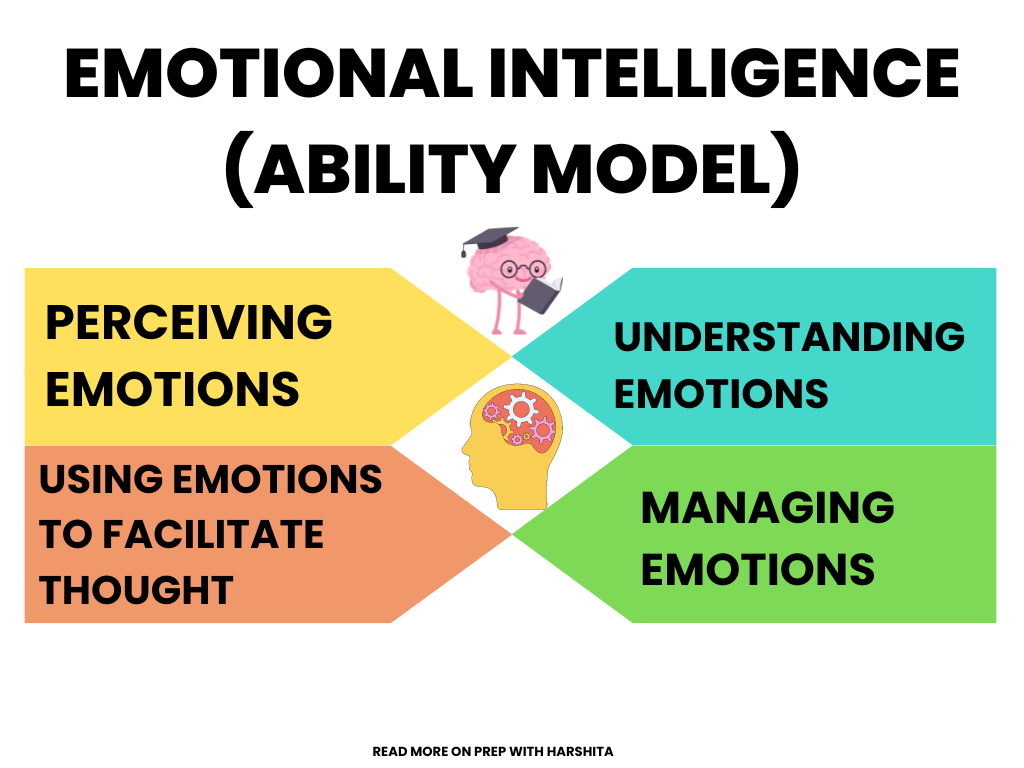
Emotional Intelligence Involves Which Of The Following Abilities

Imagine a bustling office, the air thick with deadlines and the murmur of collaboration. A project deadline looms, tensions are high, and frustration simmers just beneath the surface. But instead of erupting into chaos, the team navigates the pressure with grace, understanding, and a shared sense of purpose. What's the secret ingredient? It’s not just technical skill, but something arguably more crucial: emotional intelligence.
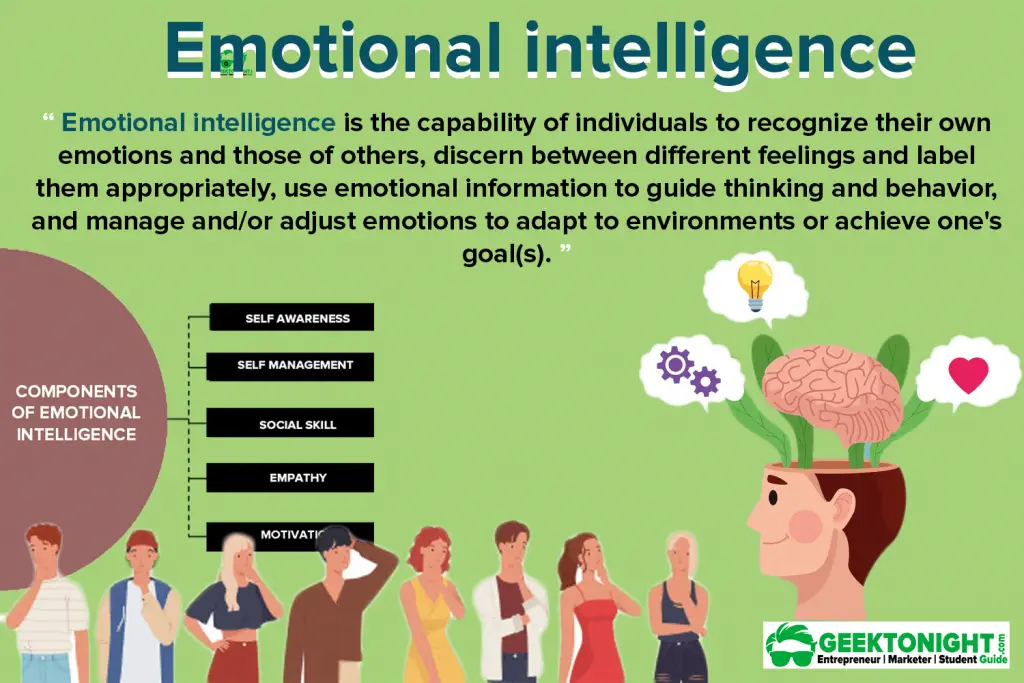
At its heart, emotional intelligence (EQ) is the ability to understand and manage your own emotions, as well as recognize and influence the emotions of those around you. It's not about being overly sensitive or "soft," but about being aware and responsive in a way that fosters better relationships and more effective outcomes. But what specific abilities make up this crucial skill set? Let's delve into the core components of emotional intelligence and see how they play out in real life.
Understanding the Building Blocks of EQ
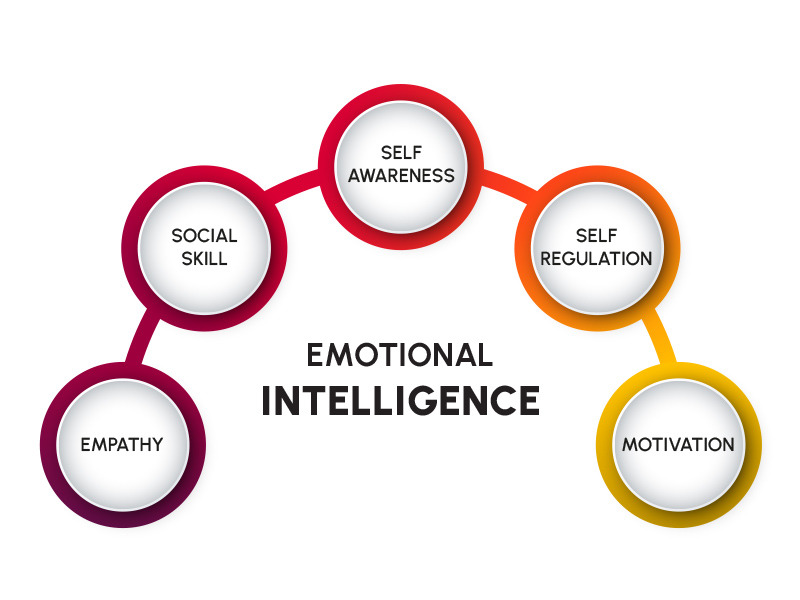
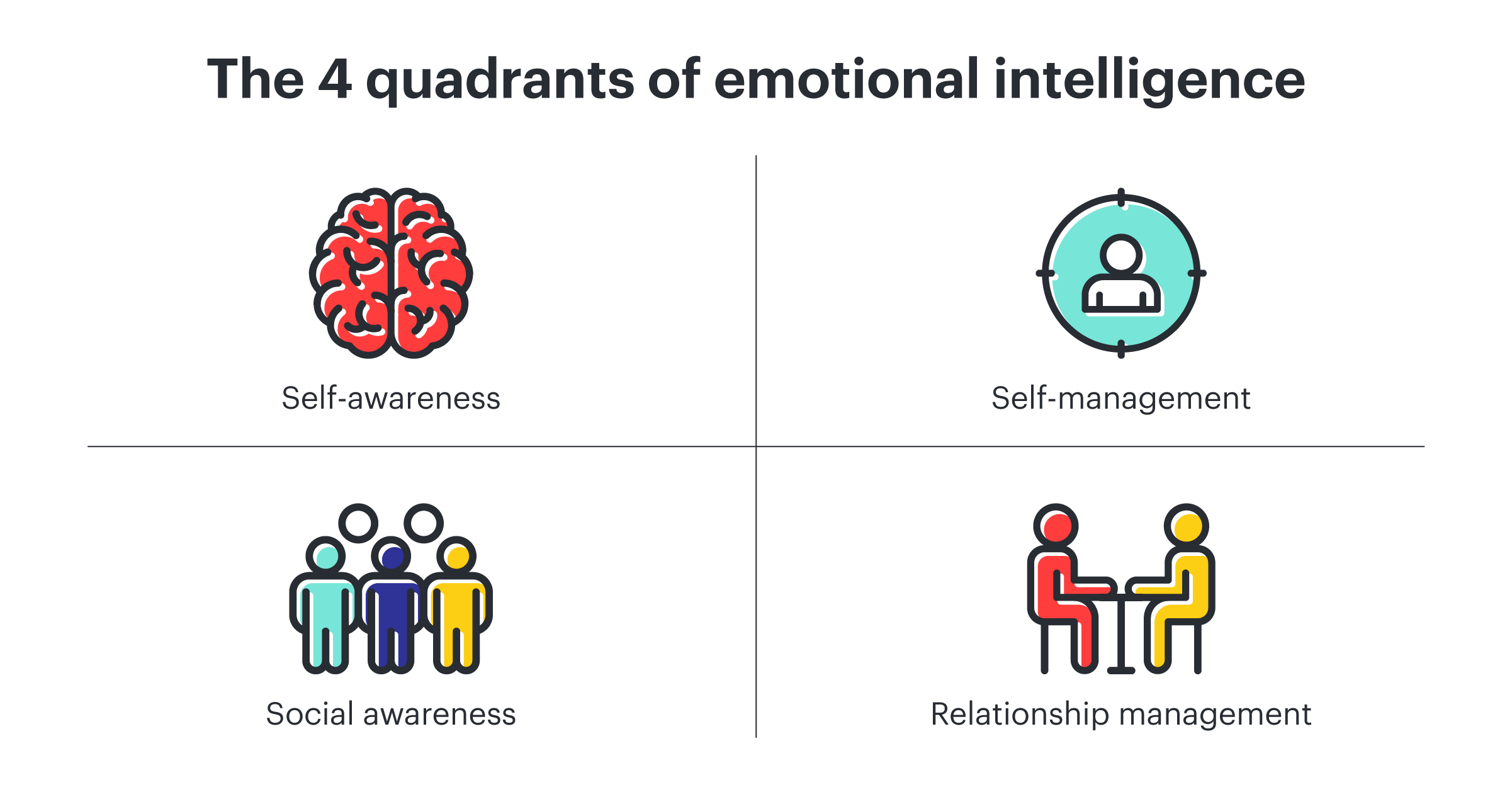
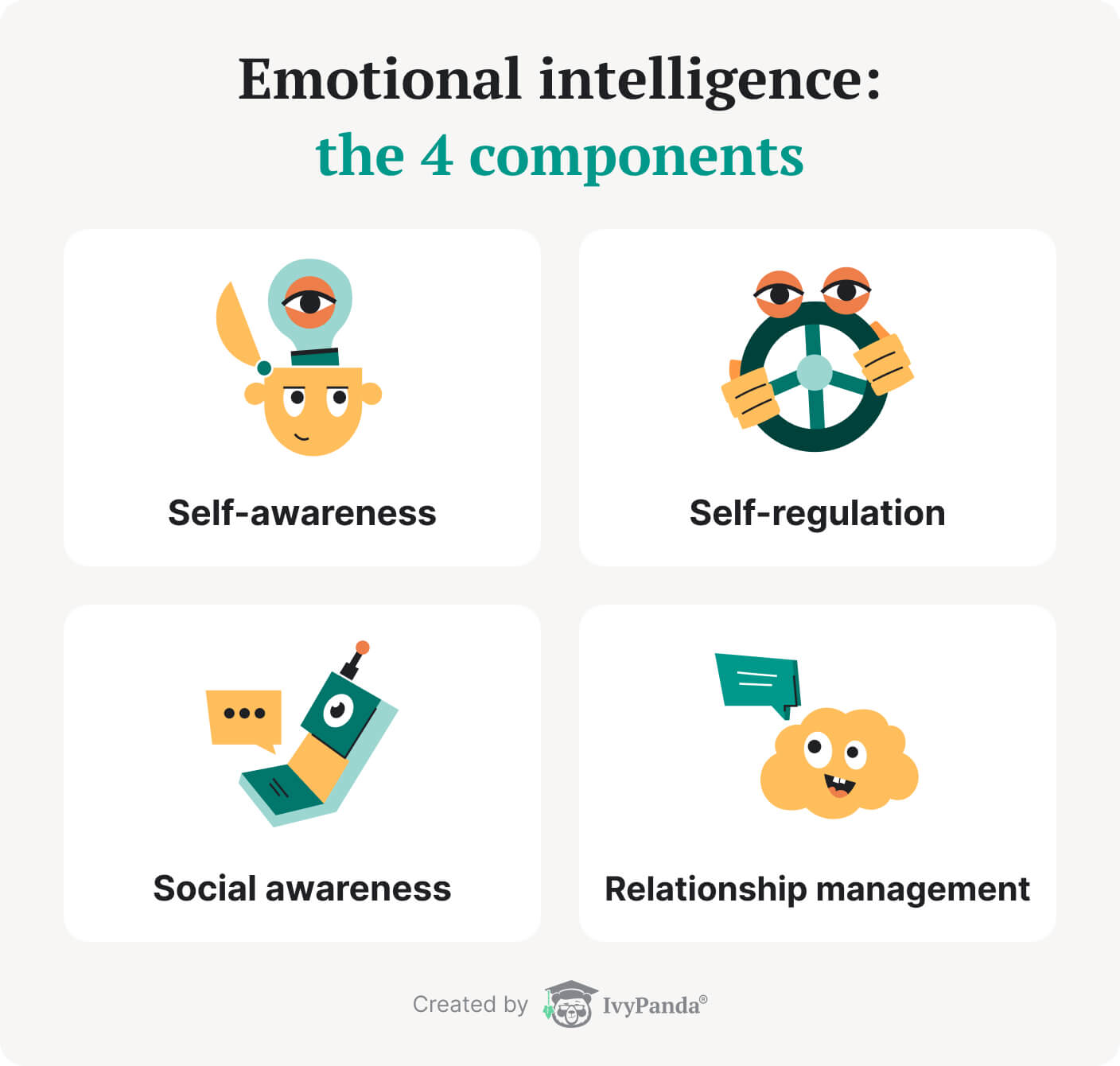
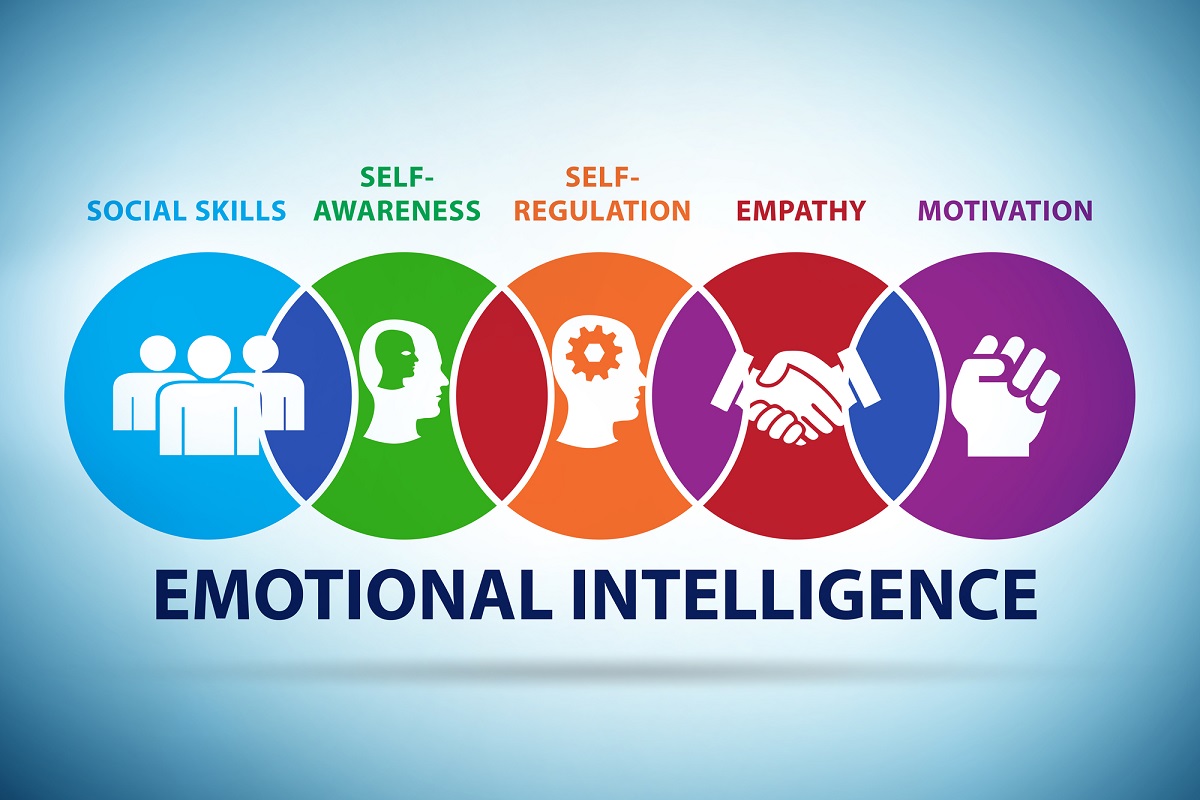
The concept of emotional intelligence gained significant traction in the 1990s, largely thanks to the work of psychologist Daniel Goleman, whose book "Emotional Intelligence" popularized the idea. While various models exist, Goleman's framework is widely recognized and breaks down EQ into five key components.
Self-Awareness: Knowing Yourself
Self-awareness is the cornerstone of emotional intelligence. It involves understanding your own emotions, strengths, weaknesses, values, and motivations. It's about having an accurate picture of yourself and knowing how your emotions impact others.
A self-aware individual recognizes when they're feeling stressed or anxious and understands the triggers behind those feelings. This enables them to manage their reactions more effectively and avoid lashing out or making impulsive decisions. They also understand their own strengths and weaknesses.
Self-Regulation: Managing Your Emotions
Once you're aware of your emotions, the next step is being able to manage them effectively. This is where self-regulation comes in. It's the ability to control impulsive feelings and behaviors, manage your emotions in healthy ways, take initiative, follow through on commitments, and adapt to changing circumstances.
Someone with strong self-regulation can remain calm and composed under pressure. They think before they act and don't let their emotions dictate their behavior. They are also able to handle stress and adapt to unexpected changes, as reported in numerous studies by the Consortium for Research on Emotional Intelligence in Organizations (CREIO).
Motivation: Driving Yourself Forward
Emotional intelligence also involves intrinsic motivation – being driven to achieve for the sake of achievement, rather than for external rewards like money or status. This includes having a passion for your work, setting challenging goals, and being resilient in the face of setbacks.
Motivated individuals are optimistic and committed to their goals. They see challenges as opportunities for growth and are willing to put in the effort required to succeed. They possess a drive that comes from within, fueling their passion and determination.
Empathy: Understanding Others
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. It involves putting yourself in someone else's shoes and seeing things from their perspective. It's about recognizing and responding to the emotional needs of others.
An empathetic person listens attentively to others, pays attention to nonverbal cues, and responds with compassion and understanding. They are able to build rapport and create strong relationships based on trust and mutual respect. This is crucial to building strong teams.
Social Skills: Managing Relationships
The final component of emotional intelligence is social skills, which encompasses a wide range of abilities, including communication, conflict management, leadership, and teamwork. It's about being able to build and maintain healthy relationships, influence others, and work effectively in a team.
Individuals with strong social skills are good communicators, able to express themselves clearly and persuasively. They can also resolve conflicts constructively and build consensus among diverse groups. They know how to work effectively with others and how to build good teams.
The Significance of Emotional Intelligence
The importance of emotional intelligence extends far beyond the workplace. It plays a crucial role in all aspects of life, from personal relationships to physical and mental well-being. Research has consistently shown that individuals with high EQ are more successful, healthier, and happier.
According to a Harvard Business Review article, emotional intelligence is a stronger predictor of leadership success than IQ. It's also linked to improved teamwork, customer service, and overall organizational performance. In personal life, EQ contributes to stronger relationships, better stress management, and greater life satisfaction.
Looking Ahead
Emotional intelligence is not a fixed trait, but rather a set of skills that can be developed and improved over time. By focusing on self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills, anyone can enhance their EQ and reap the benefits. We can all take steps to cultivate our own emotional intelligence and build a more compassionate and understanding world.
Ultimately, the power of emotional intelligence lies in its ability to connect us to ourselves and to others, fostering stronger relationships, more effective communication, and a greater sense of well-being. It's a skill that is well worth cultivating, both for personal and professional success. The skills can be improved through training and self-reflection.