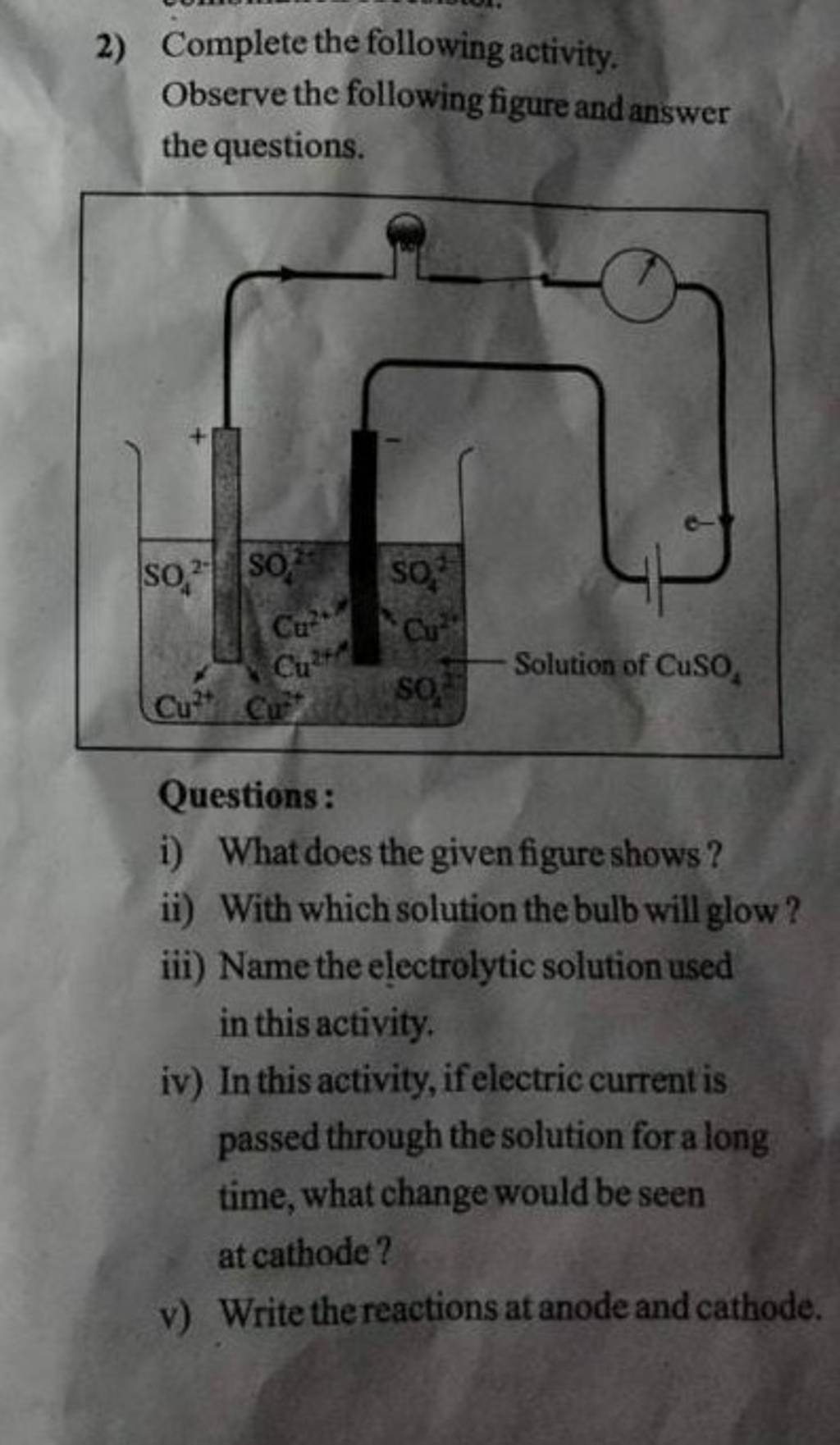
Which Of The Following Was Not Observed During This Activity
The aftermath of the controversial "Project Nightingale" simulation continues to ripple through the scientific community, with a recently released audit focusing on discrepancies in reported observations. While the exercise aimed to model real-world pandemic response scenarios, a critical review has identified key aspects that were expected but conspicuously absent from the official record.
This report, commissioned by the National Institute for Pandemic Preparedness (NIPP), scrutinizes the documentation surrounding Project Nightingale, specifically focusing on deviations between the intended simulation design and the documented outcomes. The central question being addressed is: which pre-determined parameters of the simulation were demonstrably not observed during the activity, and what implications do these omissions have for the validity of the exercise and future preparedness efforts?
Data Integrity and Protocol Adherence
One of the most significant findings of the NIPP audit concerns the consistent underreporting of mental health impacts on simulated healthcare workers. The original protocol stipulated that psychological stress, burnout rates, and requests for mental health support should be meticulously tracked throughout the simulation.
However, the audit reveals a significant gap between the expected level of reporting and the actual data collected, raising questions about the accuracy and comprehensiveness of the overall assessment. Several researchers have voiced concerns that the underreporting might stem from either a failure to accurately simulate real-world stressors or a systematic bias in data collection.
Furthermore, adherence to the established infection control protocols within the simulation was also flagged as an area of concern. While the documentation highlights overall compliance, the audit points to a lack of detailed reporting on specific protocol breaches, such as inadequate PPE usage or deviations from established quarantine procedures.
Community Engagement and Public Communication
Project Nightingale's design included a significant community engagement component, intending to simulate public reactions, misinformation spread, and the effectiveness of various communication strategies. The simulation envisioned tracking metrics such as public trust in official sources, rates of vaccine acceptance (within the simulated population), and the prevalence of conspiracy theories circulating online.
Surprisingly, the audit found limited evidence of comprehensive monitoring of these community-level indicators. The absence of detailed data on public opinion and behavior raises concerns about the simulation's ability to accurately reflect the complexities of a real-world pandemic response.
Dr. Anya Sharma, lead author of the NIPP audit, stated, "The omission of robust community engagement data undermines the simulation's capacity to inform public health messaging and strategies for managing public anxieties during a crisis." The audit report further recommends developing more realistic simulations of information dissemination and counter-misinformation strategies.
Economic Impact and Resource Allocation
The simulated economic consequences of the pandemic, including business closures, job losses, and supply chain disruptions, were also not consistently recorded. While some data on hospital resource allocation was collected, the broader economic impact on different sectors and demographic groups was poorly documented.
This lack of economic data limits the usefulness of the simulation for informing policymakers about effective economic mitigation strategies. The audit highlights the need for more comprehensive modeling of economic factors and their interplay with public health interventions in future simulations.
Ethical Considerations and Equity
Ethical considerations, particularly those related to equitable access to resources and healthcare, were supposed to be monitored closely during the simulation. The original design included tracking disparities in infection rates, hospitalization rates, and mortality rates among different demographic groups.
The audit reveals inconsistencies in the collection and reporting of data related to these disparities. While some demographic data was collected, the analysis often lacked the depth needed to identify and address potential inequities in the pandemic response. This absence raises concerns about the simulation's ability to inform policies that promote health equity during a crisis.
The report specifically noted a lack of data surrounding the disproportionate impact on marginalized communities, which severely limits the exercise’s benefit. Professor David Chen, a bioethicist consulted for the review, commented, "Without meticulous attention to equity, these exercises risk perpetuating, rather than mitigating, existing health disparities."
Moving Forward: Recommendations and Revisions
The findings of the NIPP audit have prompted calls for significant revisions to the Project Nightingale simulation protocol. The recommendations include strengthening data collection methods, enhancing community engagement strategies, and prioritizing ethical considerations related to equity.
Future simulations should incorporate more realistic models of human behavior, including the spread of misinformation and the impact of social media on public opinion. Furthermore, greater emphasis should be placed on interdisciplinary collaboration, bringing together experts from fields such as public health, economics, psychology, and communication to create more comprehensive and realistic simulations.
By addressing the gaps identified in the NIPP audit, future pandemic preparedness exercises can provide valuable insights for policymakers, healthcare professionals, and the public, ultimately improving our ability to respond effectively to future health crises. The key takeaway is that simulations are only as useful as the data they generate and the rigor with which that data is analyzed.

![Which Of The Following Was Not Observed During This Activity [ANSWERED] 9 ECG and Pulse Measurement Activity During this activity](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20220616015134734933-4583315.jpg?h=512)
![Which Of The Following Was Not Observed During This Activity [Biology Class 10] Observe the three figures given below. Which of the](https://d1avenlh0i1xmr.cloudfront.net/4bb687a5-595c-41ed-82f0-c7469f6a8210/question-11---observe-the-three-figures---teachoo.jpg)



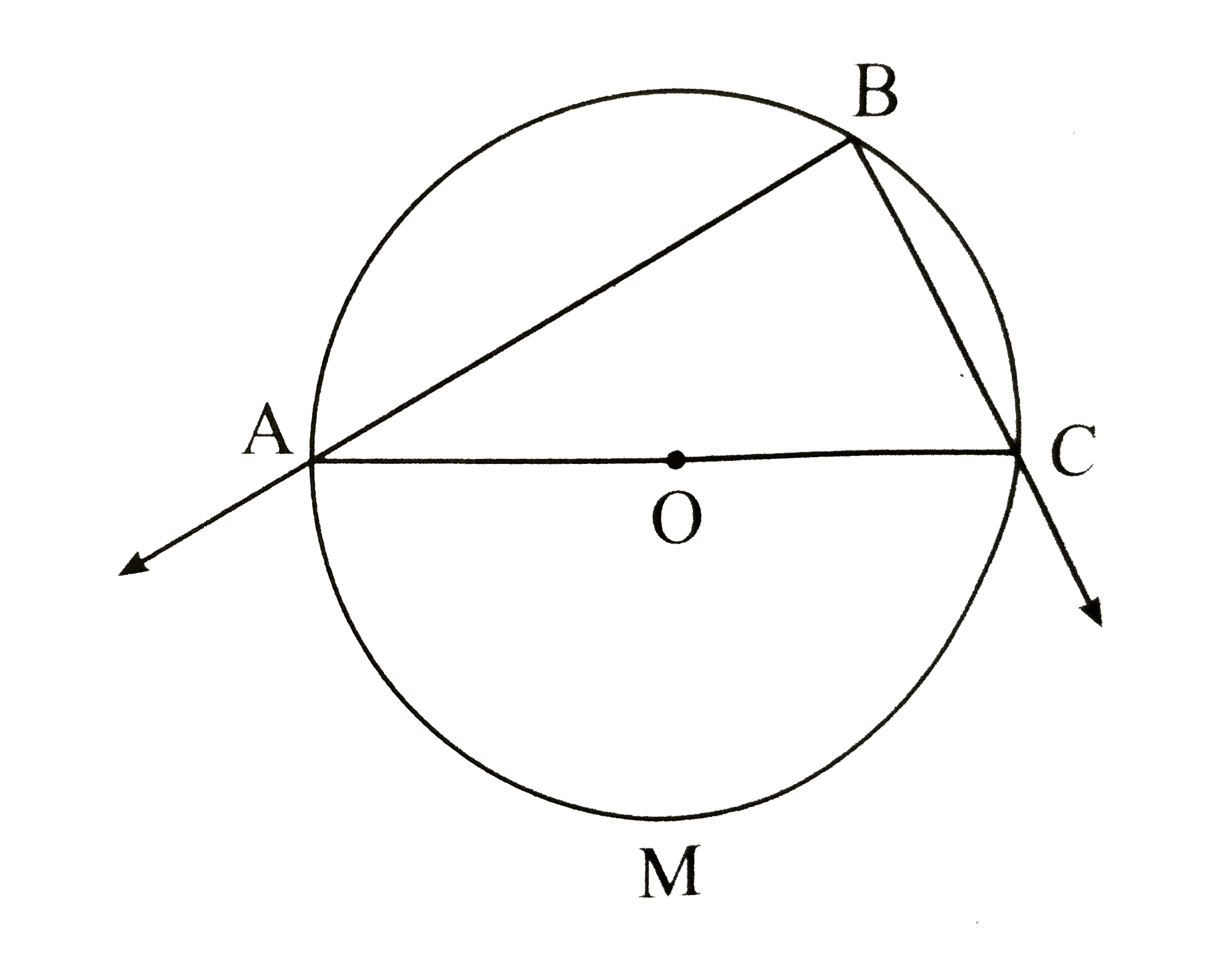

![Which Of The Following Was Not Observed During This Activity 3] Observe the figure and complete the following activity. By Inscribed a..](https://classroom-images.cdn.askfilo.com/classroom/1676624921901_vhzuqelu_3650924.jpg)
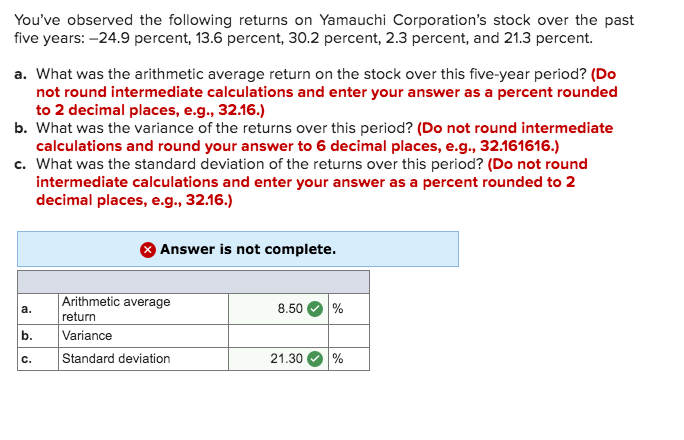
![Which Of The Following Was Not Observed During This Activity [Telugu Solution] Observe the following table showing different activi](https://d10lpgp6xz60nq.cloudfront.net/physics_images/BYD_BIO_X_P2_C09_S06_022_Q01.png)

![Which Of The Following Was Not Observed During This Activity [FREE] Suppose you are studying a new population of rock pocket mice in](https://media.brainly.com/image/rs:fill/w:1200/q:75/plain/https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/dd8/d4eddc624b6828dc20207007aff970ad.png)
