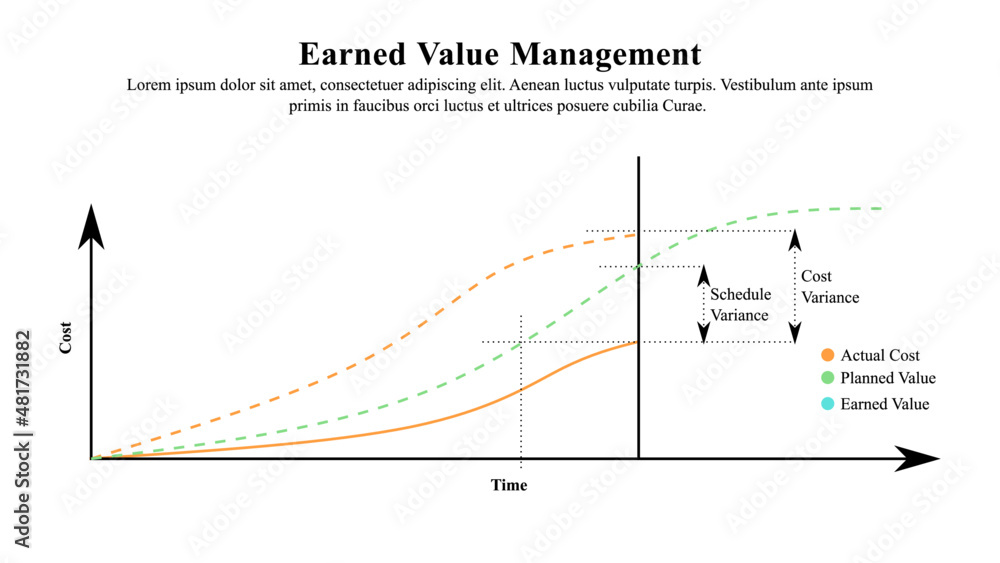
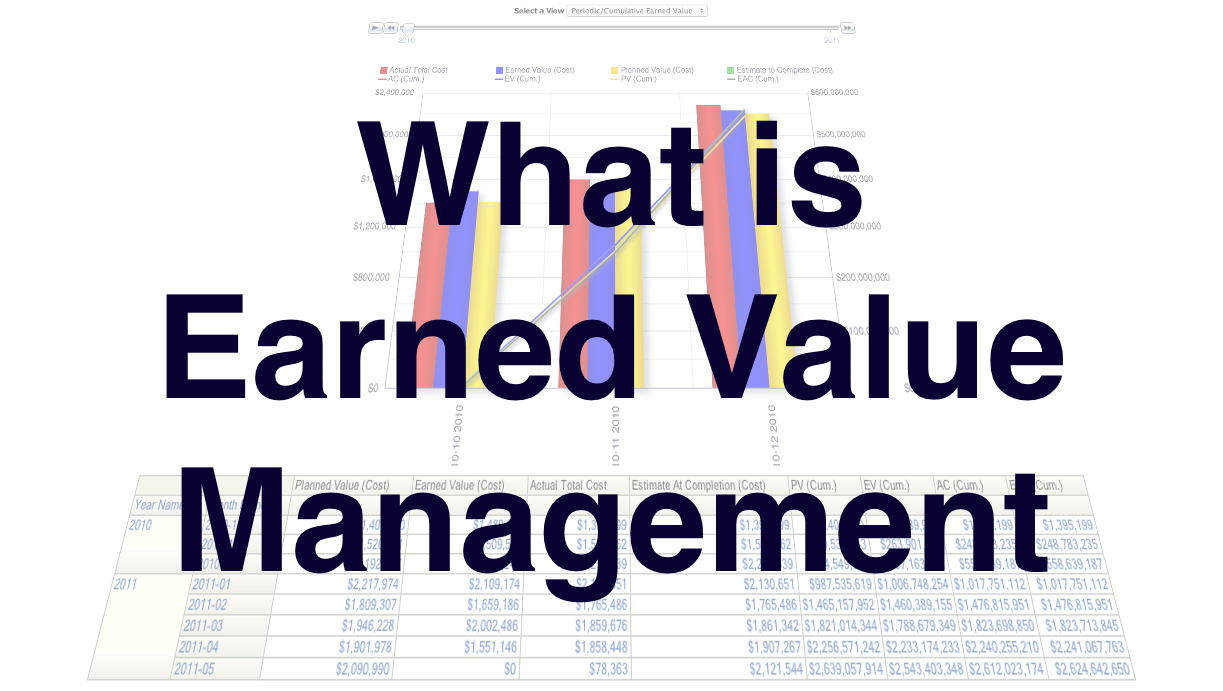
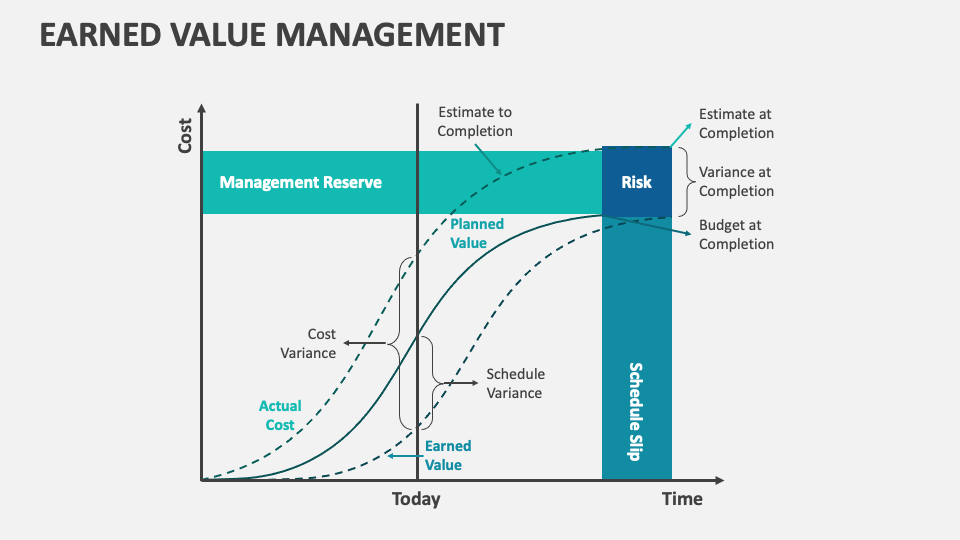
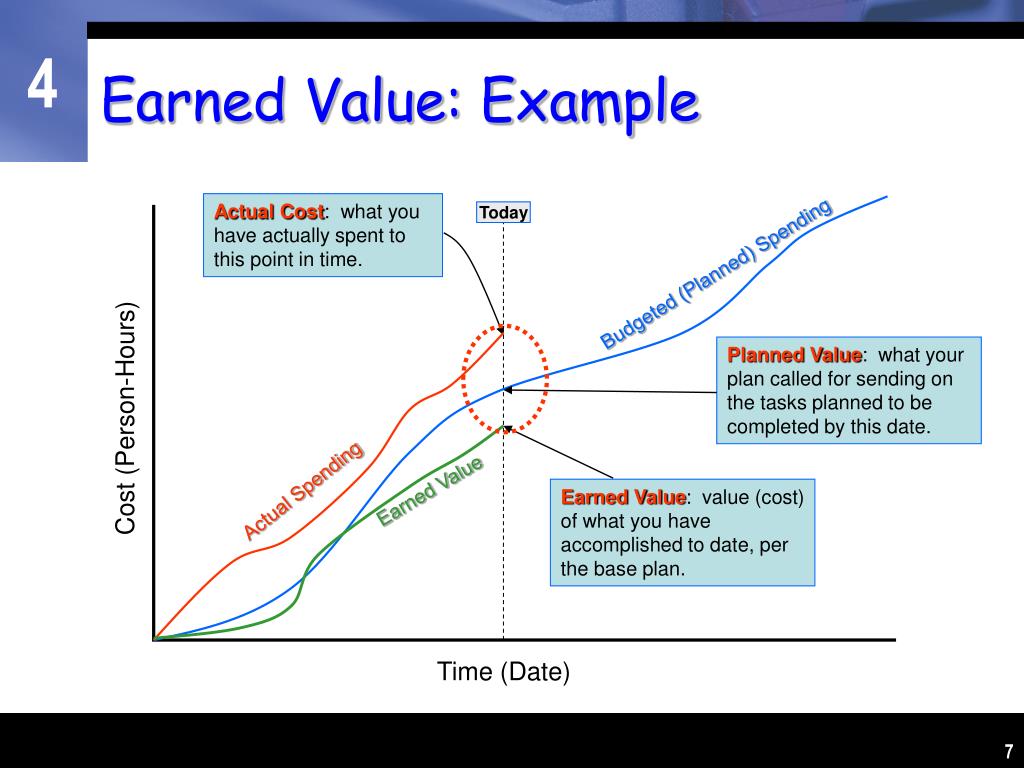
The foundation of EVM lies in three key metrics: Planned Value (PV), Actual Cost (AC), and Earned Value (EV). PV represents the budgeted cost of work scheduled to be completed, AC represents the actual cost incurred for the work performed, and EV represents the budgeted cost of the work actually completed.
By analyzing the variances between these metrics, project managers can gain valuable insights into project performance. Schedule Variance (SV) = EV - PV, and Cost Variance (CV) = EV - AC.
Benefits of Earned Value Management
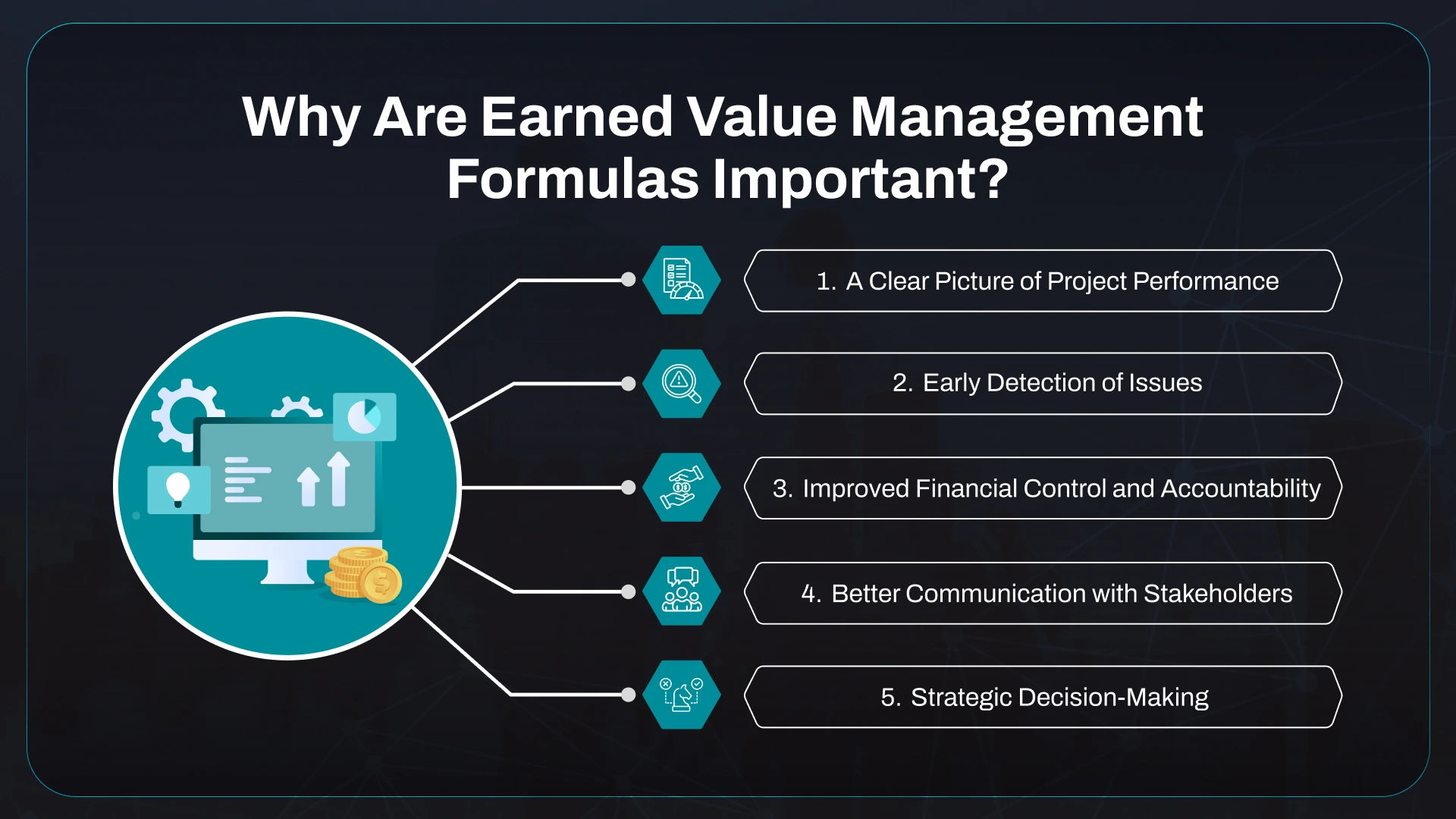
The widespread adoption of EVM is driven by its numerous benefits, including enhanced project visibility, improved decision-making, and increased project success rates. By providing a clear and objective measure of project performance, EVM enables project managers to identify potential problems early on and take corrective actions before they escalate.
EVM also facilitates better communication among stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding project progress and performance. This improved transparency fosters trust and collaboration, leading to more effective project execution.
Furthermore, EVM helps to improve project forecasting by providing a reliable basis for estimating future costs and schedules. By analyzing historical performance data, project managers can develop more accurate forecasts, allowing them to make informed decisions about resource allocation and project scope.
EVM Adoption Across Industries
Earned Value Management is not confined to a specific industry; its principles are applicable to projects of all sizes and complexities. The aerospace and defense industries have long been proponents of EVM, using it extensively to manage large-scale, complex projects with stringent regulatory requirements.
According to a 2023 report by the Project Management Institute (PMI), EVM is increasingly being adopted in the construction, IT, and engineering sectors. These industries recognize the value of EVM in improving project control, reducing costs, and mitigating risks.
For instance, in the construction industry, EVM can be used to track progress on building projects, identify cost overruns, and ensure that projects are completed on time and within budget. Similarly, in the IT industry, EVM can be used to manage software development projects, track progress on coding tasks, and identify potential delays.
Challenges in Implementing EVM
Despite its numerous benefits, implementing EVM can be challenging, requiring careful planning and execution. One of the biggest challenges is data accuracy. The accuracy of EVM metrics depends on the quality of the underlying data, including cost data, schedule data, and progress data.
Another challenge is organizational culture. EVM requires a culture of accountability and transparency, where project managers are held responsible for their performance and are willing to share information openly. Organizations that lack this culture may struggle to implement EVM effectively.
Stakeholder buy-in is also crucial for successful EVM implementation. Project stakeholders must understand the benefits of EVM and be willing to support its implementation. This requires effective communication and education.
The Future of Earned Value Management
EVM continues to evolve and adapt to the changing needs of project management. One of the key trends in EVM is the integration of EVM with agile methodologies. While EVM was traditionally used in waterfall projects, it can also be adapted for use in agile projects.
Another trend is the use of EVM with Building Information Modeling (BIM) in the construction industry. BIM is a digital representation of a physical building that can be used to track project progress, identify potential problems, and manage costs. Integrating EVM with BIM can provide a more comprehensive view of project performance.
Furthermore, advancements in technology are making EVM more accessible and user-friendly. Cloud-based EVM software solutions are becoming increasingly popular, allowing project managers to access project data from anywhere in the world.
"Earned Value Management remains a critical tool for organizations seeking to improve project performance and achieve their strategic goals," says John Smith, a leading project management consultant. "Its continued evolution ensures its relevance in the face of emerging technologies and project management methodologies."
In conclusion, Earned Value Management is a widely accepted and valuable methodology for project performance measurement. While implementation challenges exist, its benefits, including enhanced project visibility, improved decision-making, and increased project success rates, make it a worthwhile investment for organizations of all sizes. As technology advances and project management methodologies evolve, EVM will continue to adapt and remain a cornerstone of successful project management.






.jpg)