Ethylene Oxide Industry Capacity And Capex

The global ethylene oxide (EO) industry is undergoing a period of significant expansion, fueled by rising demand in key downstream sectors and strategic investments aimed at bolstering production capacities. Chemical companies worldwide are committing substantial capital expenditure (capex) to construct new EO plants and upgrade existing facilities. This surge in investment signals a long-term bullish outlook for EO and its derivatives.
This article delves into the current state of ethylene oxide industry capacity and capital expenditure. We will examine the primary drivers behind this growth, key regions leading the charge, and the potential implications for the global chemical market.
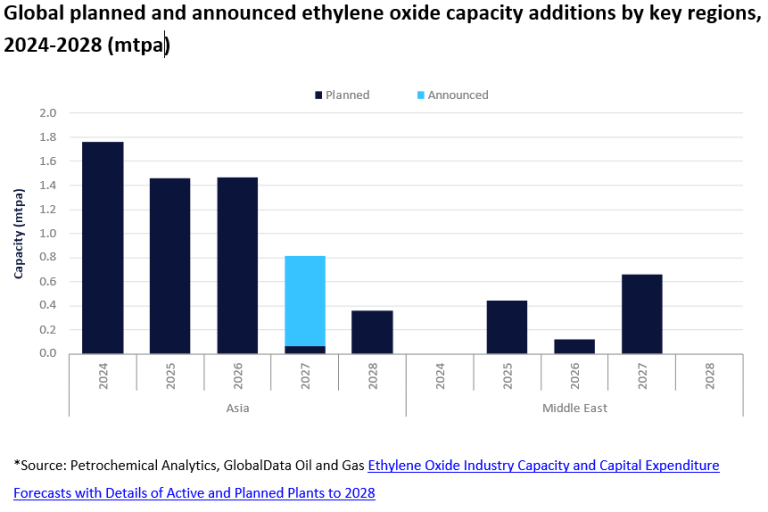
Global EO Capacity Expansion: A Snapshot
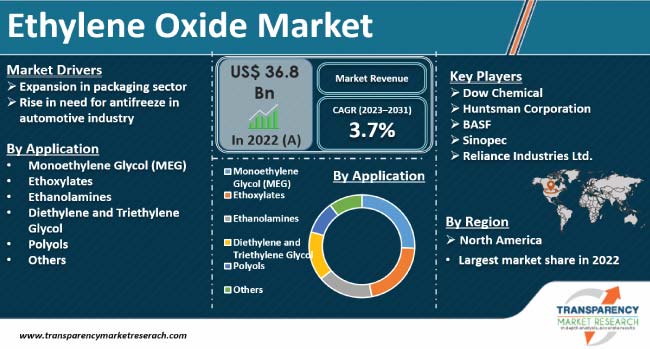
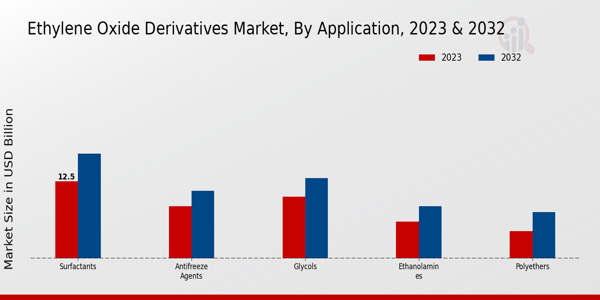
Ethylene oxide is a crucial intermediate in the production of various chemicals, including ethylene glycols (MEG, DEG, TEG), surfactants, ethanolamines, and polyether polyols. MEG, the primary derivative, is predominantly used in the manufacture of polyester fibers and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) resins. Strong demand for these end products has pushed the EO industry to increase its production capacity.
The Asia-Pacific region is at the forefront of this expansion, with China and India leading the way in terms of new plant construction and capacity additions. North America and Europe are also witnessing increased investment in EO production, albeit at a slower pace than Asia.
Key Projects and Investments
Several major projects highlight the current wave of EO capacity expansion. Shell, for example, recently completed a significant expansion of its EO production facility in Geismar, Louisiana. This project increased Shell's EO production capacity at the site by a substantial margin, strengthening its position in the North American market.
In China, multiple large-scale EO plants are under construction by both domestic and international companies. These projects are strategically located in coastal regions to leverage access to feedstocks and export markets. Sinopec and PetroChina are among the major players investing heavily in new EO capacity.
India is also experiencing a surge in EO production capacity, driven by increasing domestic demand for MEG and other derivatives. Reliance Industries and other Indian companies are undertaking significant expansion projects to meet this growing demand.
Drivers of Growth
The expansion of EO production capacity is driven by a confluence of factors. The most significant is the robust growth in demand for polyester fibers and PET resins, particularly in Asia.
The increasing use of PET in packaging applications, driven by the food and beverage industry, is also fueling demand for MEG and, consequently, EO. The growing global population and rising living standards, particularly in developing countries, are contributing to this trend.
The construction industry's demand for insulation materials, which utilizes polyether polyols derived from EO, further supports EO market growth. Moreover, the increasing adoption of surfactants in various applications, including detergents and personal care products, contributes to the overall demand for EO.
Capex Trends and Outlook
Capital expenditure in the EO industry is expected to remain high in the coming years, as companies continue to invest in new plants and upgrades. These investments are aimed at increasing production capacity, improving operational efficiency, and reducing environmental impact.
Companies are also investing in research and development to develop new and more sustainable EO production technologies. The use of bio-based feedstocks and the development of more energy-efficient processes are key areas of focus.
The competitive landscape is also a factor influencing capex decisions. Companies are investing to maintain or improve their market share and to gain a competitive edge over their rivals.
Potential Impact and Challenges
The expansion of EO production capacity has several potential implications for the global chemical market. Increased supply could lead to lower prices for EO and its derivatives, benefiting consumers and downstream industries.
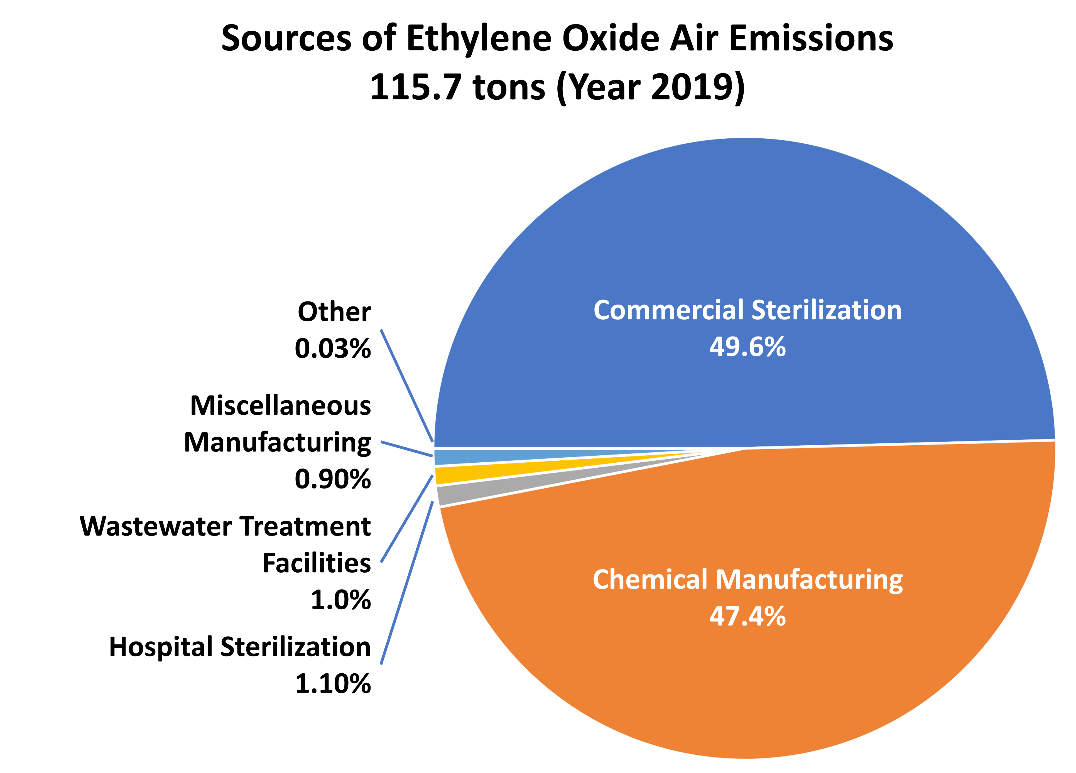
However, it could also put pressure on producers, particularly those with older, less efficient plants. The environmental impact of EO production is also a concern, and companies need to invest in technologies to reduce emissions and minimize waste.
One notable challenge is managing the volatility of feedstock prices, particularly ethylene. Fluctuations in ethylene prices can significantly impact the profitability of EO production.
Conclusion
The global ethylene oxide industry is currently experiencing a period of significant growth and investment. Driven by strong demand in key downstream sectors, companies are committing substantial capital expenditure to expand production capacity and improve operational efficiency.
While the expansion of EO capacity offers several potential benefits, it also presents challenges, including managing feedstock price volatility and mitigating environmental impacts. The industry's ability to address these challenges will be crucial to its long-term success.
Ultimately, the continued growth of the EO industry will depend on sustained demand for its derivatives and the industry's ability to adapt to changing market conditions and technological advancements. It's a dynamic sector to watch, shaping various industries from packaging to construction.












![Ethylene Oxide Industry Capacity And Capex [GET ANSWER] Production of Ethylene oxide Ethylene oxide (C2H4O) is](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/c7cc3dd1931a4b18b22597d4ec865bd9.jpg)
