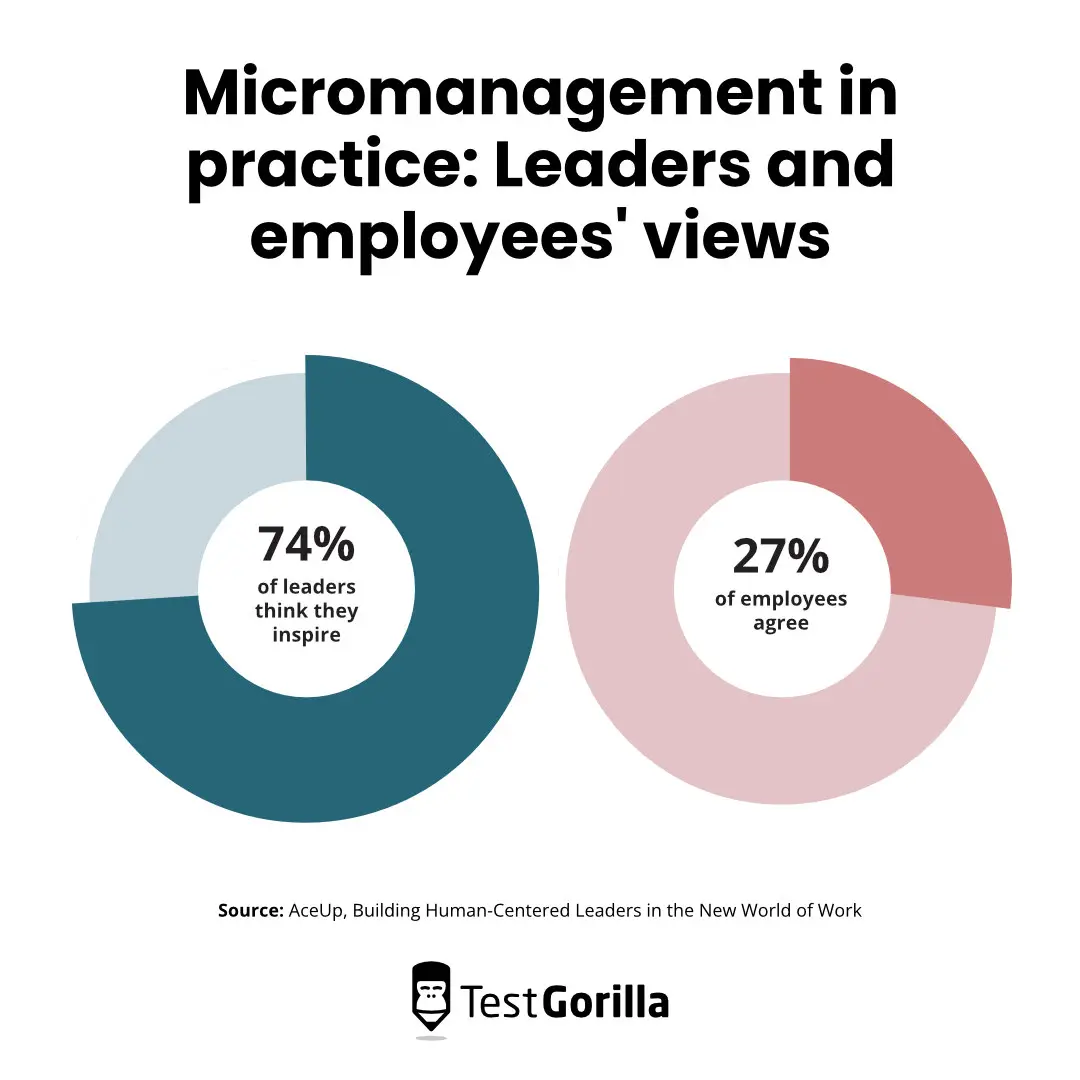
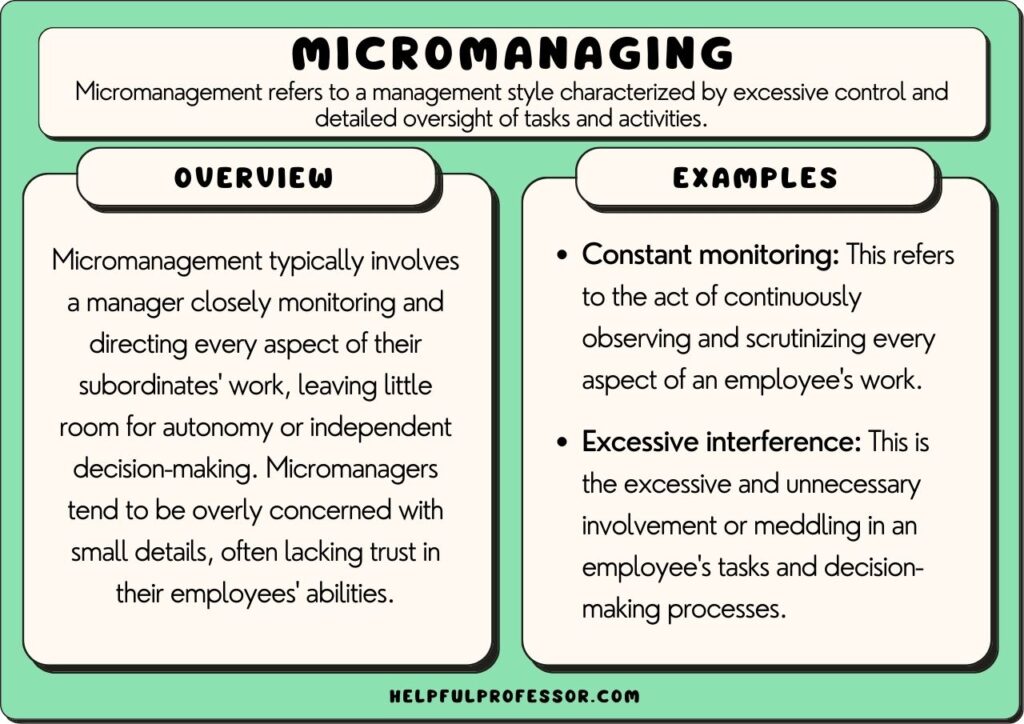
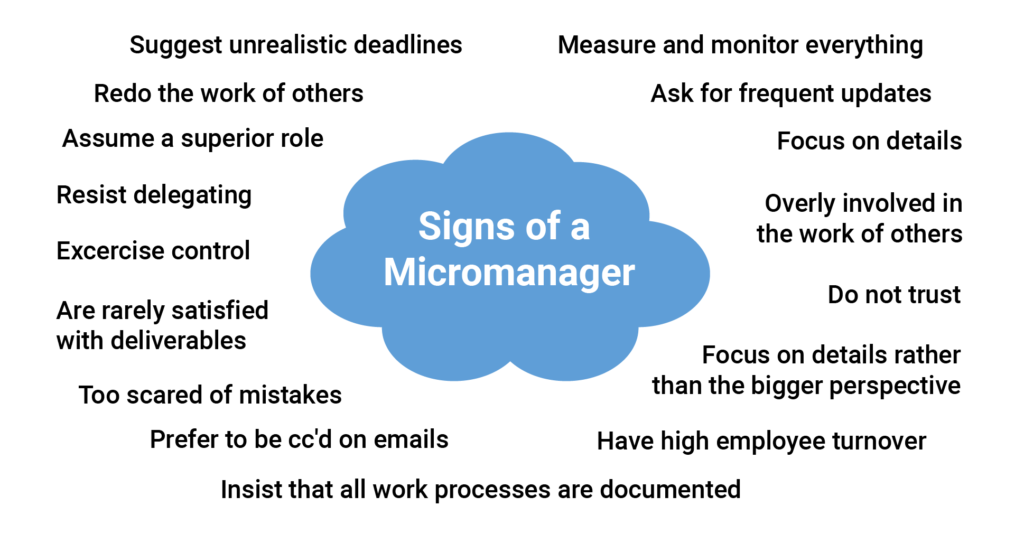
Effects Of Micromanagement On Employees Pdf

In today's dynamic work environment, the spectre of micromanagement looms large, casting a shadow over employee morale, productivity, and overall organizational health. A growing body of evidence, detailed in numerous research papers and case studies, paints a grim picture of the detrimental effects this management style has on the workforce.
This article delves into the far-reaching consequences of micromanagement, drawing upon credible sources to illustrate its impact on employee well-being, performance, and the bottom line. We will explore how this counterproductive approach stifles creativity, breeds resentment, and ultimately undermines the very goals it purports to achieve.
The Stifling Grip: Understanding Micromanagement
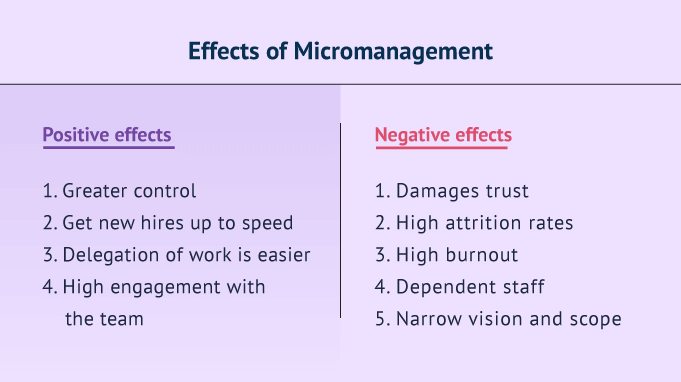
Micromanagement, at its core, involves excessive control and oversight by a manager over their subordinates' work. It's characterized by a lack of trust, a constant need for updates, and an insistence on doing things the manager's way, even when alternative approaches might be more efficient or innovative.
Often driven by anxiety or a perceived lack of competence in their team, micromanagers create a suffocating environment that can quickly erode employee confidence and motivation. This managerial style is a significant obstacle to creating a positive and productive workplace.
Deteriorating Employee Well-being: Stress, Anxiety, and Burnout
The constant scrutiny inherent in micromanagement leads to heightened stress and anxiety among employees. Knowing that every action is being monitored and potentially criticized creates a climate of fear, hindering creativity and innovation.
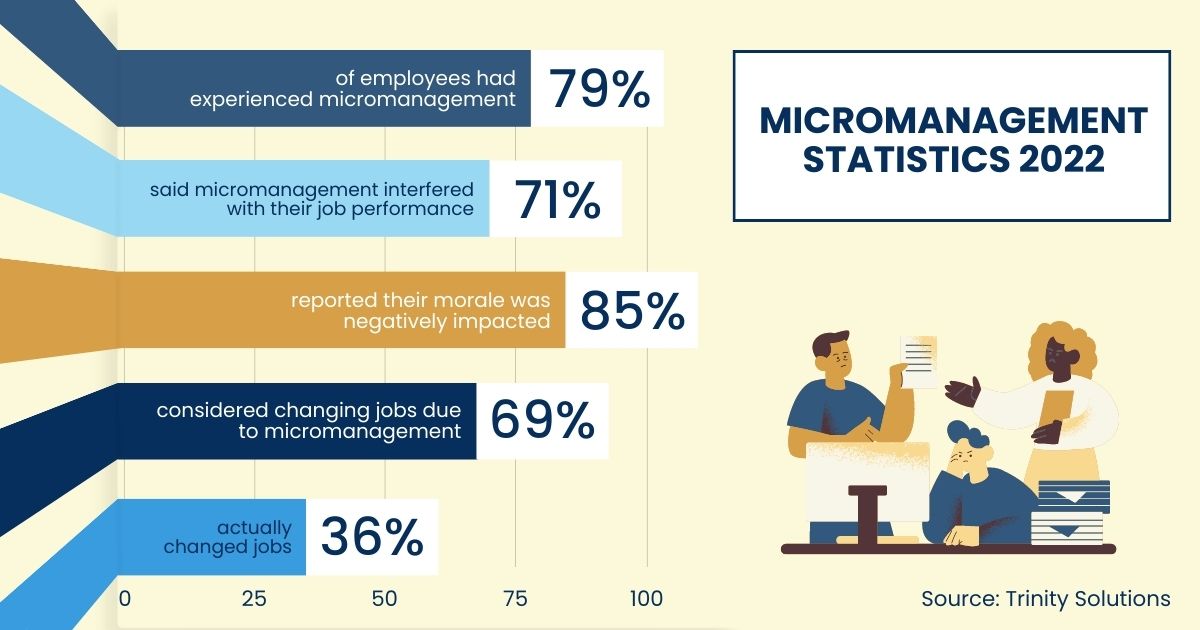
Burnout, a state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion caused by prolonged or excessive stress, is a common consequence. Studies, including those published by the American Psychological Association (APA), highlight the strong correlation between micromanagement and increased levels of employee burnout.
This constant pressure can lead to decreased job satisfaction, higher rates of absenteeism, and even employees actively seeking alternative employment, impacting retention rates significantly.
Impact on Productivity and Performance: A Counterproductive Approach
Contrary to the belief that close monitoring improves performance, micromanagement often has the opposite effect. Employees subjected to excessive oversight feel disempowered and undervalued, leading to decreased motivation and engagement.
A study by Gallup found that employees who feel their manager does not trust them are significantly less likely to be engaged at work. This lack of engagement translates directly into lower productivity, reduced quality of work, and a decline in overall team performance.
By stifling autonomy and independent thinking, micromanagement hinders the development of valuable skills and ultimately limits the potential of the workforce. It undermines the very efficiency it is trying to achieve.
The Ripple Effect: Organizational Costs and Culture
The negative effects of micromanagement extend beyond individual employees, impacting the entire organization. High employee turnover, a direct result of dissatisfaction and burnout, incurs significant recruitment and training costs.
Moreover, a culture of micromanagement can stifle innovation and creativity, as employees are less likely to take risks or propose new ideas for fear of criticism. This can lead to a stagnant and uncompetitive organization.
Ultimately, a toxic work environment fosters resentment and distrust, hindering collaboration and teamwork, further diminishing the organization's performance.
Alternatives to Micromanagement: Fostering Trust and Empowerment
The antidote to micromanagement lies in fostering a culture of trust, empowerment, and open communication. Managers should focus on setting clear expectations, providing adequate resources, and offering constructive feedback, rather than constantly scrutinizing every detail.
Investing in training programs that equip managers with the skills to delegate effectively and empower their teams is crucial. This involves providing employees with the autonomy to make decisions, encouraging them to take ownership of their work, and recognizing their contributions.
By shifting from a control-oriented approach to a coaching-oriented one, managers can unlock the full potential of their teams and create a more positive and productive work environment.
Looking Ahead: Creating a Culture of Trust
Combating micromanagement requires a fundamental shift in management philosophy, prioritizing trust, empowerment, and employee well-being. Organizations must actively cultivate a culture where employees feel valued, supported, and empowered to excel.
By embracing a more collaborative and empowering approach, organizations can unlock the full potential of their workforce, fostering innovation, increasing productivity, and ultimately achieving greater success. The future of work hinges on creating environments where employees thrive, not just survive.
Further research and ongoing dialogue on effective leadership styles are crucial to ensuring that organizations adapt and create workplaces that foster growth, engagement, and overall well-being. Embracing these changes is imperative for creating truly successful and sustainable organizations.
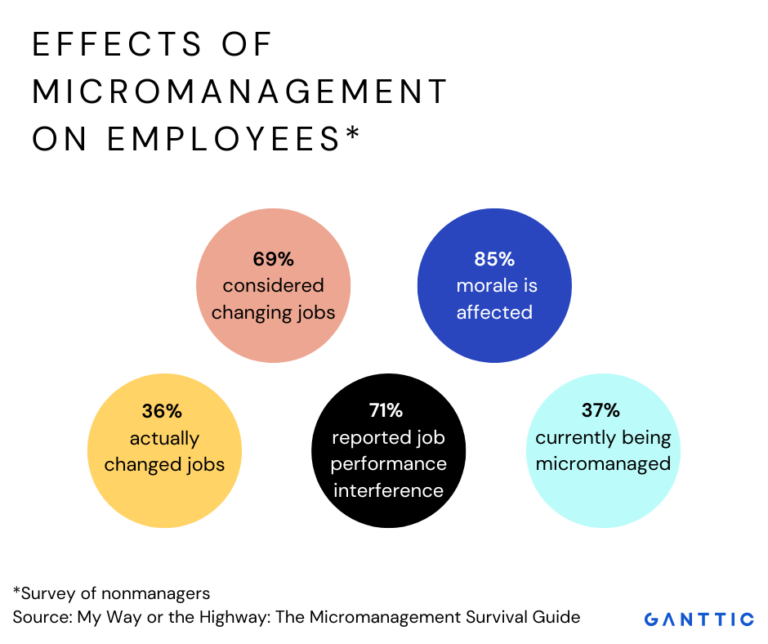




![Effects Of Micromanagement On Employees Pdf 12 Examples Of Micromanagement At Work [with Infographic] – Eggcellent Work](https://eggcellentwork.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/examples-of-micromanagement-1-512x1024.jpg)