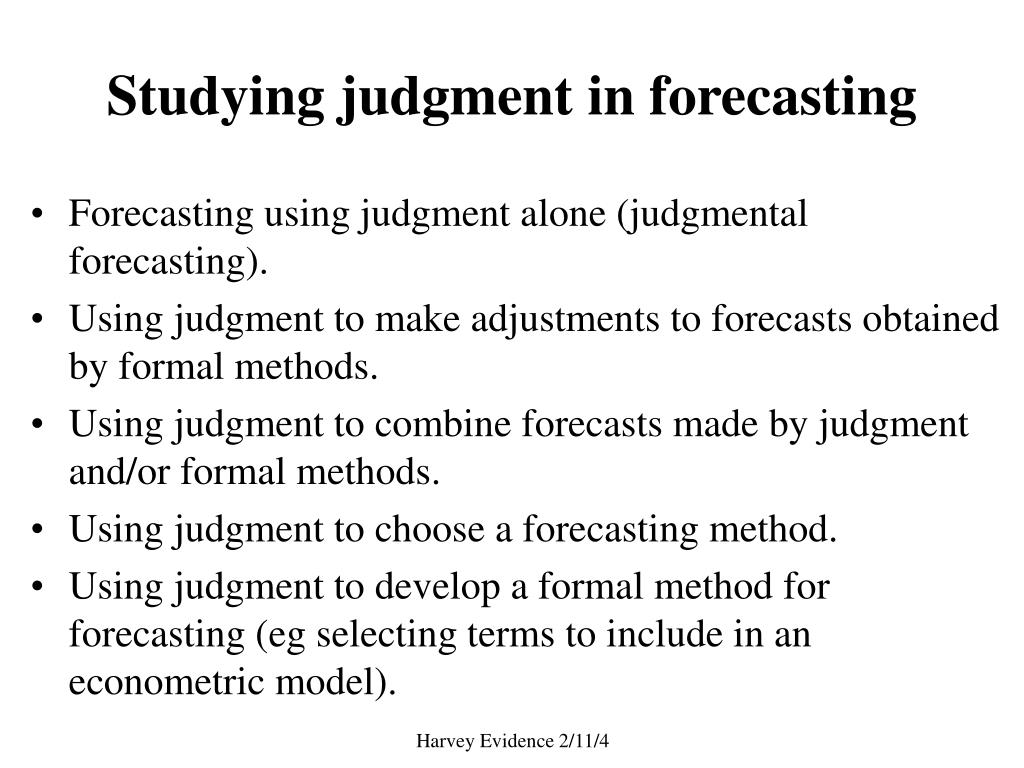
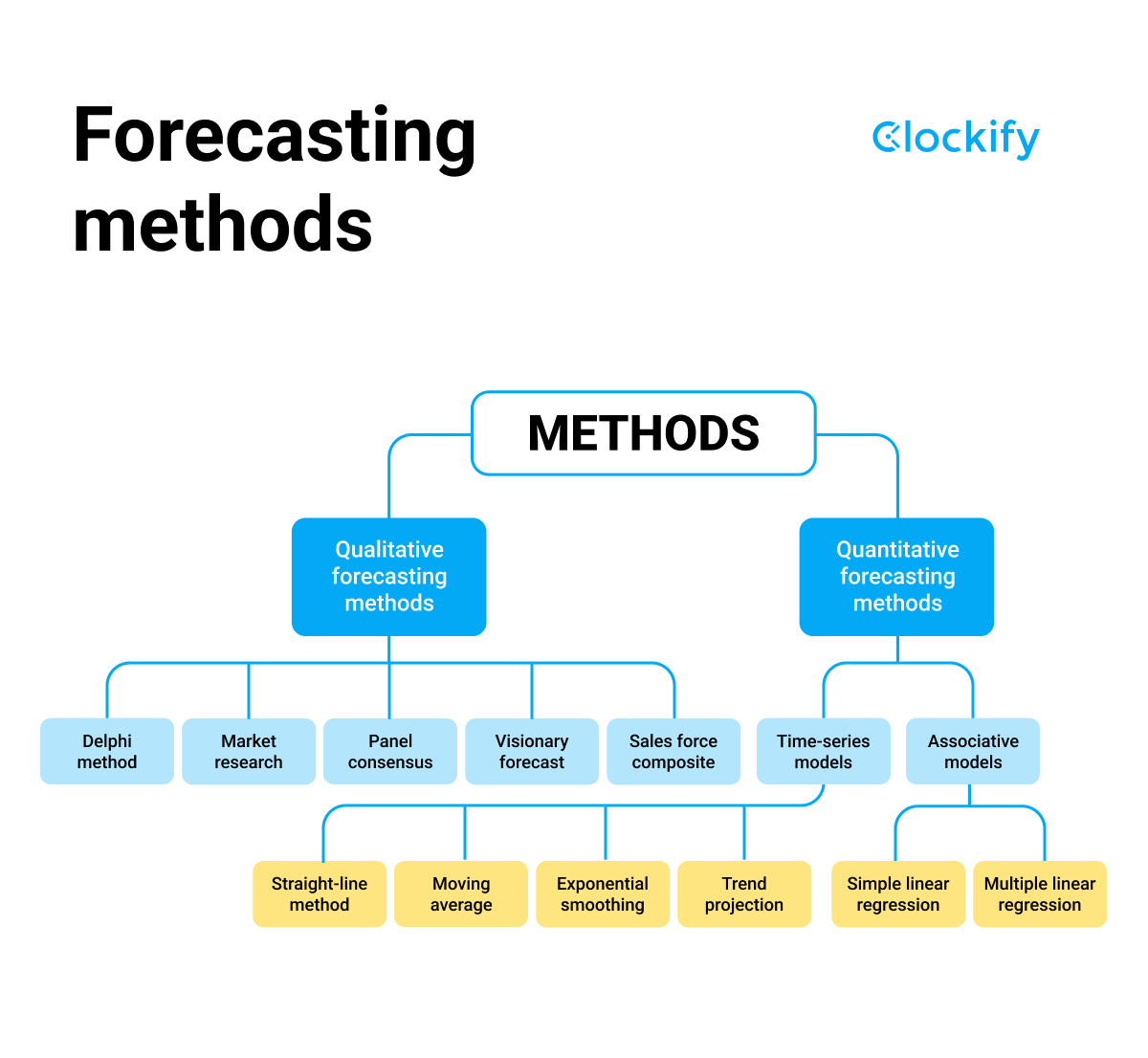
Forecasts Based On Judgment And Opinion Do Not Include

The global economic landscape is increasingly volatile, buffeted by geopolitical tensions, technological disruptions, and climate change impacts. Traditional forecasting methods, heavily reliant on historical data and econometric models, are struggling to keep pace, leading to growing concerns about the accuracy and reliability of predictions influencing critical policy decisions.
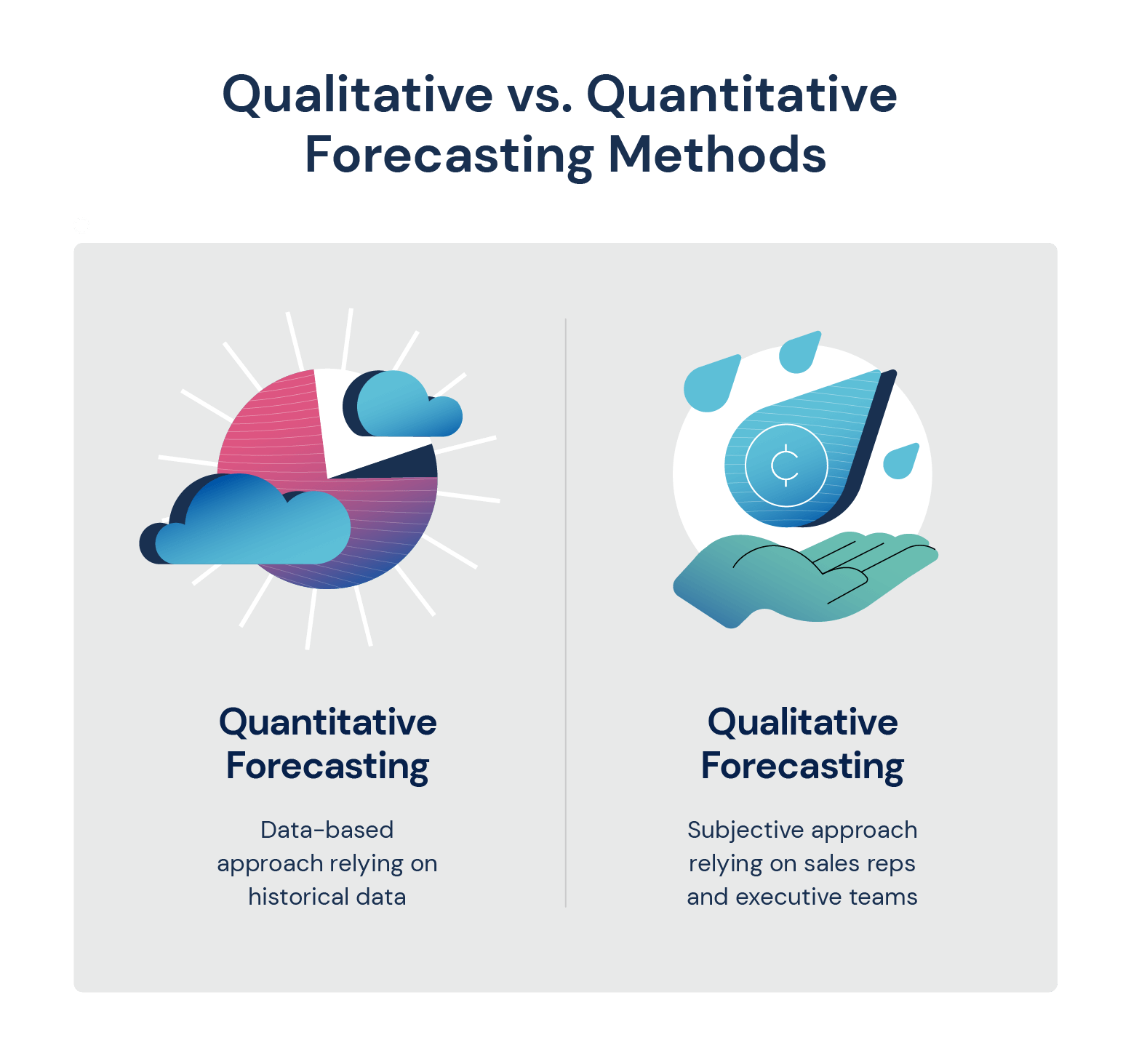
The core issue lies in the limitations of purely quantitative forecasts. While valuable, they often fail to incorporate the qualitative elements – the human judgments, expert opinions, and unpredictable events – that significantly shape future outcomes. This deficiency necessitates a re-evaluation of how forecasts are constructed and interpreted, emphasizing a more holistic approach that balances data-driven analysis with informed subjective assessments.
The Rise of Quantitative Forecasting and Its Limitations
For decades, quantitative forecasting has been the dominant paradigm in economics and finance. These models use statistical techniques to analyze past data and project future trends. They are favored for their perceived objectivity and mathematical rigor.
However, the 2008 financial crisis and the recent COVID-19 pandemic exposed the inherent limitations of relying solely on quantitative models. These events demonstrated that unforeseen shocks and shifts in sentiment can render purely data-driven forecasts inaccurate and even misleading.
Econometric models, for instance, often assume stable relationships between variables. But these relationships can break down during periods of rapid change or systemic crisis.
The Importance of Expert Judgment and Qualitative Insights
Recognizing the limitations of quantitative approaches, many experts are advocating for incorporating expert judgment and qualitative insights into the forecasting process. This involves soliciting opinions from industry leaders, policymakers, and academics who possess deep domain knowledge and an understanding of the nuances that quantitative models may miss.
Qualitative factors, such as political stability, regulatory changes, technological breakthroughs, and shifts in consumer behavior, can have a profound impact on economic outcomes. These factors are often difficult to quantify but must be considered in any comprehensive forecast.
According to a report by the International Monetary Fund (IMF), "While quantitative models provide a valuable starting point, they should be complemented by expert judgment and scenario analysis to account for uncertainties and potential disruptions."
Challenges in Integrating Qualitative and Quantitative Data
Integrating qualitative and quantitative data presents several challenges. One of the primary hurdles is the subjective nature of expert opinions. Different experts may hold conflicting views, and their biases can influence their judgments.
Another challenge is the difficulty in translating qualitative assessments into quantitative inputs for forecasting models. This requires careful consideration of how to weigh different opinions and how to incorporate them into the model's parameters.
The World Bank notes that "Developing a robust framework for incorporating expert judgment requires transparency, accountability, and a clear understanding of the limitations of both qualitative and quantitative approaches."
The Role of Scenario Planning
Scenario planning is a valuable tool for incorporating uncertainty and exploring a range of potential future outcomes. This involves developing multiple scenarios based on different assumptions about key drivers and uncertainties.
Each scenario outlines a plausible future, and the potential implications for the economy or specific sectors are analyzed. Scenario planning allows forecasters to move beyond single-point forecasts and consider the range of possibilities.
By exploring different scenarios, policymakers and businesses can prepare for a variety of potential outcomes and develop strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities. This proactive approach enhances resilience in the face of uncertainty.
Improving Forecasting Accuracy and Reliability
To improve forecasting accuracy and reliability, several steps can be taken. First, forecasters should embrace a more holistic approach that integrates quantitative and qualitative data.
Second, they should prioritize transparency and clearly articulate the assumptions and limitations of their models. Third, they should actively seek out diverse perspectives and challenge their own biases.
Furthermore, continuous monitoring and evaluation are essential. Forecasts should be regularly updated as new data become available, and the performance of different forecasting methods should be tracked to identify areas for improvement.
The Future of Forecasting
The future of forecasting will likely involve a greater emphasis on artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns that humans may miss.
However, AI-powered forecasting tools are not a silver bullet. They still require human oversight and careful validation to ensure accuracy and avoid biases. The ideal approach will likely involve a collaboration between humans and machines, leveraging the strengths of both.
The need for critical thinking and judgment remains paramount. In an increasingly complex and uncertain world, the ability to synthesize information, assess risks, and make informed decisions will be more valuable than ever before.
Ultimately, successful forecasting requires a balance between quantitative rigor and qualitative insight. By embracing a more holistic approach, forecasters can provide more accurate and reliable predictions that inform better decision-making.





![Forecasts Based On Judgment And Opinion Do Not Include [Solved]: Two independent methods of forecasting based](https://media.cheggcdn.com/study/e82/e8280bcf-27fc-4406-973e-b49546a95c17/image.jpg)