Function Generator Circuit Using Ic 8038

Critical information has emerged regarding the construction and utilization of a function generator circuit leveraging the IC 8038. This development allows for the generation of various waveforms, impacting electronics prototyping and educational applications.
This article breaks down the core components and functionalities of a function generator circuit based on the IC 8038, offering insights for enthusiasts and professionals.
Core Components and Functionality
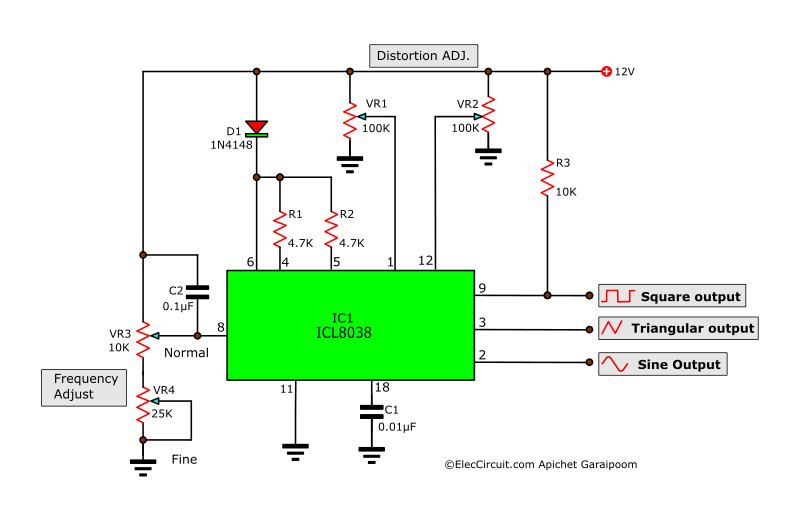
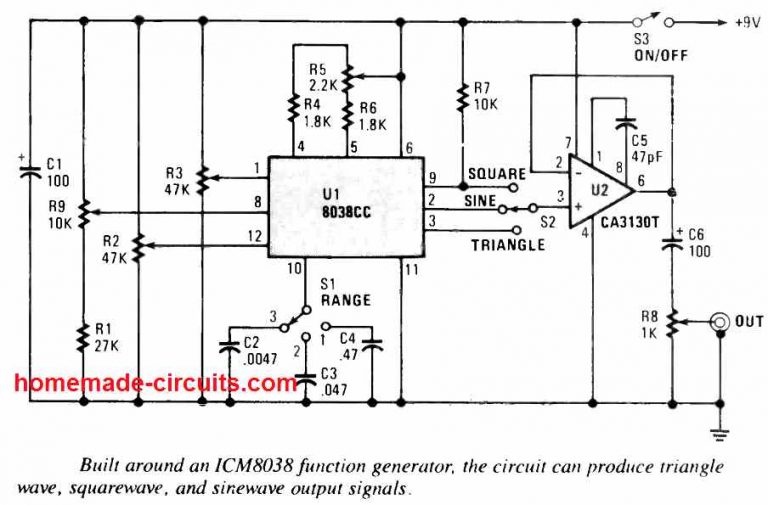
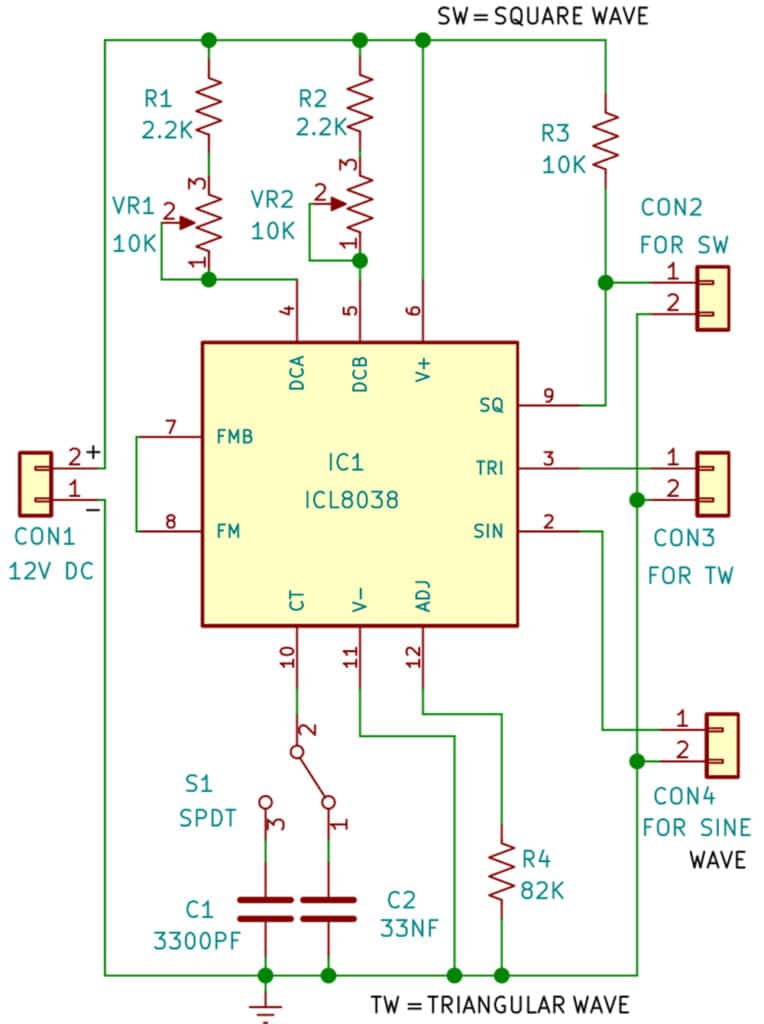
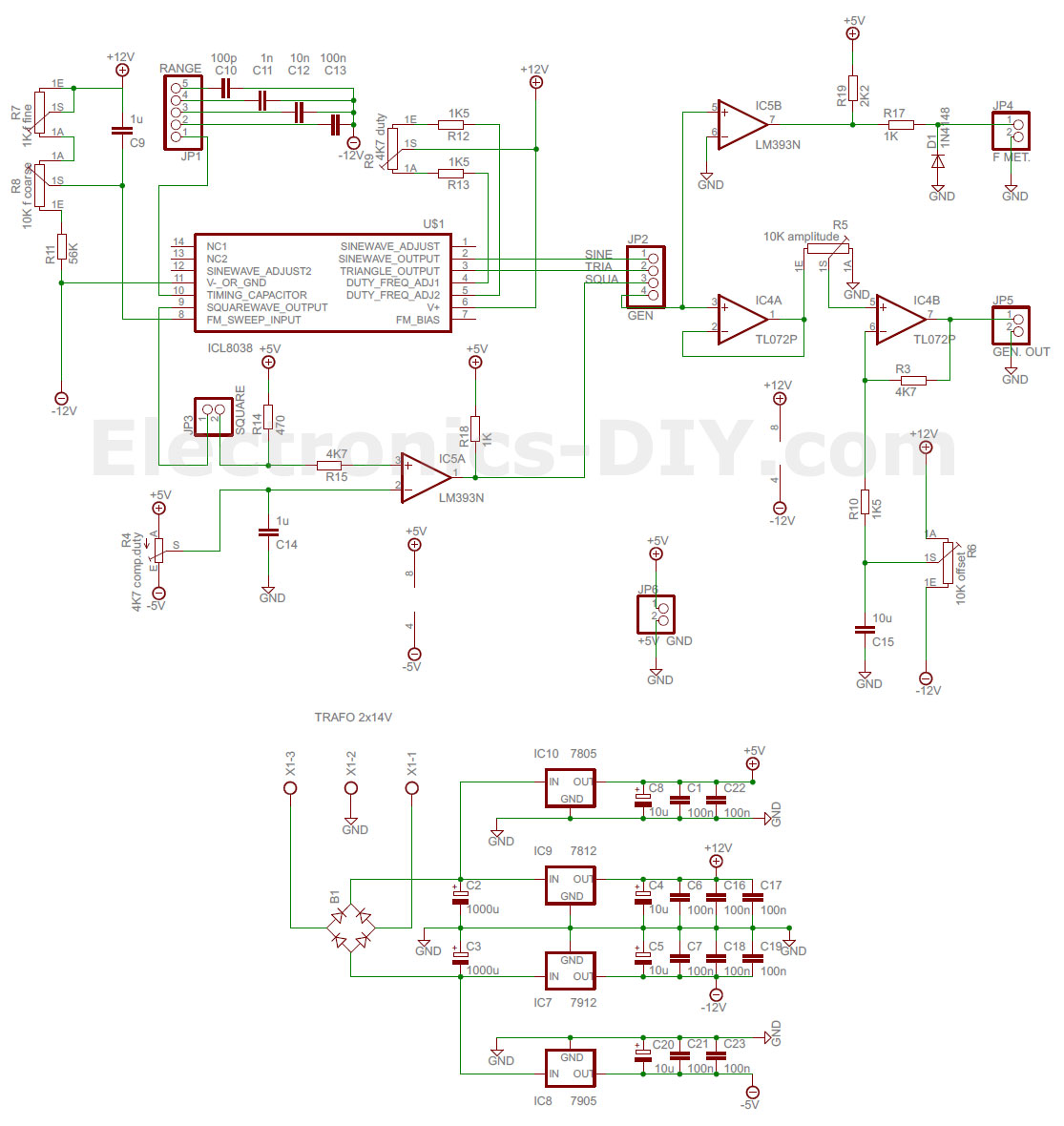
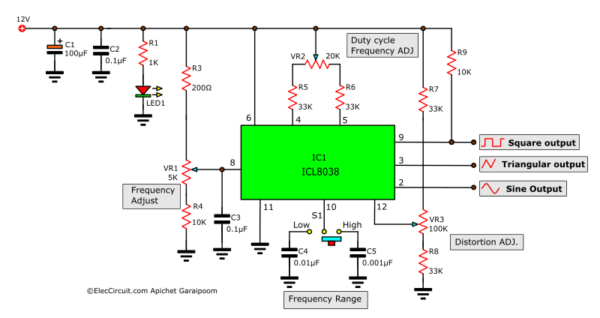
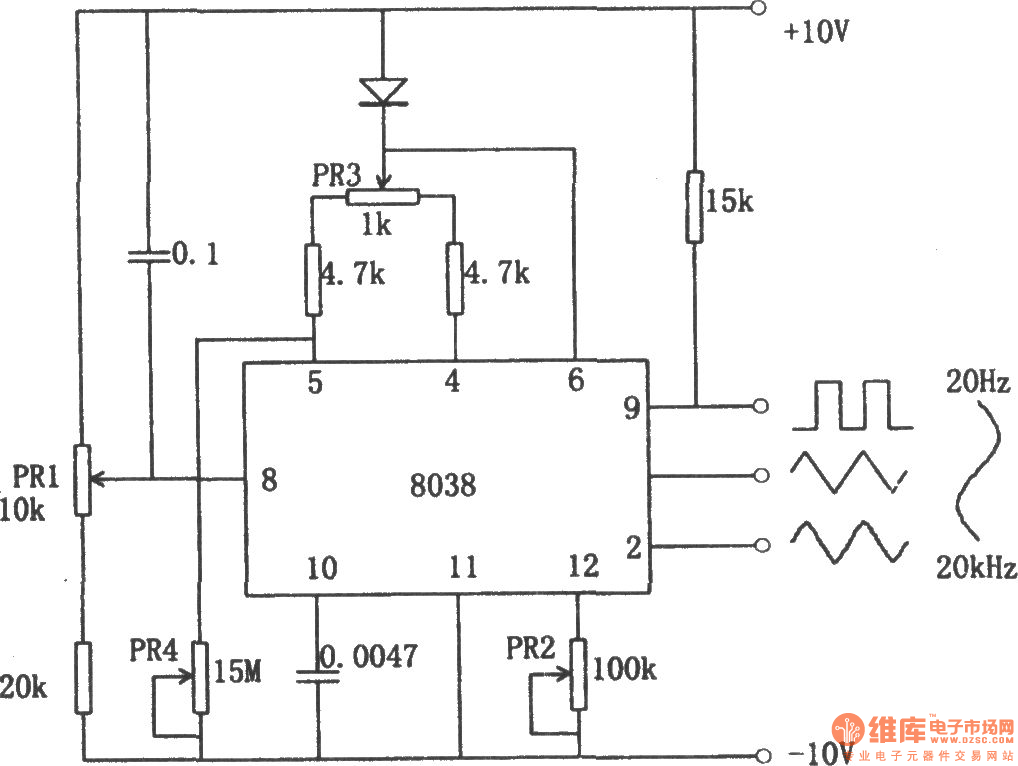
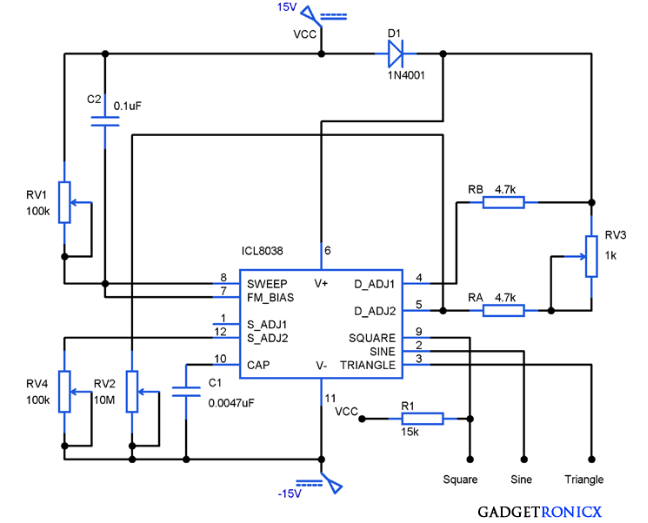
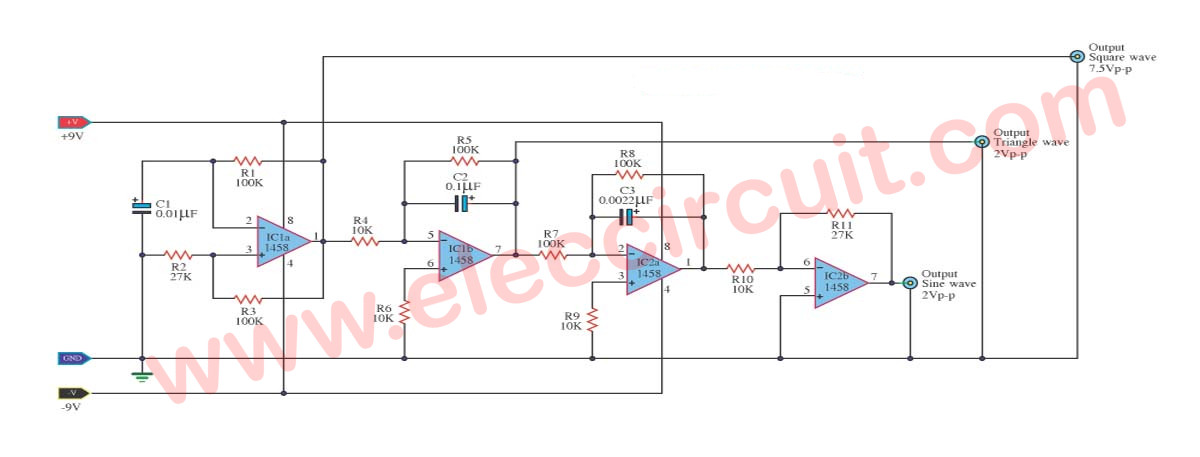
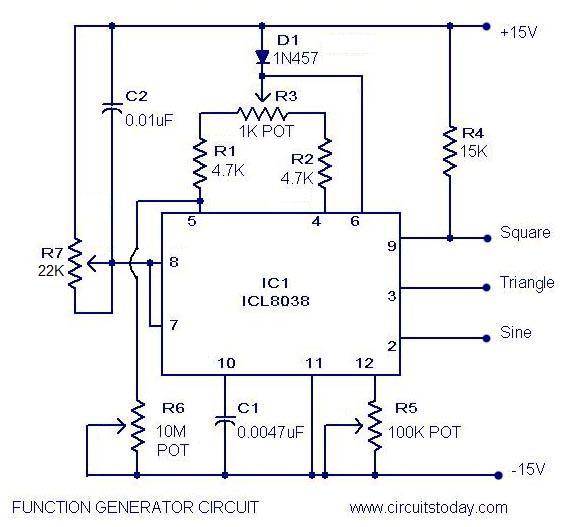
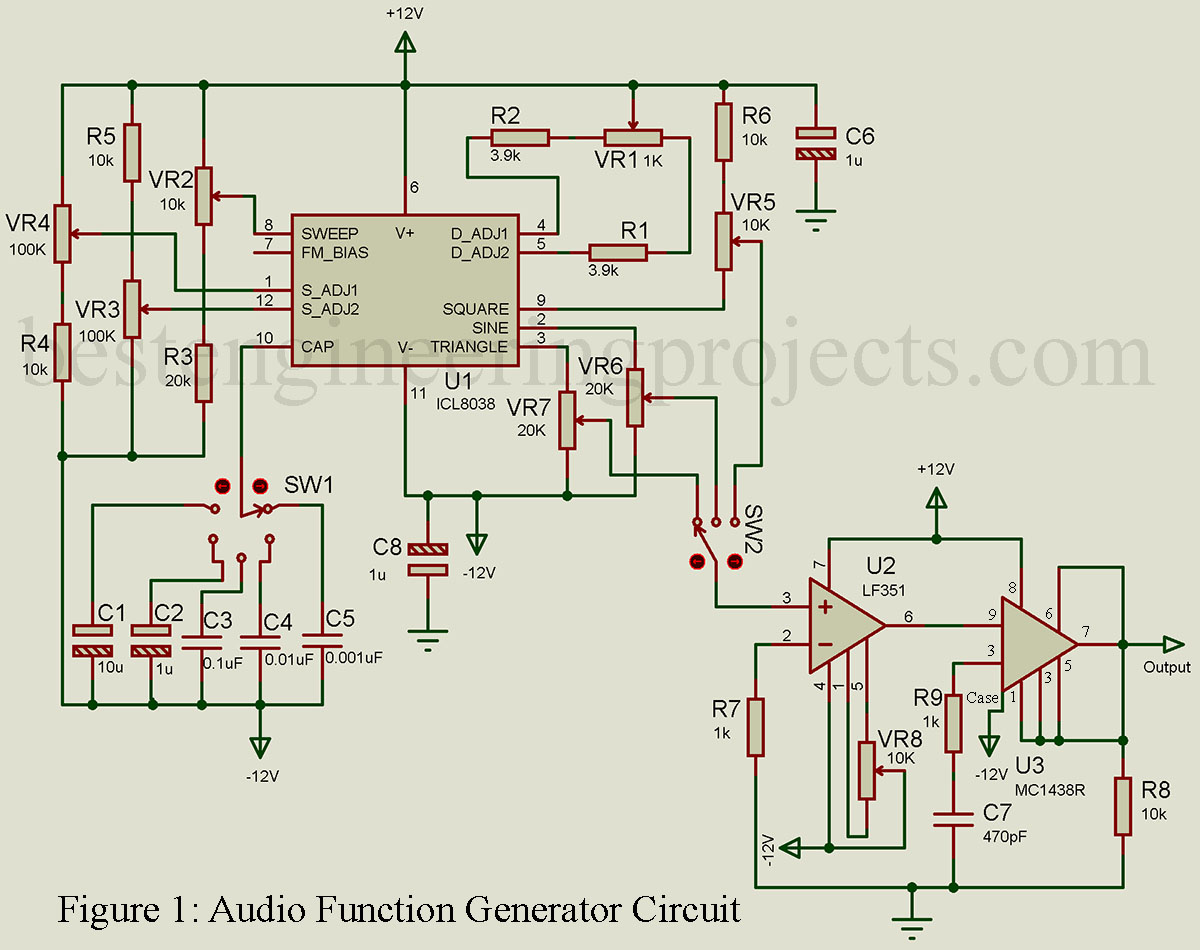
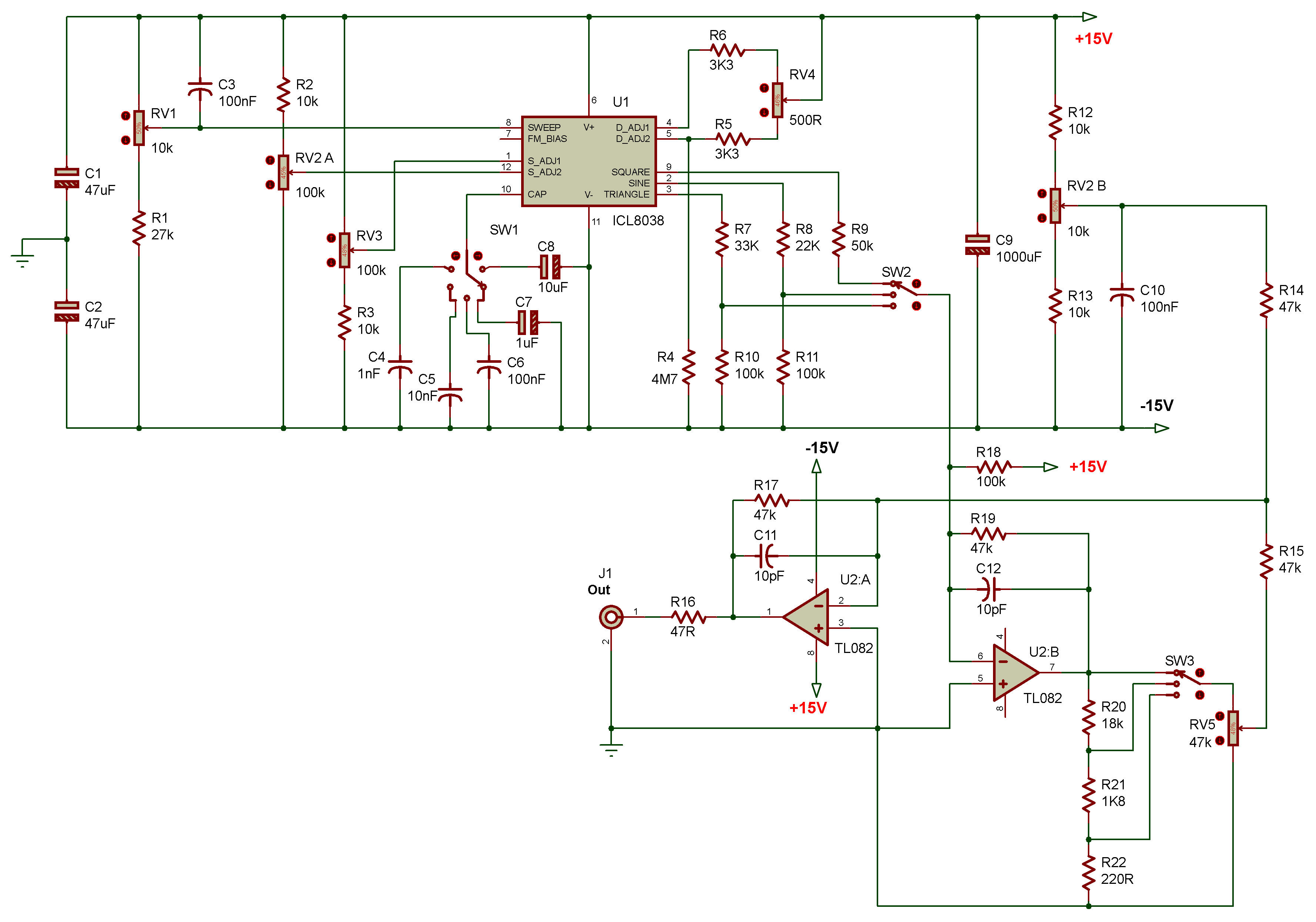
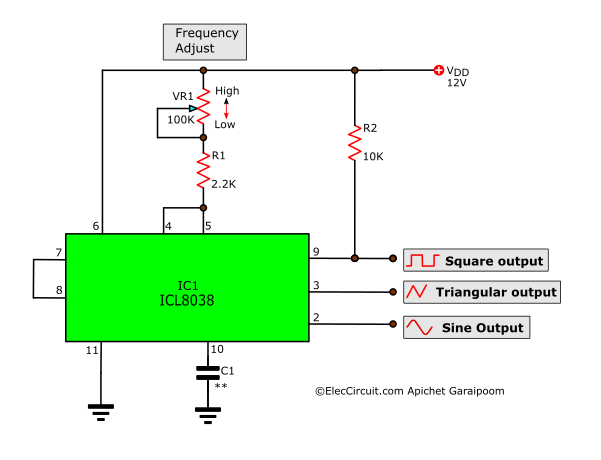
The IC 8038 is the central component. It’s a monolithic function generator capable of producing sine, square, triangular, sawtooth and pulse waveforms with low distortion.
External resistors and capacitors determine the frequency of the generated waveform. These components set the charge and discharge rates within the IC.
Pin configurations dictate the specific waveform output. Manipulating these connections allows users to select the desired output signal.
Circuit Construction Essentials
A stable power supply is crucial for reliable operation. Typically, a dual power supply ranging from ±5V to ±15V is needed to power IC 8038.
Resistors are used to fine-tune the duty cycle and frequency. Precision resistors are recommended for accurate waveform generation.
Capacitors influence the frequency range of the output. Select capacitors with low leakage for optimal performance.
Waveform Characteristics
The frequency range is inversely proportional to the capacitor value. Smaller capacitor values yield higher frequencies.
Adjusting external resistors allows for duty cycle modulation. This influences the shape of the generated pulse or square wave.
Sine wave distortion is a common consideration. External trimming potentiometers can minimize distortion.
Applications and Implications
Educational institutions find value in this circuit for electronics courses. It allows students to understand analog circuit design and waveform generation.
Electronics hobbyists benefit from a simple yet versatile function generator. This facilitates circuit prototyping and testing.
Professional engineers can use this circuit for basic signal generation needs. This is particularly relevant where cost-effectiveness is a priority.
Key Considerations
Proper heat sinking is crucial for the IC 8038. Overheating can lead to inaccurate output or damage to the IC.
Careful selection of components is necessary for stable output. Temperature drift in resistors and capacitors can affect performance.
Shielding the circuit from external electromagnetic interference can reduce noise. This improves the quality of the generated waveforms.
Practical Implementation Tips
Use a breadboard or prototype board for initial testing. This allows easy modification of the circuit.
Employ an oscilloscope to visualize the generated waveforms. Verify the frequency, amplitude, and distortion levels.
Document all component values and circuit connections. This aids in troubleshooting and future modifications.
Ongoing Developments
Researchers are exploring improved versions of function generator circuits. The focus is on higher frequency ranges and lower distortion.
Advanced control methods using microcontrollers are being integrated. These methods enhance programmability and waveform customization.
Further investigation and experimentation are encouraged. This will lead to deeper understanding and innovative applications of the IC 8038 and similar function generator circuits.
Future reports will detail specific circuit schematics and performance benchmarks. Stay tuned for further updates.