Federal Student Loans Vs Private Student Loans Yelofunding
The landscape of financing higher education is complex, with students and families often navigating a maze of options to cover the rising costs of tuition, fees, and living expenses. Two primary avenues for student loans exist: federal student loans, backed by the government, and private student loans, offered by banks and other financial institutions. A lesser-known, emerging alternative called yelofunding is also starting to gain traction, presenting a different approach to funding education.
Understanding the nuances of each option is crucial for borrowers to make informed decisions, minimize debt burdens, and achieve their educational goals. This article will delve into the key differences between federal student loans, private student loans, and yelofunding, analyzing their terms, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
Federal Student Loans: Government-Backed Assistance
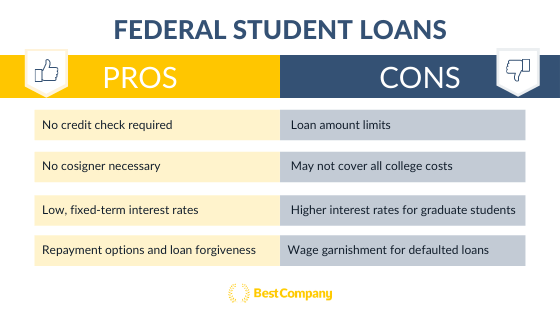
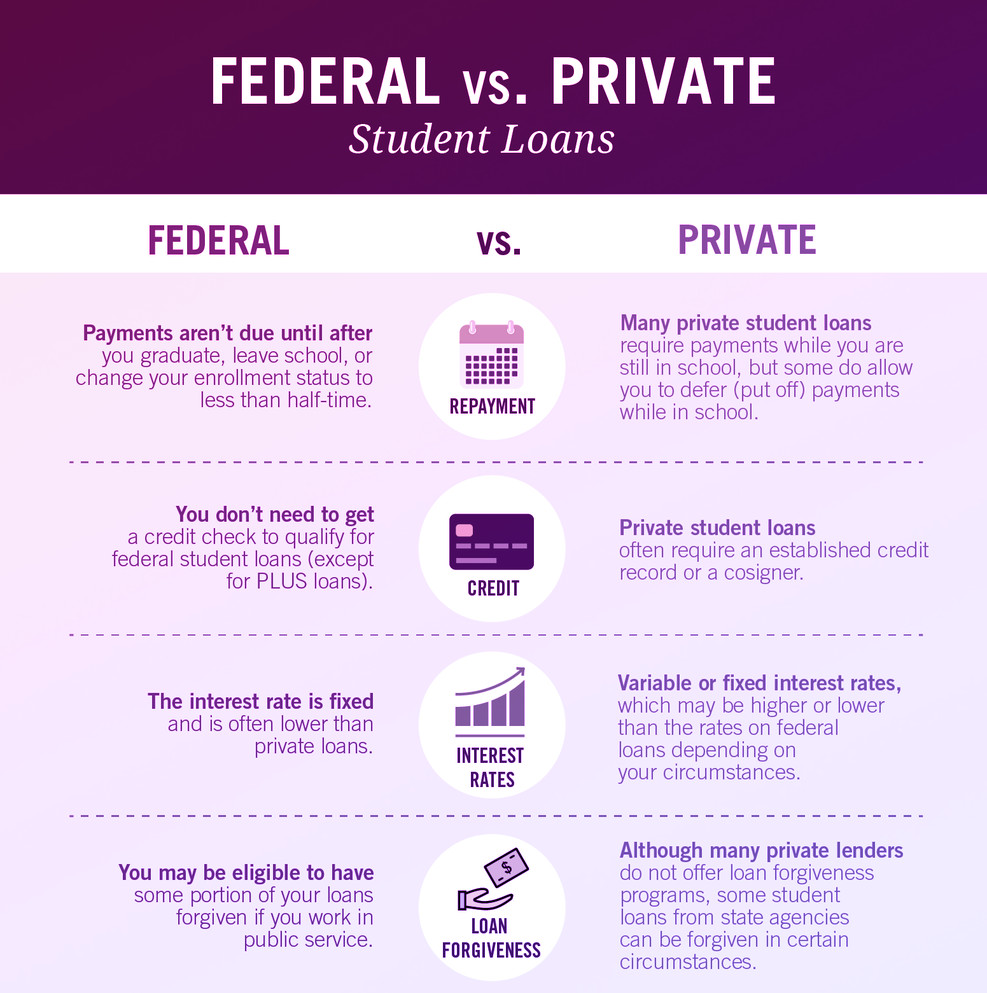
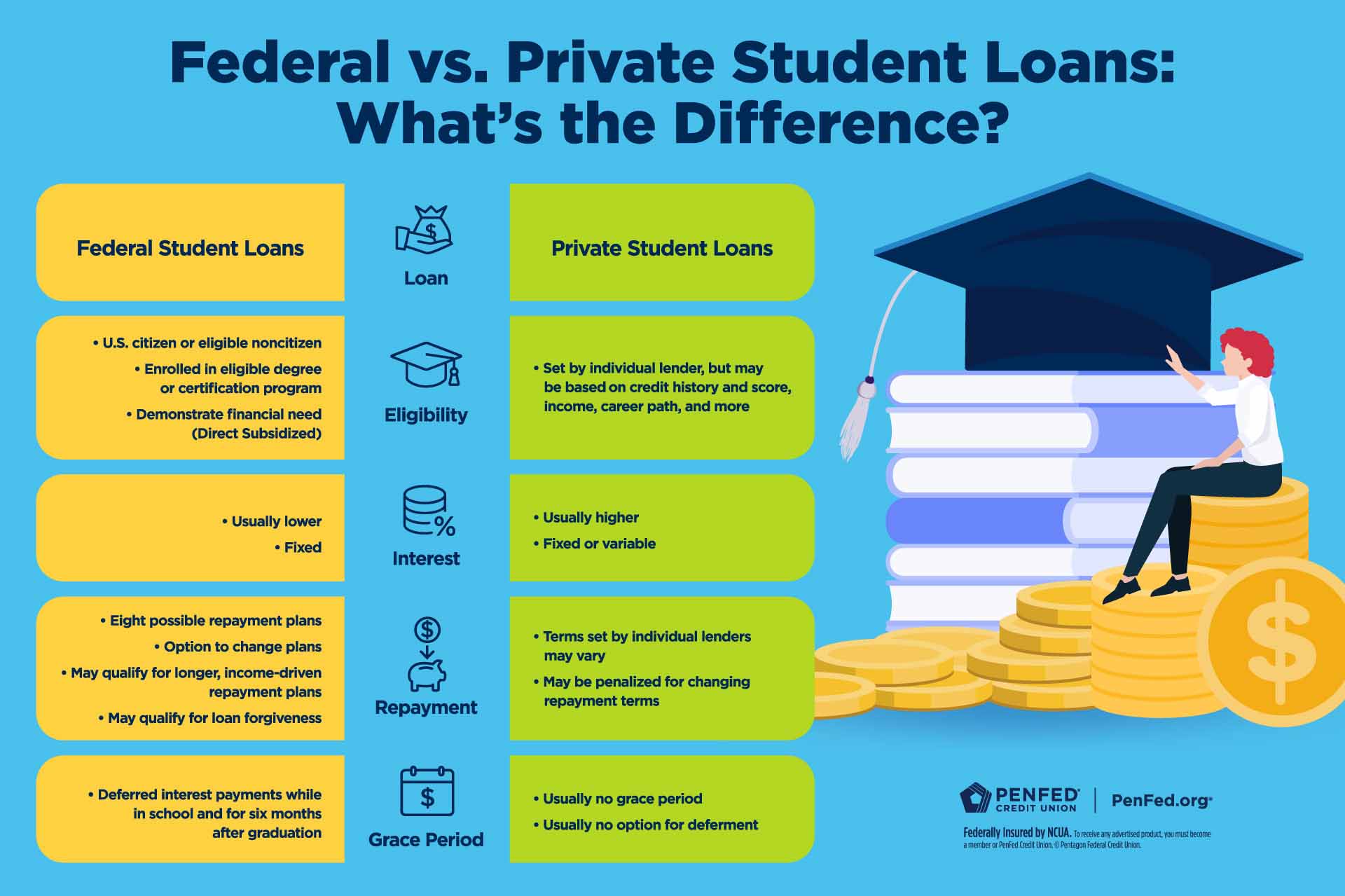
Federal student loans are provided by the U.S. Department of Education and offer several advantages not typically found in private loans. These advantages often include lower interest rates, flexible repayment options, and access to loan forgiveness programs.
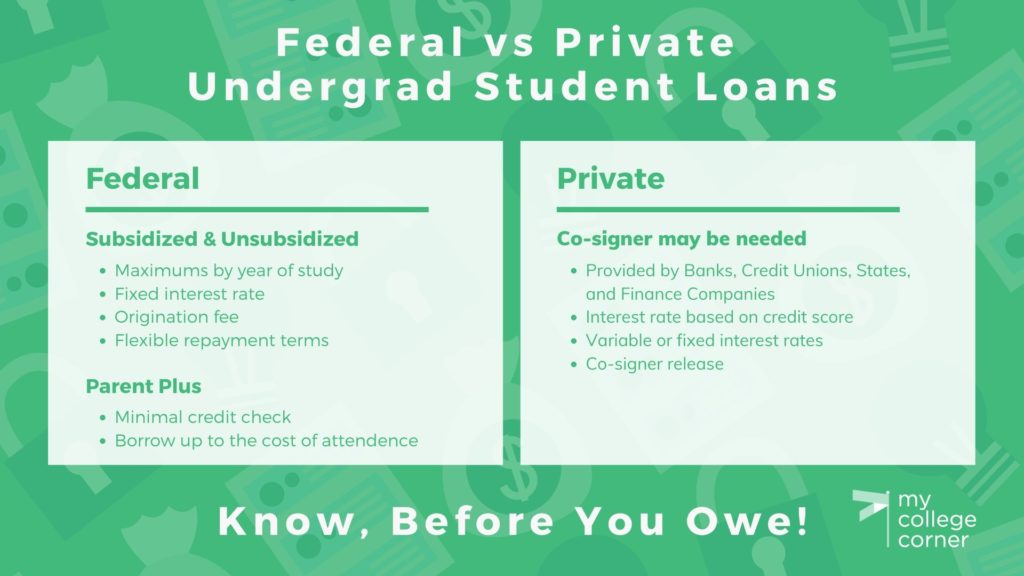
There are several types of federal student loans, including Direct Subsidized Loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, and Direct PLUS Loans. Subsidized loans are available to undergraduate students with demonstrated financial need, and the government pays the interest while the student is in school and during grace periods. Unsubsidized loans are available to both undergraduate and graduate students, regardless of financial need, but interest accrues from the time the loan is disbursed.
PLUS Loans are available to graduate or professional students and parents of dependent undergraduate students to help pay for education expenses not covered by other financial aid. Federal student loans also offer income-driven repayment (IDR) plans, which adjust monthly payments based on the borrower's income and family size. These plans can provide significant relief to borrowers struggling to manage their debt.
Furthermore, certain federal student loan programs offer the possibility of loan forgiveness for borrowers who work in public service or meet other specific criteria. For example, the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program forgives the remaining balance on Direct Loans after 120 qualifying monthly payments made while working full-time for a qualifying employer.
Private Student Loans: Market-Driven Financing
Private student loans are offered by banks, credit unions, and other private lenders. Unlike federal loans, private loans are not backed by the government and typically have stricter eligibility requirements and less flexible repayment options.
Interest rates on private student loans are generally higher than those on federal loans, and they are often variable, meaning they can fluctuate over time. This can make budgeting and repayment unpredictable. Approval for private student loans is often based on creditworthiness, and borrowers with limited credit history may need a co-signer to qualify.
Private student loans typically do not offer the same income-driven repayment plans or loan forgiveness options as federal loans. While some private lenders may offer deferment or forbearance options in cases of financial hardship, these are often limited and come with specific conditions.
However, private student loans can be useful for students who have exhausted their federal loan options or who need to borrow more than the federal loan limits allow. They can also be beneficial for borrowers with strong credit scores who may be able to secure a lower interest rate than offered by federal unsubsidized loans.
Yelofunding: A Novel Approach
Yelofunding represents a relatively new and innovative approach to financing education. It essentially works as a form of income share agreement (ISA), where students receive funding for their education in exchange for a percentage of their future income for a set period.
Instead of accruing debt, students enter into an agreement to share a portion of their earnings once they graduate and secure employment. The percentage of income shared and the duration of the agreement vary depending on the terms of the yelofunding provider.
Yelofunding can be an attractive option for students pursuing fields with uncertain job prospects or those who are hesitant to take on traditional student loan debt. It aligns the interests of the student and the funding provider, as the provider's return on investment is directly tied to the student's success.
However, yelofunding also has potential drawbacks. If a student's income is significantly higher than expected, they may end up paying back more than they would have with a traditional loan. Additionally, the terms of yelofunding agreements can be complex, and it is crucial for students to carefully review and understand the implications before entering into an agreement.
Weighing the Options: A Comparative Analysis
Choosing the right financing option for education requires careful consideration of individual circumstances and financial goals. Federal student loans generally offer the most borrower-friendly terms and protections, including lower interest rates, flexible repayment options, and access to loan forgiveness programs.
Private student loans can be a viable option for students who need to borrow more than the federal loan limits allow or who have strong credit scores. However, borrowers should carefully compare interest rates and repayment terms and be aware of the risks associated with variable interest rates and limited repayment flexibility.
Yelofunding presents an interesting alternative, but it is essential to fully understand the terms and potential implications before committing to an agreement. Students should carefully consider their career prospects and potential income before deciding whether yelofunding is the right choice for them.
Ultimately, the best approach to financing education is to explore all available options, carefully compare the terms and benefits of each, and make an informed decision that aligns with individual financial circumstances and educational goals. Seeking advice from a financial advisor can also be beneficial in navigating the complex world of student loan financing.